In any scientific analysis, sample preparation is the foundational step that dictates the quality of your final results. It is the process of treating your raw material to make it suitable for measurement, and its importance cannot be overstated; proper preparation is the basis for achieving reliable, accurate, and reproducible data.
The core purpose of sample preparation is to ensure that your instrument is measuring the true properties of your sample, not the random variations or interferences introduced by inconsistent handling. It transforms a raw material into a standardized specimen, making your results both accurate and meaningful.
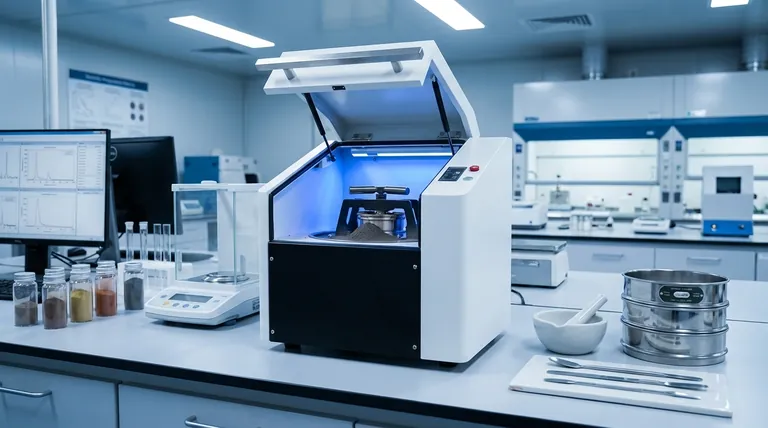

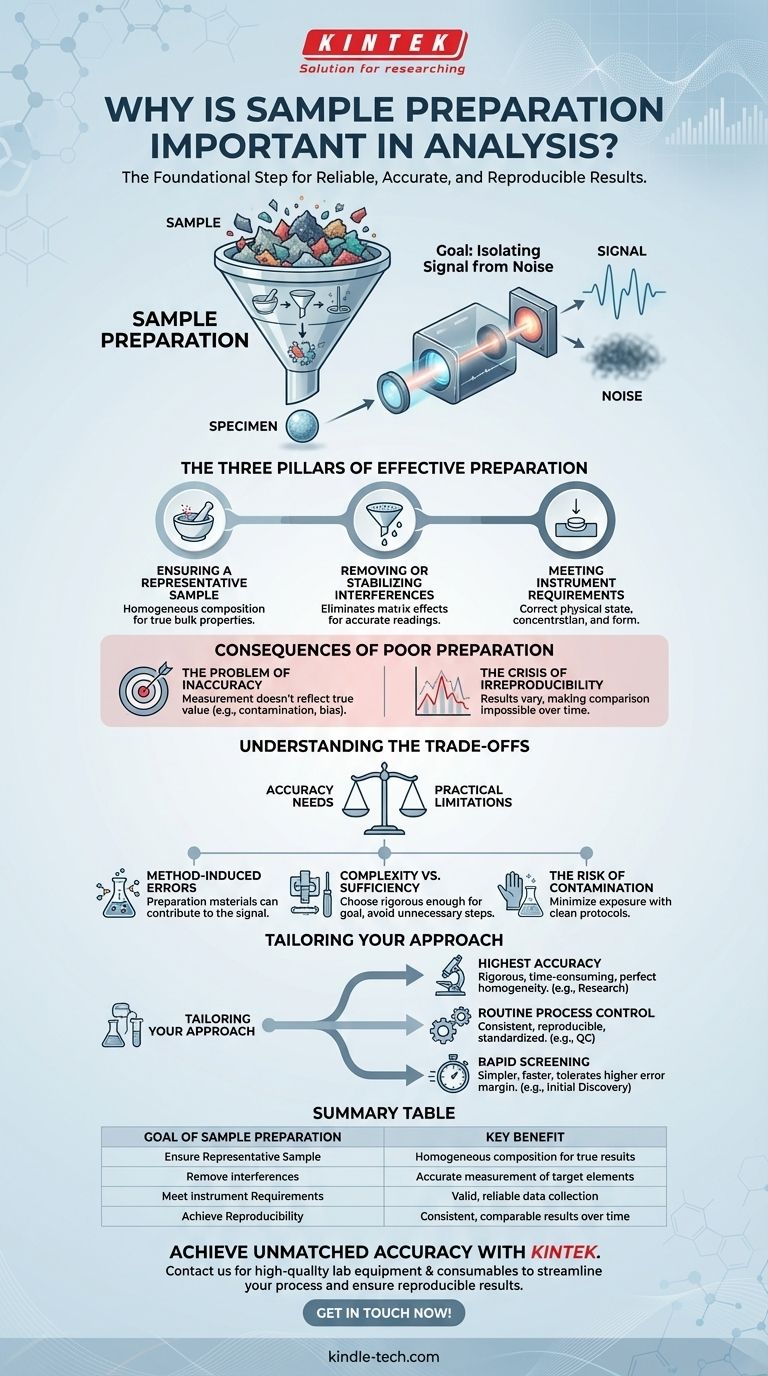
The Goal: Isolating Signal from Noise
Effective analysis depends on the instrument detecting a clear "signal" from the substance of interest. Sample preparation is the disciplined process of maximizing this signal while minimizing background "noise" that can obscure or alter the results.
