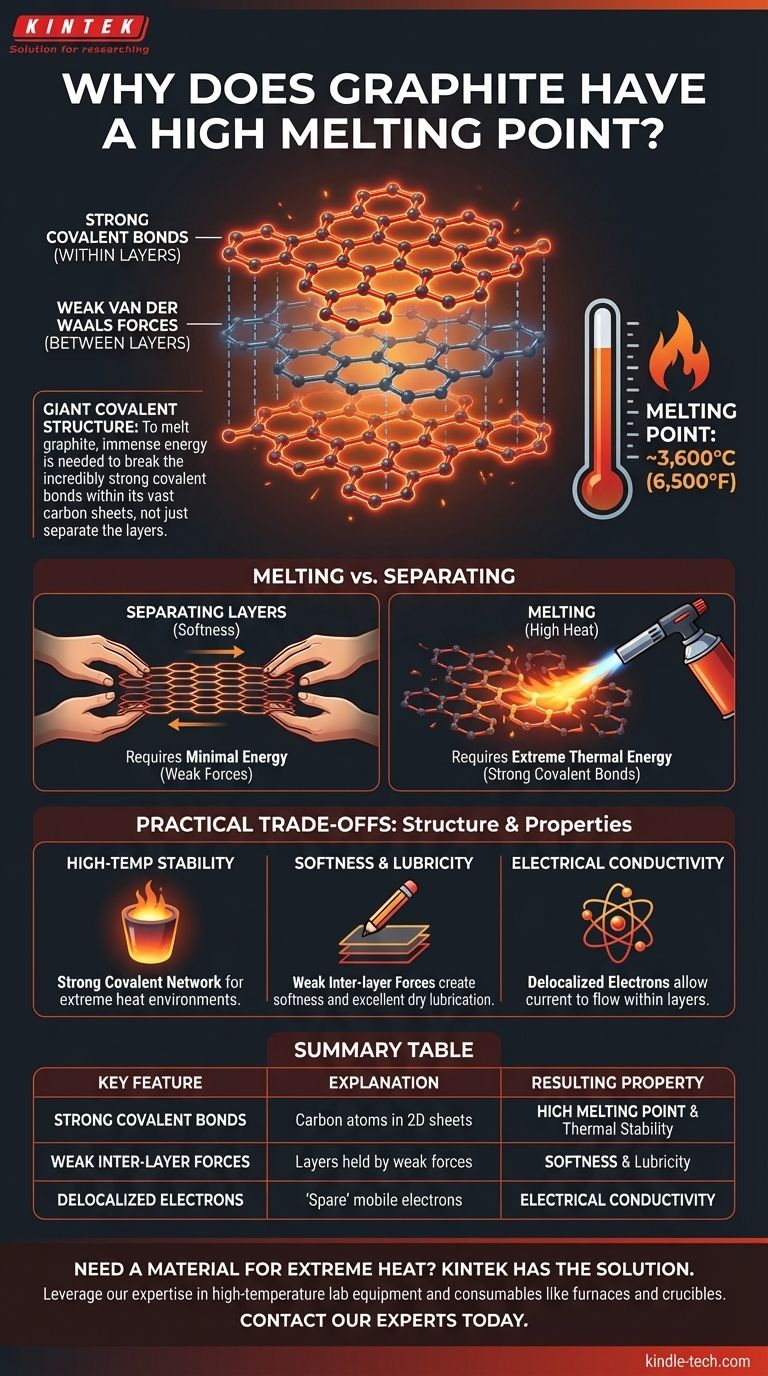
At its core, graphite's exceptionally high melting point (around 3,600°C or 6,500°F) is a direct result of its atomic structure. To melt graphite, you must provide an enormous amount of energy to break the incredibly strong covalent bonds that link its carbon atoms together into vast, two-dimensional sheets.
The crucial insight is that graphite is a giant covalent structure. Melting it doesn't mean simply sliding its layers apart; it means tearing apart the powerful network of carbon-carbon bonds within those layers, a process that requires extreme thermal energy.

