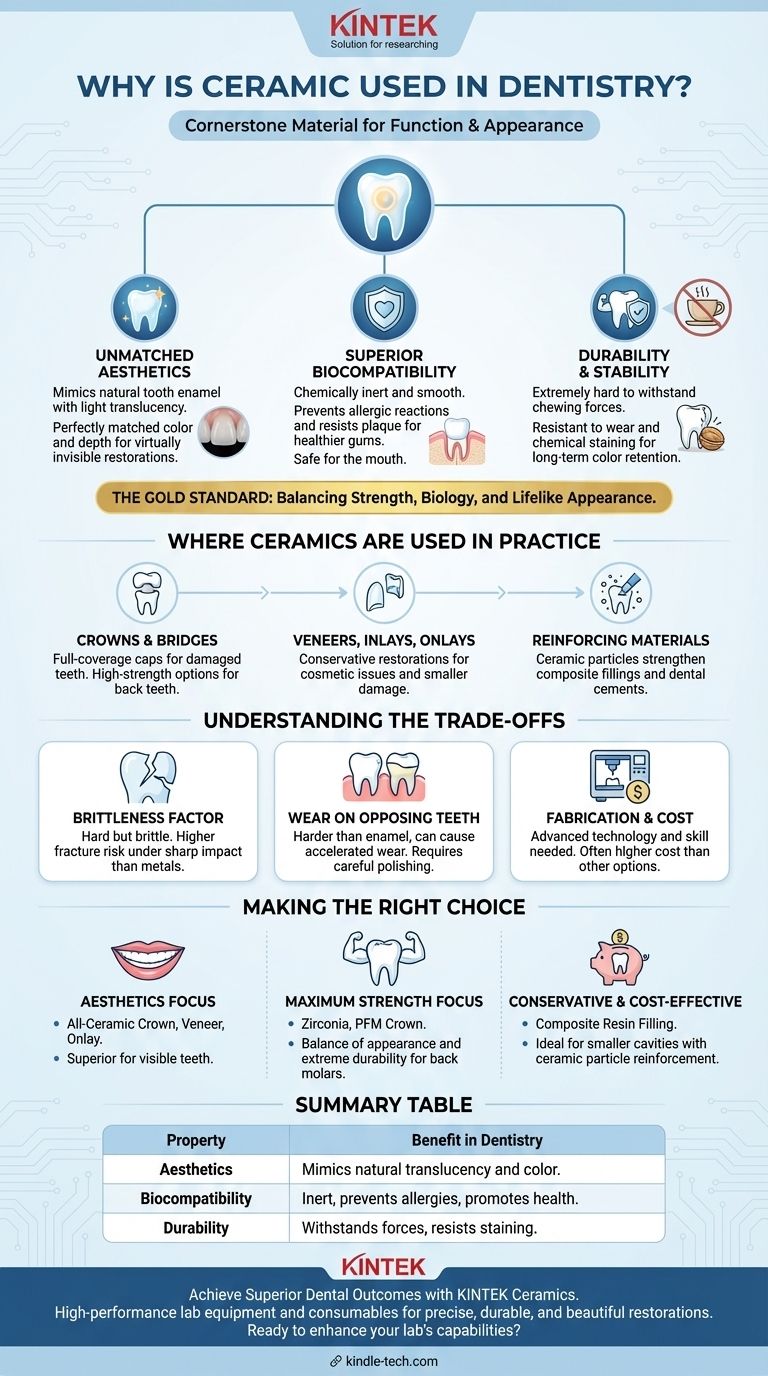
In modern dentistry, ceramics are a cornerstone material for restoring the function and appearance of teeth. They are used because they uniquely combine three critical properties: excellent aesthetics that mimic natural tooth enamel, high biocompatibility with the tissues in your mouth, and impressive durability to withstand the forces of chewing. This combination allows dentists to create restorations that are both beautiful and long-lasting.
The use of ceramic is not merely a cosmetic choice; it is a sophisticated engineering decision. It balances the demands of strength, biological safety, and lifelike appearance in a way that very few materials can, making it the gold standard for many permanent dental restorations.

The Three Pillars of Dental Ceramics
The decision to use ceramic materials is based on a foundation of three distinct advantages that directly address the primary goals of restorative dentistry: form, function, and health.