Ensuring a Representative Sample
An instrument only analyzes a small portion of the material you provide. Sample preparation ensures this small portion is homogeneous—meaning it has the same composition as the bulk material.
For example, a powdered sample must be ground and mixed thoroughly. If not, the instrument might measure a particle that isn't representative of the whole, leading to a completely incorrect result.
Removing or Stabilizing Interferences
Most raw samples contain substances, known as the sample matrix, that can interfere with the measurement of the target element or compound.
A proper preparation protocol is designed to remove these interferences or lock them in a stable form so they do not affect the final reading. This is critical for achieving accuracy.
Meeting Instrument Requirements
Every analytical instrument has specific requirements for the samples it can measure. Samples may need to be in a specific physical state (solid, liquid), concentration range, or form factor.
In X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF), for instance, solid samples are often pressed into smooth, flat pellets. An uneven or broken surface can deflect the x-ray beam, invalidating the measurement.
How Poor Preparation Invalidates Results
Failing to properly prepare a sample doesn't just reduce accuracy slightly; it can render the entire analysis scientifically useless. The consequences fall into two main categories.
The Problem of Inaccuracy
An inaccurate result is a measurement that does not reflect the true value. This can be caused by contamination, interfering elements, or an unrepresentative sample. Decisions based on inaccurate data are fundamentally flawed.
The Crisis of Irreproducibility
Perhaps worse than a single inaccurate result is the inability to get the same result twice. If your preparation method is not reproducible, your results will vary with each test, even on the same material.
This inconsistency makes it impossible to compare data over time, track trends, or trust that any single measurement is correct. It undermines the very purpose of scientific analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sample preparation method is not always straightforward. You must balance the need for accuracy against practical limitations and potential new sources of error.
Method-Induced Errors
The preparation process itself can introduce errors. For example, the binders used to create pressed powder pellets or the thin films used to hold liquid samples can contain trace elements.
If you are trying to measure one of those elements, the preparation material itself will contribute to the signal, creating a falsely high reading. An expert chooses materials that are free of the target elements.
Complexity vs. Sufficiency
Methods range from simple grinding to complex, multi-step acid digestions. The key is to select a method that is rigorous enough for your analytical goal without being unnecessarily complex.
For a simple quality control check, a quick, reproducible method may be sufficient. For high-stakes research or regulatory reporting, a more demanding and validated protocol is non-negotiable.
The Risk of Contamination
Every time the sample is handled, transferred, or exposed to a new container or reagent, there is a risk of contamination. A robust preparation protocol includes steps to minimize this risk, such as using ultra-clean labware and high-purity reagents.
Tailoring Your Approach to the Analytical Goal
The right sample preparation strategy is defined by your ultimate objective. Before you begin, clarify what you need your data to do.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible accuracy: Your preparation must be rigorous, aiming to remove all possible interferences and create a perfectly homogeneous sample, even if it is time-consuming.
- If your primary focus is routine process control: Your preparation must be exceptionally consistent and reproducible, ensuring that every sample is treated exactly the same way to allow for valid comparisons over time.
- If your primary focus is rapid screening or initial discovery: A simpler, faster preparation method may be acceptable, provided you understand and can tolerate a higher margin of error.
Ultimately, treating sample preparation as an integral part of the measurement, rather than a preliminary chore, is the mark of a disciplined and effective analyst.
Summary Table:
| Goal of Sample Preparation | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Ensure Representative Sample | Homogeneous composition for true results |
| Remove Interferences | Accurate measurement of target elements |
| Meet Instrument Requirements | Valid, reliable data collection |
| Achieve Reproducibility | Consistent, comparable results over time |
Achieve Unmatched Accuracy in Your Lab
Proper sample preparation is the foundation of reliable data. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed to streamline your sample preparation process, minimize contamination, and ensure reproducible results every time. Whether you're involved in rigorous research, routine quality control, or rapid screening, our solutions are tailored to meet your specific analytical goals.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and data integrity. Let's build a foundation of trust in your results together. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Vibration Mill
- XRD Sample Holder X-ray Diffractometer Powder Slide
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-energy vibrating ball mill? Transform Mg-Y-Cu Into Superior Metallic Glass Powders
- What is the core function of a high-energy vibratory ball mill? Unlock Advanced Mechanochemical Synthesis
- What function does a laboratory vibratory mill serve? Achieve 1–5 µm Precision for Cs-Aluminosilicate Powder
- What is the role of a high-energy ball mill in Ti-based amorphous composite preparation? Master Mechanical Alloying
- What is the role of a high-energy vibratory ball mill in YSZ-SiC preparation? Achieve Perfect Core-Shell Structures












