At its core, porcelain's heat resistance stems from its dense, vitrified structure and the immense strength of its atomic bonds, all forged at temperatures far exceeding those of any kitchen or common application. This high-temperature manufacturing process locks its components into an incredibly stable, non-porous form that is inherently slow to absorb and transfer thermal energy.
Porcelain is not "heat-proof," but highly heat-resistant due to its creation at extreme temperatures. Its true limitation isn't the maximum heat it can withstand, but its vulnerability to thermal shock—rapid changes in temperature that can cause it to crack.

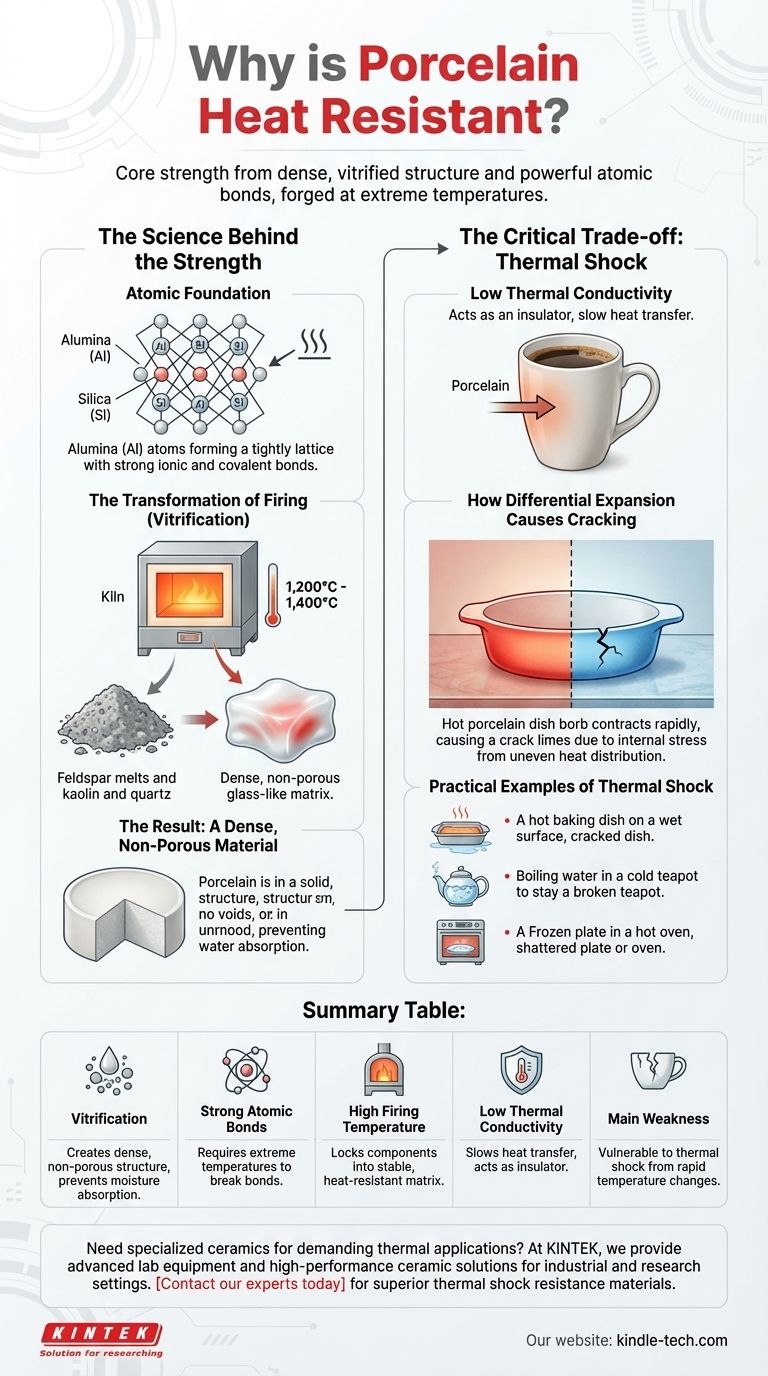
The Science Behind the Strength
Porcelain's ability to resist heat is not a single property but the result of its fundamental material composition and the transformative process it undergoes.
