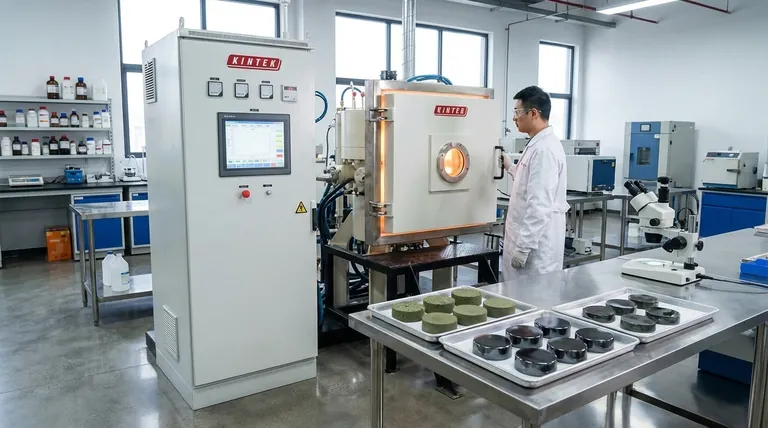
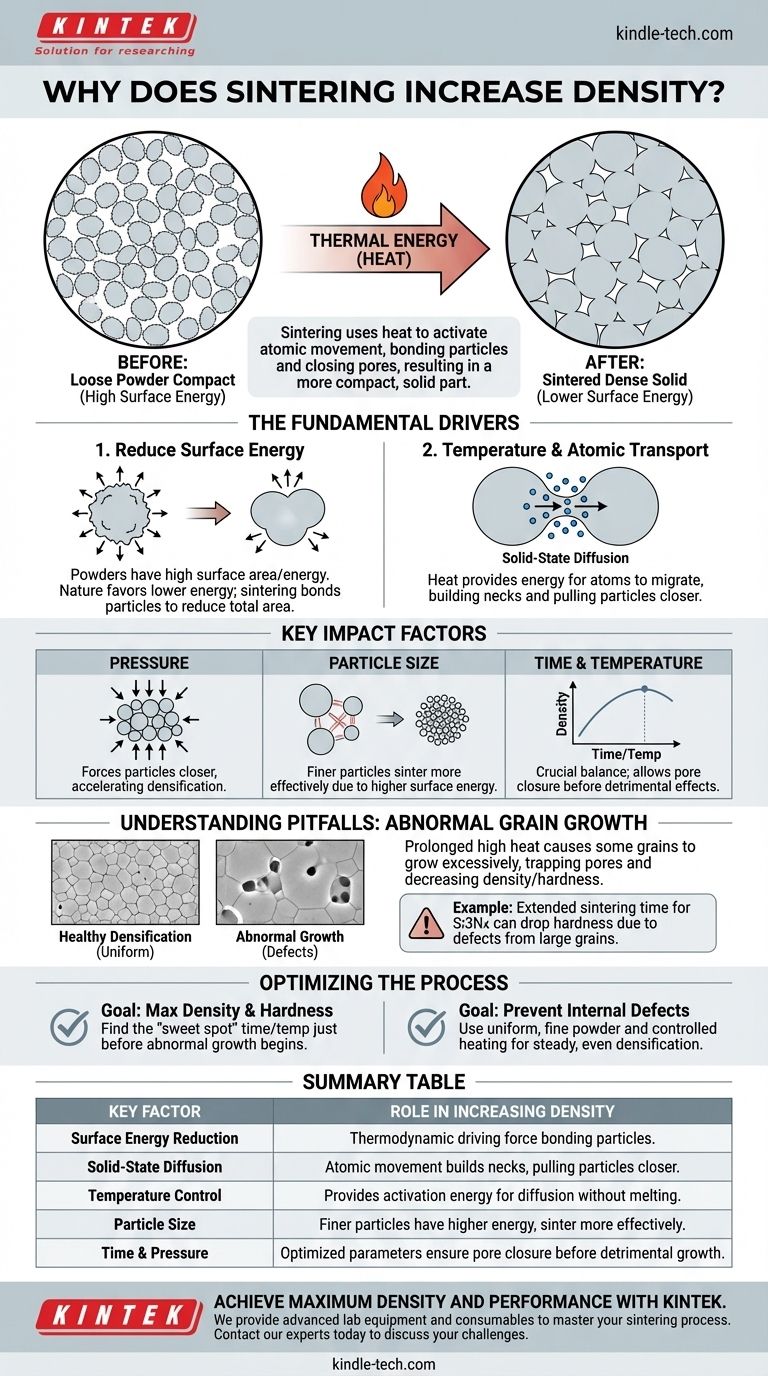
At its core, sintering increases density by using thermal energy to eliminate the empty spaces between individual material particles. High temperatures, typically below the material's melting point, activate atomic movement, allowing particles to bond together and gradually close the pores, resulting in a more compact and solid final part.
