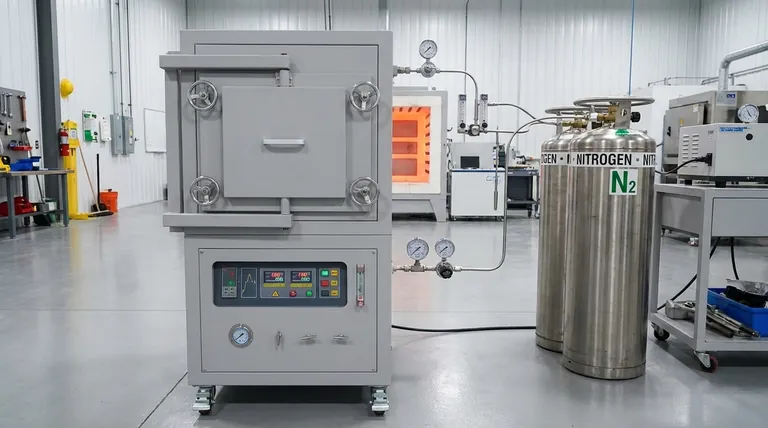
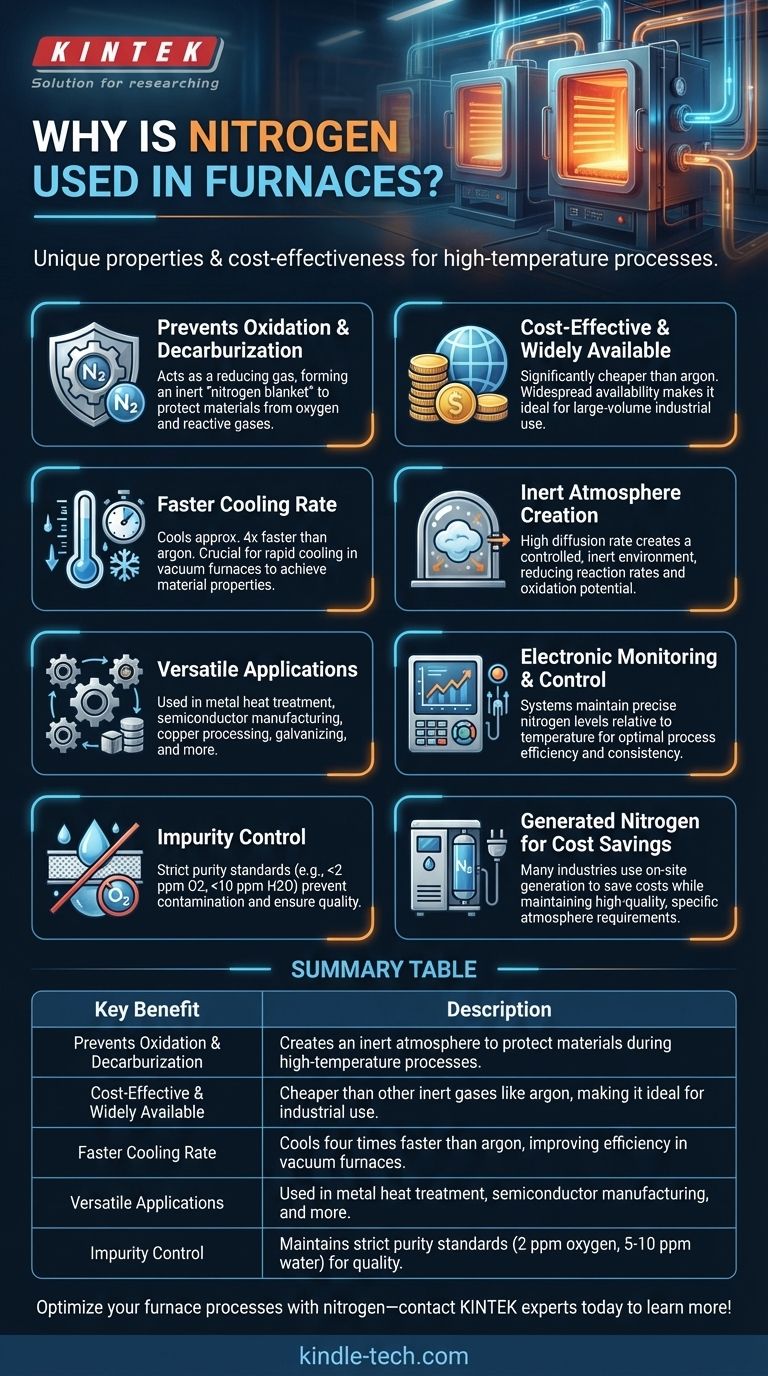
Nitrogen is extensively used in furnaces due to its unique properties and cost-effectiveness. It serves as a protective gas to prevent oxidation and decarburization of materials during high-temperature processes, such as annealing, sintering, and heat treatment. Nitrogen's high diffusion rate and inert nature make it ideal for creating a controlled atmosphere, ensuring the quality and integrity of processed materials. Additionally, its faster cooling rate compared to gases like argon, combined with its lower cost, makes it a preferred choice for cooling and purging applications in furnaces. The use of nitrogen also supports efficient thermal processing by maintaining specific gas compositions and reducing reaction rates.

