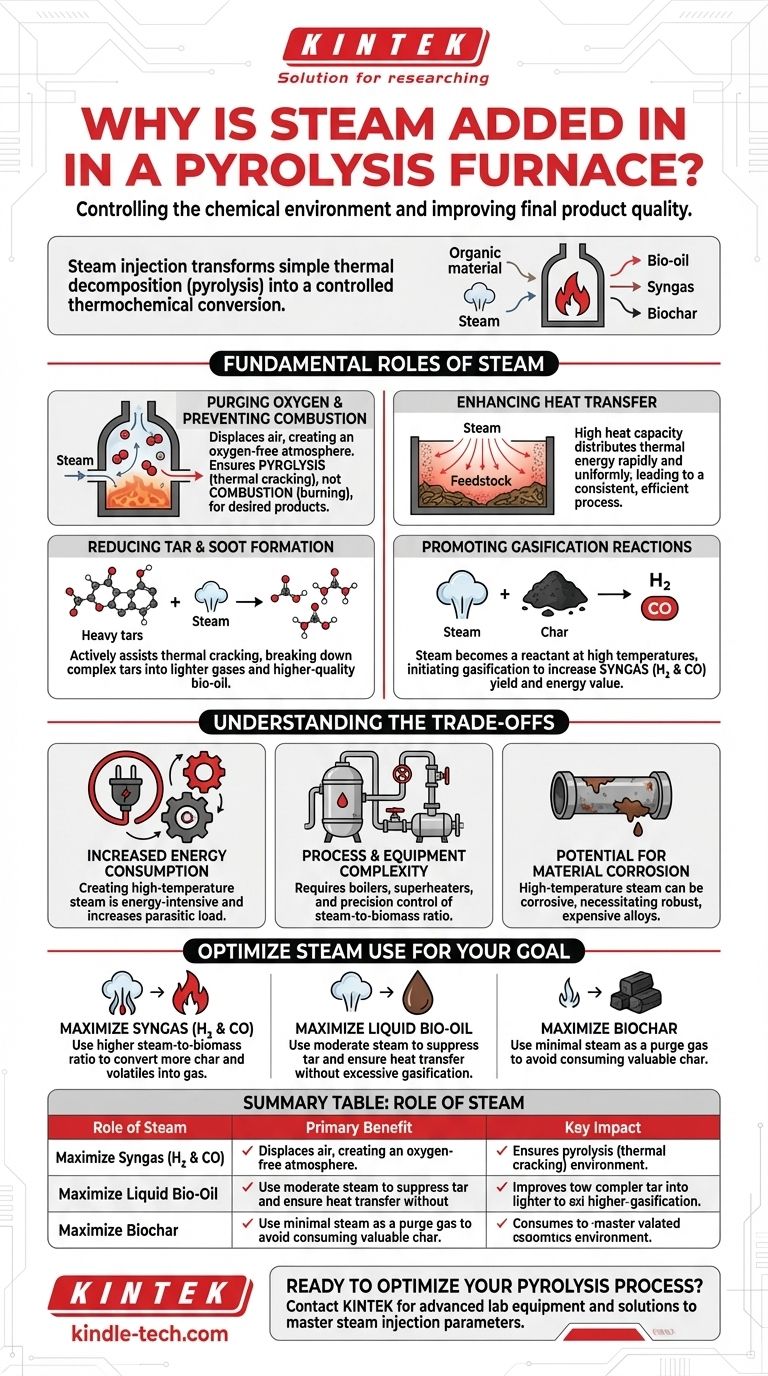
At its core, steam is added to a pyrolysis furnace to control the chemical environment and improve the quality of the final products. While pyrolysis is technically the thermal decomposition of organic material in the absence of oxygen, injecting steam serves several critical functions, from preventing unwanted combustion to actively participating in chemical reactions that upgrade the resulting gases and liquids.
The decision to add steam marks a fundamental shift in process strategy. You are no longer just breaking down material with heat (pyrolysis); you are using steam as a tool to actively influence reaction pathways, reduce undesirable byproducts like tar, and enhance the yield of valuable gases like hydrogen.
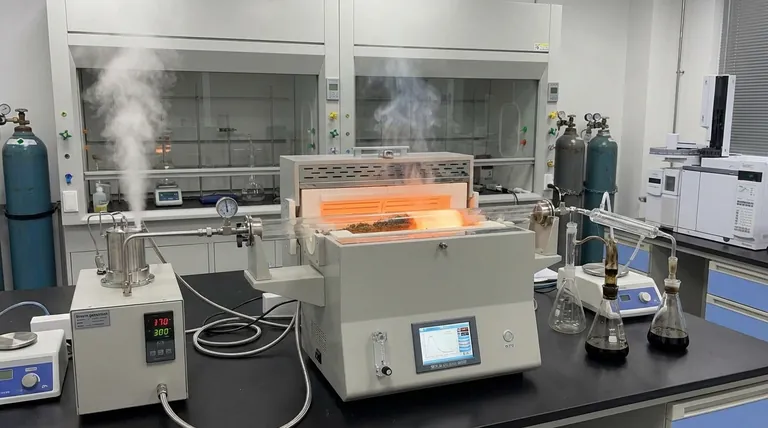

The Fundamental Roles of Steam in Pyrolysis
Injecting steam into a pyrolysis furnace is a deliberate engineering choice that serves multiple purposes simultaneously. It moves the process beyond simple thermal decomposition into a more controlled and versatile thermochemical conversion.