The Atomic Foundation
The raw materials in porcelain, primarily kaolin clay and minerals like quartz and feldspar, are composed of alumina and silica. These atoms are linked by powerful ionic and covalent bonds.
Think of these bonds as a tightly woven, rigid lattice. Heat is simply the vibration of atoms. To break this material down, you must introduce enough energy to overcome these incredibly strong bonds, which requires extremely high temperatures.
The Transformation of Firing (Vitrification)
Raw porcelain is porous and relatively weak. Its legendary properties are unlocked during firing in a kiln at temperatures between 1,200°C and 1,400°C (2,200°F and 2,600°F).
During this process, the feldspar melts and acts as a flux, flowing around the other particles. As it cools, it solidifies into a glass-like substance, binding the kaolin and quartz into a single, dense matrix. This process is called vitrification.
The Result: A Dense, Non-Porous Material
Vitrification eliminates the pores that exist in other ceramics like earthenware. This non-porous structure is critical because it prevents water from seeping into the material, which would turn to steam and expand destructively when heated.
This density also makes porcelain incredibly hard and durable, contributing to its overall resilience.
The Critical Trade-off: Thermal Shock
While porcelain handles high, stable temperatures exceptionally well, its greatest weakness is a sudden change in temperature. This vulnerability is known as thermal shock.
Low Thermal Conductivity
A key property of porcelain is its low thermal conductivity. It is a poor conductor of heat, which is why a porcelain mug handle doesn't immediately get hot when you pour in coffee. It acts as an insulator.
While this seems like a benefit, it is the direct cause of its vulnerability to thermal shock.
How Differential Expansion Causes Cracking
When you expose porcelain to a sudden temperature change—for example, by placing a hot dish on a cold granite countertop—its low conductivity prevents the heat from distributing evenly.
The surface in contact with the cold counter contracts rapidly, while the rest of the dish remains hot and expanded. This difference in size creates immense internal stress, which is relieved by the only means possible: a fracture.
Practical Examples of Thermal Shock
This principle is behind the most common porcelain failures:
- A baking dish cracking when moved from a hot oven to a cool, wet surface.
- A teapot breaking when boiling water is poured into it on a very cold day.
- A plate cracking when taken from the freezer and immediately placed in a hot oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this distinction between heat resistance and thermal shock is crucial for using porcelain effectively and safely.
- If your primary focus is cooking or baking: Always pre-heat porcelain with the oven and avoid placing hot dishes on cold or wet surfaces. Let dishes cool gradually.
- If your primary focus is everyday use (mugs, plates): Avoid extreme temperature changes, like pouring boiling water into a very cold mug or running a hot plate under cold water.
- If your primary focus is industrial or lab applications: For environments with rapid temperature cycling, consider technical ceramics like alumina or zirconia, which are specifically engineered for superior thermal shock resistance.
By understanding that porcelain's main enemy is not heat but rapid temperature change, you can leverage its strengths for decades of reliable use.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Contribution to Heat Resistance |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Creates a dense, non-porous structure that prevents moisture absorption and steam expansion |
| Strong Atomic Bonds | Requires extremely high temperatures to break the ionic and covalent bonds in alumina and silica |
| High Firing Temperature | Manufacturing at 1,200-1,400°C locks components into a stable, heat-resistant matrix |
| Low Thermal Conductivity | Acts as an insulator, slowing heat transfer through the material |
| Main Weakness | Vulnerable to thermal shock from rapid temperature changes due to differential expansion |
Need specialized ceramics for demanding thermal applications? At KINTEK, we provide advanced lab equipment and high-performance ceramic solutions for industrial and research settings. Whether you require materials with superior thermal shock resistance or custom ceramic components, our expertise ensures your laboratory operates at peak efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific thermal processing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of zirconia ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why are 3mm zirconia grinding balls selected for Na3FePO4CO3 synthesis? Optimize Energy and Purity
- Why are zirconia grinding balls preferred for NiCrAlY-Mo-Ag powders? Ensure Maximum Purity and Durability
- What is the purpose of using high-hardness zirconia grinding balls? Ensure Purity & Power in Electrolyte Milling
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials



