The Two-Dimensional Architecture of Graphite
To understand the high melting point, you must first visualize graphite's two distinct types of bonding, which give it a unique combination of properties.
The Strong Covalent Layers
Graphite is composed of countless layers of carbon atoms. Within each individual layer, every carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds.
These atoms arrange themselves into a honeycomb-like pattern of interconnected hexagonal rings. This creates a vast, flat, and exceptionally stable sheet known as graphene.
The Weak Inter-Layer Forces
While the bonds within a layer are immensely strong, the forces that hold the different layers together are very weak.
These forces are known as van der Waals forces. They are easily overcome, which allows the layers to slide past one another with minimal effort. This is what gives graphite its characteristic softness and makes it an excellent dry lubricant.
Why This Structure Demands Extreme Heat
The key to graphite's high melting point is understanding what "melting" actually means for a giant covalent structure.
Melting vs. Separating
Melting a substance requires breaking the bonds that hold its atoms or molecules in a fixed lattice, allowing them to move freely as a liquid.
For graphite, this process is not about overcoming the weak van der Waals forces between the layers. It's about supplying enough energy to break the strong covalent bonds within the layers themselves.
The Sheer Energy of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds, where atoms share electrons, are among the strongest forms of chemical bonding. Each carbon-carbon bond in graphite is exceptionally stable and requires a massive input of thermal energy to sever.
Because a piece of graphite contains a colossal number of these bonds, an extremely high temperature is needed to break enough of them to transition the entire structure into a liquid state.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Graphite's dual-bonding nature creates a material of contrasts. Its properties are highly dependent on which aspect of its structure is being tested.
High-Temperature Stability
The network of strong covalent bonds makes graphite one of the most thermally stable materials known. This is why it is used for applications like industrial crucibles for melting metals and as a lining for high-temperature furnaces.
Mechanical Softness and Lubricity
Conversely, the weak forces between the layers make graphite mechanically soft and an excellent lubricant. The layers easily shear off, which is the principle behind a graphite pencil leaving a mark on paper.
Electrical Conductivity
The same bonding structure that provides thermal stability also allows graphite to conduct electricity. Each carbon atom has a "spare" delocalized electron that is free to move along the plane of the layer, enabling current to flow. This is a rare property for a non-metal.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding this structure-property relationship is key to selecting the right material for an application.
- If your primary focus is thermal resistance: Graphite's giant covalent network makes it a premier choice for high-temperature environments where structural integrity under heat is paramount.
- If your primary focus is lubricity or softness: The weak inter-layer forces are the key property, making graphite ideal for dry lubricants or writing implements.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity in a lightweight material: Graphite's mobile electrons offer a conductive solution without the weight of most metals.
Ultimately, graphite's high melting point is a direct consequence of the immense strength of the chemical bonds holding its fundamental structure together.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Explanation | Resulting Property |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Covalent Bonds | Carbon atoms form strong covalent bonds in 2D sheets (graphene). | High Melting Point & Thermal Stability |
| Weak Inter-layer Forces | Layers are held by weak van der Waals forces. | Softness & Lubricity |
| Delocalized Electrons | 'Spare' electrons can move freely within layers. | Electrical Conductivity |
Need a Material for Extreme Heat? KINTEK Has the Solution.
Understanding the properties of materials like graphite is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your lab. Whether you require high-temperature furnaces with graphite elements, durable crucibles, or other lab equipment built to withstand extreme conditions, KINTEK's expertise is your advantage.
We specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables that leverage the unique properties of advanced materials. Let us help you achieve precision and durability in your high-temperature applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal property of graphite? Mastering Extreme Heat Management
- What is the largest disadvantage of biomass as an energy source? The Hidden Costs of Low Energy Density
- What role does a laboratory high-temperature furnace play in PHT? Engineer Nano-Scale Coating Durability
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- How does a high-temperature furnace contribute to the post-synthesis heat treatment of Fe-Cr-Mn-Mo-N-C composites?



