Key Points Explained:
-
Prevention of Oxidation and Decarburization:
- Nitrogen acts as a reducing gas in high-temperature furnaces, preventing the oxidation of ferrous metals and decarburizing the surface of steel products. This is achieved through a process called nitrogen blanketing, where nitrogen is introduced into the furnace chamber via flowmeters and expelled through an exhaust port. This creates an inert atmosphere that protects materials from reacting with oxygen or other reactive gases.
-
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability:
- Nitrogen is significantly cheaper than other inert gases like argon, making it a cost-effective choice for industrial applications. Its widespread availability and relatively low cost contribute to its popularity in furnace operations, especially for processes requiring large volumes of gas.
-
Faster Cooling Rate:
- Nitrogen has a cooling rate approximately four times faster than argon. This property is particularly beneficial in vacuum furnaces, where rapid cooling is often required to achieve specific material properties or to improve process efficiency.
-
Inert Atmosphere Creation:
- Nitrogen is favored for creating an inert atmosphere due to its high diffusion rate and ability to reduce reaction rates and oxidation potentials. This is critical in processes like annealing, sintering, and heat treatment, where maintaining a controlled environment is essential for achieving desired material characteristics.
-
Versatility in Applications:
- Nitrogen is used in a wide range of furnace applications, including metal heat treatment, powder metallurgy, magnetic materials, copper processing, wire mesh, galvanizing wire, semiconductor manufacturing, and powder reduction. Its versatility stems from its ability to provide a clean, safe, and effective environment for various high-temperature processes.
-
Electronic Monitoring and Control:
- In high-temperature furnaces, electronic monitoring systems are often used to maintain specific nitrogen composition levels relative to the chamber's temperature. This ensures optimal process conditions and enhances the efficiency and consistency of thermal treatments.
-
Impurity Control:
- Nitrogen used in furnaces must meet strict purity standards, with permissible impurity levels of approximately 2 ppm of oxygen and 5-10 ppm of water by volume. This ensures that the gas does not introduce contaminants that could compromise the quality of the processed materials.
-
Generated Nitrogen for Cost Savings:
- Many industries opt for generated nitrogen for heat treat atmospheres to save costs while maintaining high-quality processing. Working with experienced nitrogen generator suppliers ensures that the nitrogen-blended atmospheres meet the specific requirements of thermal processing applications.
By leveraging nitrogen's properties, industries can achieve efficient, high-quality, and cost-effective furnace operations across a wide range of applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation & Decarburization | Creates an inert atmosphere to protect materials during high-temperature processes. |
| Cost-Effective & Widely Available | Cheaper than other inert gases like argon, making it ideal for industrial use. |
| Faster Cooling Rate | Cools four times faster than argon, improving efficiency in vacuum furnaces. |
| Versatile Applications | Used in metal heat treatment, semiconductor manufacturing, and more. |
| Impurity Control | Maintains strict purity standards (2 ppm oxygen, 5-10 ppm water) for quality. |
Optimize your furnace processes with nitrogen—contact our experts today to learn more!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization



















