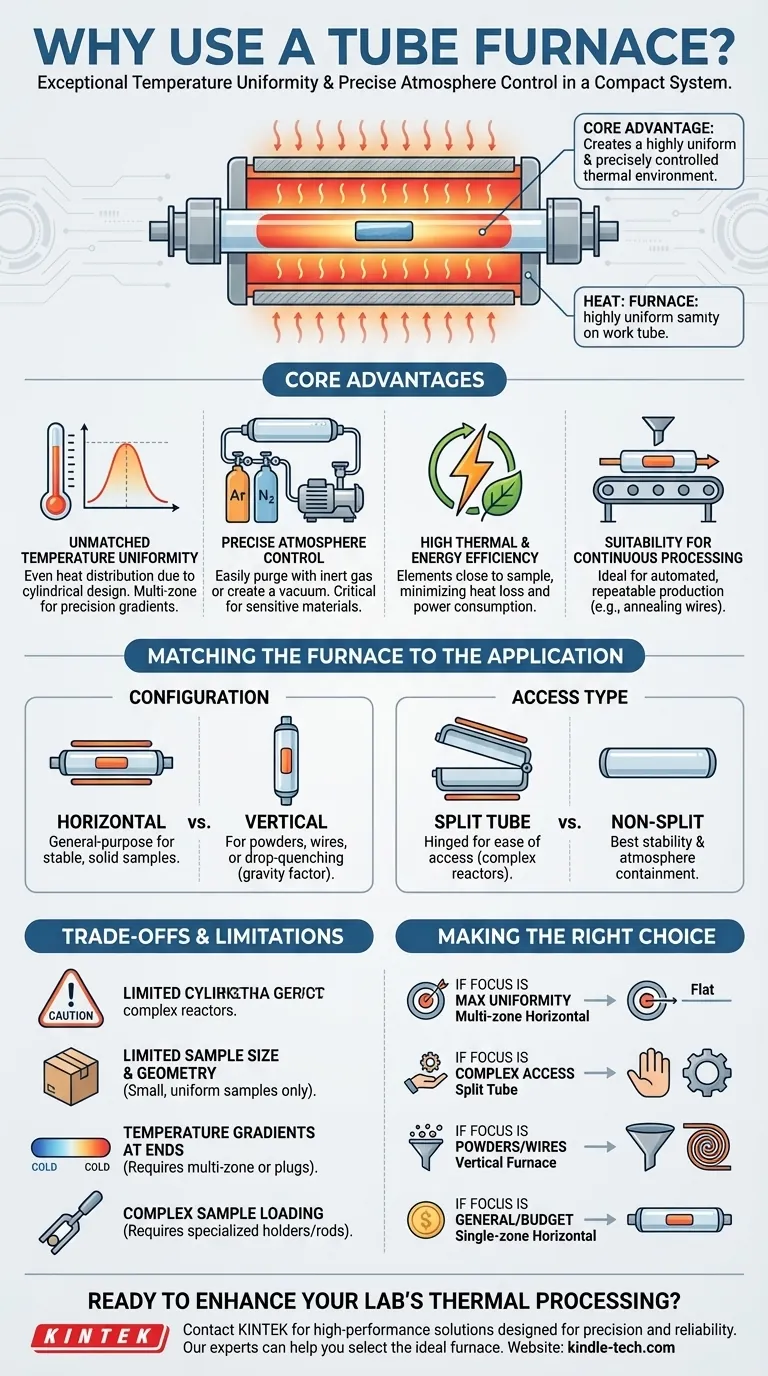
At its core, a tube furnace is used for its exceptional ability to create a highly uniform and precisely controlled thermal environment. It excels at heating samples within a contained atmosphere, making it indispensable for processes where temperature consistency and atmospheric purity are critical. Its cylindrical design allows heating elements to be arranged symmetrically, ensuring that the sample experiences the same temperature from all sides.
The decision to use a tube furnace is driven by the need for superior temperature uniformity and atmosphere control within a compact, efficient system. The specific type of tube furnace—be it horizontal, vertical, or split-tube—is then selected to match the exact physical requirements of the sample and the process.

The Core Advantages of a Tube Furnace
A tube furnace's unique design provides several distinct operational advantages over other heating methods, such as box furnaces or ovens. These benefits are rooted in its geometry and sealed nature.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The primary reason to choose a tube furnace is its ability to deliver exceptional temperature uniformity. The cylindrical heating chamber allows elements to be wrapped around the work tube, distributing heat evenly.