Unmatched Aesthetics and Translucency
Natural teeth have a complex relationship with light. They are translucent, meaning light passes partially through them, and reflect it in a way that gives them depth and vitality.
Ceramics are one of the few materials that can perfectly replicate this optical behavior. They can be precisely color-matched to your adjacent teeth and layered to create a restoration that is virtually indistinguishable from a natural tooth.
Superior Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility refers to how a material interacts with the living tissues of the body. Dental ceramics are chemically inert, meaning they do not corrode, release substances, or cause allergic reactions.
This is a significant advantage over some metal alloys, which can occasionally cause sensitivity or allergic responses in certain patients. Furthermore, the smooth, glass-like surface of ceramic is resistant to plaque accumulation, which helps promote healthier gum tissue around the restoration.
Durability and Chemical Stability
Dental ceramics are extremely hard and resistant to wear, allowing them to withstand the significant compressive forces generated by chewing, especially in posterior teeth.
They are also chemically stable. Unlike other materials, they will not stain or discolor over time from exposure to coffee, tea, or other foods. This ensures the restoration maintains its original color and appearance for many years.
Where Ceramics Are Used in Practice
Based on their properties, ceramics are deployed in a range of applications, from full-coverage crowns to the microscopic particles that strengthen other materials.
Crowns and Bridges
A crown is a full-coverage cap placed over a damaged tooth. Ceramics are the ideal material for crowns, especially for front teeth, due to their aesthetic qualities. For back teeth, high-strength ceramics like zirconia are used to handle greater chewing forces.
Veneers, Inlays, and Onlays
These are considered more conservative restorations. Veneers are thin ceramic shells bonded to the front of teeth to correct cosmetic issues. Inlays and onlays are used to repair smaller areas of damage within the cusps of a tooth, serving as a more durable and aesthetic alternative to traditional fillings.
Reinforcing Other Materials
Ceramics also play a critical role as a component in other dental materials. Tiny ceramic particles are used as a filler in resin-composite fillings to increase their strength, wear resistance, and stability. They are also found in some dental cements used to bond crowns and bridges permanently in place.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single material is perfect for every situation. While ceramics offer profound benefits, it is important to understand their limitations to make an informed decision.
The Brittleness Factor
While ceramics are very hard (resistant to scratching and wear), they can also be brittle. This means that under a very sharp, specific impact or flexing force, a ceramic restoration has a higher chance of fracturing compared to a more malleable material like a gold alloy.
Potential Wear on Opposing Teeth
Because certain types of dental ceramic are harder than natural tooth enamel, they can cause accelerated wear on the opposing teeth over time. Dentists carefully select the type of ceramic and polish the final restoration to minimize this effect.
Fabrication and Cost
High-quality ceramic restorations often require advanced technology, such as CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing), and significant artistic skill from the dental laboratory technician. This specialized process can result in a higher cost compared to other restorative options like metal alloys or direct composite fillings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Restoration
The best material is always the one that solves the specific clinical problem while meeting your personal goals.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and biocompatibility: An all-ceramic crown, veneer, or onlay is often the superior choice, especially for teeth visible in your smile.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for a back molar: A high-strength ceramic like zirconia, or a porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crown, may be recommended to balance appearance with extreme durability.
- If your primary focus is a conservative and cost-effective repair: A composite resin filling (which contains ceramic particles) is often the ideal solution for smaller cavities.
Understanding these material properties empowers you to have a more informed discussion with your dental professional about the best long-term solution for your health.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit in Dentistry |
|---|---|
| Aesthetics | Mimics natural tooth translucency and color for invisible restorations. |
| Biocompatibility | Chemically inert; prevents allergic reactions and promotes gum health. |
| Durability | Withstands chewing forces and resists staining for long-term performance. |
Achieve Superior Dental Outcomes with KINTEK Ceramics
Whether you're fabricating crowns, bridges, or veneers, the quality of your ceramic materials is paramount. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables that support the precise fabrication of dental ceramics. Our products are trusted by dental laboratories to create restorations that are not only beautiful but also exceptionally durable and biocompatible.
Ready to enhance your dental lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific needs in dental ceramic production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges



