Purging Oxygen and Preventing Combustion
The most basic function of steam is to act as a purging agent. It displaces ambient air—and specifically oxygen—from the furnace.
By creating an oxygen-free (anaerobic) atmosphere, steam ensures that the organic feedstock undergoes pyrolysis (thermal cracking) rather than combustion (burning). This is the foundational requirement for producing bio-oil, syngas, or biochar instead of just ash and flue gas.
Enhancing Heat Transfer
Steam has a high heat capacity and is an excellent medium for transferring thermal energy.
When superheated steam is injected, it distributes heat more rapidly and uniformly throughout the feedstock than radiant heat alone. This ensures all the material reaches the target pyrolysis temperature quickly, leading to a more consistent and efficient process.
Reducing Tar and Soot Formation
One of the biggest challenges in pyrolysis is the formation of complex, heavy hydrocarbons known as tars. These tars can clog equipment and lower the quality of the desired liquid (bio-oil) and gas products.
Steam actively assists in thermal cracking, breaking down these large tar molecules into smaller, lighter, and more valuable gaseous compounds. This results in a cleaner gas stream and a higher-quality bio-oil with lower viscosity.
Promoting Gasification Reactions
This is the most advanced function of steam. At the high temperatures of a pyrolysis furnace, steam ceases to be an inert fluid and becomes a chemical reactant.
It initiates gasification reactions, primarily the steam-reforming reaction and the water-gas shift reaction. Steam reacts with the solid char and volatile hydrocarbons to produce more syngas—a mixture of hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO). This significantly increases the yield and energy value of the gaseous product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While beneficial, adding steam injection to a pyrolysis system is not without its costs and complexities. It's an engineering decision with clear trade-offs.
Increased Energy Consumption
Creating high-temperature, high-pressure steam is an energy-intensive process. This energy input, known as a parasitic load, must be factored into the overall energy balance of the plant. If not managed carefully, it can reduce the net energy output.
Process and Equipment Complexity
A system with steam injection requires boilers, superheaters, and precision control valves. The steam-to-biomass ratio becomes a critical operating parameter that must be carefully monitored and controlled to achieve the desired product distribution.
Potential for Material Corrosion
At high temperatures, steam can be corrosive to certain metals. The reactor and downstream piping must be constructed from more robust and expensive alloys to withstand the harsh operating environment, increasing the capital cost of the plant.
How to Optimize Steam Use for Your Goal
The amount of steam you add directly influences the final product slate. The choice is determined entirely by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality syngas (H₂ and CO): You will use a higher steam-to-biomass ratio to maximize gasification and convert as much of the char and volatiles as possible into gas.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil yield: You will use a more moderate amount of steam, enough to suppress tar formation and ensure good heat transfer, but not so much that it begins to gasify your valuable liquid precursors.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar: You will use minimal steam, just enough to serve as a purge gas to remove oxygen, as any excess steam will react with and consume the very char you are trying to create.
Ultimately, injecting steam transforms the pyrolysis furnace from a simple heating chamber into a highly controllable chemical reactor.
Summary Table:
| Role of Steam | Primary Benefit | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Purging Oxygen | Prevents Combustion | Ensures pyrolysis, not burning |
| Enhancing Heat Transfer | Uniform Heating | Consistent & efficient process |
| Reducing Tar Formation | Cleaner Products | Higher-quality bio-oil & gas |
| Promoting Gasification | Increased Syngas Yield | More hydrogen (H₂) & carbon monoxide (CO) |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for thermochemical conversion research. Whether you're developing processes to maximize syngas, bio-oil, or biochar yield, our reactors and systems are designed for precise control and reliable performance.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment to master steam injection parameters and achieve your specific product goals. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your pyrolysis research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the discharge effect of a DC pulse power supply affect SPS nickel-based alloys? Achieve Rapid Densification
- What metal Cannot be brazed? Overcoming Surface Chemistry for Strong Joints
- Which machine is used for sintering? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Materials
- Why do copper and graphite green bodies require long-term heating? Ensure Structural Integrity During Sintering
- What are the steps of the hardening process? Master the 3-Step Heat Treatment for Superior Metal Strength
- What is the difference between pyrolysis and plasma gasification? A Guide to Advanced Thermal Conversion
- What is powder sintering? A Guide to Efficient High-Performance Part Manufacturing
- What temperature does a sealed quench furnace run at? A Guide to Optimizing Your Heat Treatment



