For even greater precision, multi-zone tube furnaces feature independent heating zones along the tube's length. This allows you to either create an extended, highly uniform flat zone or establish a precise temperature gradient for specialized processes.
Precise Atmosphere Control
The enclosed work tube makes it simple to control the processing atmosphere. This is critical for materials sensitive to oxygen or other ambient gases.
You can easily purge the tube with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, or create a vacuum environment. This capability is fundamental for applications in materials science, semiconductor research, and chemistry.
High Thermal and Energy Efficiency
By design, the heating elements are positioned very close to the sample, minimizing wasted volume and heat loss. This results in high thermal efficiency and lower power consumption compared to larger chamber furnaces.
This efficiency makes them ideal for both rapid heating and cooling cycles and for sustained, long-duration thermal processing, saving significant energy costs over time.
Suitability for Continuous Processing
The linear, tubular format is well-suited for continuous or automated production. Samples can be systematically pushed or pulled through the heated zone, enabling consistent, repeatable processing for applications like annealing wires or synthesizing materials.
Matching the Furnace to the Application
Not all tube furnaces are the same. The configuration you choose is directly tied to your specific material, sample shape, and process goals.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Furnaces
A horizontal furnace is the most common configuration, used for general-purpose heat treatment of stable, solid samples.
A vertical furnace, by contrast, is specifically designed for applications where gravity is a factor. It is ideal for processing powders, wires, or small parts that benefit from bottom-loading, or for processes like drop-quenching where the sample must be quickly removed from the heat zone.
Split Tube vs. Non-Split Furnaces
A standard non-split furnace is a solid cylinder that the work tube slides into. This design generally offers the best temperature stability and atmosphere containment.
A split tube furnace is hinged, allowing it to be opened and closed like a clamshell. Its key advantage is ease of access. This is essential when using work tubes with end flanges or multi-part reaction vessels that cannot be easily inserted into a solid furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Limited Sample Size and Geometry
The most obvious limitation is the small and restrictive internal diameter. Tube furnaces are unsuitable for heating large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects. Their strength lies in processing small, uniform samples.
Temperature Gradients at the Ends
In simple, single-zone models, the temperature naturally drops off near the ends of the tube. While insulation plugs can mitigate this, achieving perfect uniformity across the entire length requires a more advanced multi-zone furnace.
Complexity in Sample Loading
Compared to the simple door on a box furnace, inserting a delicate sample into the center of a long, hot tube can be challenging. This requires specialized sample holders or push rods, adding a layer of operational complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace, focus on the primary demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity: A multi-zone horizontal tube furnace provides the most precise control over the heated length.
- If your primary focus is processing samples with complex connections or reactors: A split tube furnace offers the necessary access for easy installation and removal.
- If your primary focus is working with powders, wires, or drop-quenching: A vertical tube furnace is specifically designed to handle these applications effectively.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating of small samples on a budget: A single-zone, non-split horizontal furnace is the most economical and straightforward option.
By understanding these core designs, you can select a furnace that functions as a precise and efficient tool for your specific thermal processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Cylindrical design ensures even heat distribution; multi-zone models offer extended flat zones or gradients. |
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed work tube allows for inert gas purging or vacuum environments, ideal for sensitive materials. |
| Thermal Efficiency | Compact design minimizes heat loss, leading to lower power consumption and faster heating/cooling cycles. |
| Process Flexibility | Horizontal, vertical, and split-tube configurations suit various sample types and loading requirements. |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing capabilities?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance tube furnaces designed for precision and reliability. Whether your application requires unmatched temperature uniformity, precise atmosphere control, or a specific configuration like vertical or split-tube, our experts can help you select the ideal solution for your laboratory needs.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing in a Controlled Atmosphere
- How does a high-precision tube furnace contribute to the testing of EuOBr catalysts? Ensure Stability & Accuracy
- What role does a multi-stage zone refining furnace play in obtaining high-purity TlBr? Achieve Deep Material Purification
- How is a laboratory tube heating furnace configured for high-temperature failure studies? Master Reactor Precision
- What factors determine the maximum temperature in a vacuum tube furnace? Unlock the True Limits of Your System
- What is the function of a tube furnace in CVD SiC synthesis? Achieving Ultra-Pure Silicon Carbide Powders
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- Is quartz chemically reactive? The Hidden Danger of Freshly Fractured Dust



