Sintering is fundamentally a process of reducing a material's high surface energy. By heating a powder compact, you provide the energy needed for atoms to migrate and fuse particles together, effectively trading the high-energy surface area of many small particles for the lower-energy state of a single, dense solid.

The Fundamental Drivers of Sintering
To understand how sintering achieves densification, we must look at the principles governing the process at the microscopic level. It's a carefully controlled transformation driven by thermodynamics and atomic motion.
The Quest to Reduce Surface Energy
A loose collection of fine powder has an enormous amount of surface area relative to its volume. This high surface area represents a state of high surface free energy.
Nature always favors lower energy states. Sintering leverages this principle by using heat to allow the system to reduce its total surface area, which it accomplishes by bonding particles together and eliminating the surfaces of internal pores.
The Role of Temperature and Atomic Transport
Heat provides the critical activation energy for atoms to move, a process known as solid-state diffusion. At high temperatures, atoms can migrate from the bulk of the particles to the contact points between them.
This migration of material builds "necks" at the particle contact points. As these necks grow, they pull the centers of the particles closer together, shrinking the voids between them and increasing the overall density of the compact.
The Impact of Pressure and Particle Size
While not always required, external pressure can significantly accelerate densification by physically forcing particles closer together, enhancing the contact points where diffusion occurs.
The process is also highly dependent on particle size. Finer particles possess a higher radius of curvature and greater surface energy, which provides a stronger thermodynamic driving force for sintering to occur, often at lower temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Achieving high density is a primary goal, but the sintering process is a delicate balance. Pushing the parameters too far can be counterproductive and degrade the final material's properties.
The Risk of Abnormal Grain Growth
While densification requires atomic motion, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to a detrimental effect: abnormal grain growth.
In this scenario, a few grains grow disproportionately large by consuming their smaller neighbors. This is not the same as the uniform grain growth that accompanies healthy densification.
How Excessive Growth Creates Defects
This abnormal growth can trap pores within the large grains, making them impossible to eliminate. This process can lead to a decrease in final density or hardness.
For example, extending the sintering time for a Si3N4 ceramic from 8 hours to 12 hours can cause hardness to drop significantly because the resulting large grains introduce structural defects.
Balancing Time and Temperature
The key is to hold the material at the optimal temperature for just long enough to close the pores and achieve maximum density. The process must be stopped before significant abnormal grain growth begins to dominate and reverse the gains in material properties.
Optimizing the Sintering Process for Your Goal
Controlling sintering is about manipulating time, temperature, and starting materials to achieve a specific microstructural outcome. Your approach should depend directly on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and hardness: Your goal is to find the "sweet spot" in your process—the combination of time and temperature that completes densification just before the onset of rapid, abnormal grain growth.
- If your primary focus is preventing internal defects: Prioritize using a uniform, fine-grained starting powder and a carefully controlled heating schedule to promote steady, even densification across the entire part.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about successfully driving the process of pore elimination while carefully managing the competing phenomenon of grain growth.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Increasing Density |
|---|---|
| Surface Energy Reduction | Thermodynamic driving force that bonds particles together. |
| Solid-State Diffusion | Atomic movement builds necks between particles, pulling them closer. |
| Temperature Control | Heat provides activation energy for diffusion without melting. |
| Particle Size | Finer particles have higher surface energy, sintering more effectively. |
| Time & Pressure | Optimized parameters ensure complete pore closure before detrimental grain growth. |
Achieve Maximum Density and Performance with KINTEK
Are you looking to optimize your sintering process to achieve superior material density, hardness, and structural integrity? The precise balance of time, temperature, and material selection is critical to avoiding pitfalls like abnormal grain growth.
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables you need to master this delicate process. Whether you are working with ceramics, metals, or other powders, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for consistent, high-quality results.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your materials. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific sintering challenges and discover how our solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What technical functions does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace provide? Optimize CoCrFeNi Alloy Coatings
- What critical processing conditions does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace provide for high-density VC/Cu?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al



















