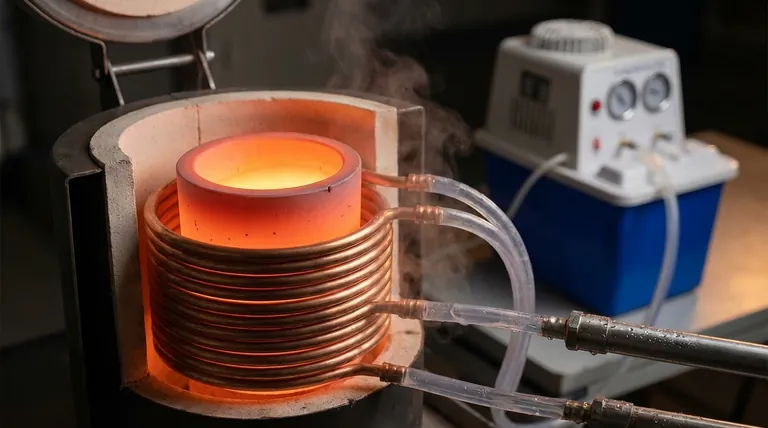
At its core, water is used in an induction furnace for a single, critical purpose: to cool the induction coil and power-delivery components. Without a continuous flow of cooling water, the immense electrical currents used to generate the melting heat would quickly cause the furnace's own copper coil to overheat and destroy itself.
The primary misunderstanding is that the water is involved in the melting process. In reality, the water acts as a heat removal system, managing the massive waste heat generated by the electrical components, which is an unavoidable byproduct of the induction process.
The Core Principle: Heat Where You Want It, and Where You Don't
To understand the need for water, you must first distinguish between the intended heat and the unwanted heat generated within an induction furnace system.
How Induction Heating Works
An induction furnace operates by passing a very high alternating current through a large copper coil. This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
When conductive material, like scrap metal, is placed inside this field, the magnetic field induces strong electrical currents (called eddy currents) within the metal itself. The metal's resistance to these eddy currents generates extreme heat, causing it to melt.
The Source of Unwanted Heat: The Coil
The same principle that heats the metal also applies, to a lesser degree, to the copper coil. Although copper is an excellent conductor, it still has some electrical resistance.
The massive amount of current flowing through the coil generates a significant amount of "waste heat" due to this resistance. If this heat is not continuously removed, the temperature of the coil will rise uncontrollably.
Why the Coil Fails Without Cooling
The copper coil is the heart of the furnace. If its temperature rises too high, it will soften, deform under the magnetic forces, and ultimately melt.
This would lead to a catastrophic failure of the furnace, potentially causing a short circuit and creating a severe safety hazard. Water cooling is the active measure that prevents this from ever happening.
Water as the Ideal Coolant
Water is chosen as the cooling medium for several practical and scientific reasons. It is the essential component that allows the furnace to operate safely and continuously at high power.
High Heat Capacity
Water has a very high specific heat capacity, meaning it can absorb a large amount of thermal energy without a significant increase in its own temperature. This makes it extremely effective at transferring heat away from the coil.
Constant Circulation
The water in an induction furnace is not static. It is constantly circulated by powerful pumps through hollow passages within the copper coil and power cables.
The water absorbs heat from the copper, flows to an external heat exchanger or cooling tower where it releases the heat into the atmosphere, and is then pumped back to the furnace to repeat the cycle.
The Importance of Water Purity
Industrial systems almost always use deionized or distilled water, not tap water. This is because tap water contains minerals that are electrically conductive and can cause short circuits.
These minerals can also precipitate out of the water as "scale" on the inside of the coil's cooling channels. This scale acts as an insulator, drastically reducing cooling efficiency and leading to overheating and component failure.
Understanding the Risks and Trade-offs
While essential, the use of water in a high-temperature metallurgical environment introduces specific challenges and risks that must be managed.
The Danger of Leaks
The most significant risk is a water leak. If water from a compromised coil comes into contact with the molten metal inside the furnace, it will flash into steam instantaneously.
This rapid expansion of volume creates a steam explosion, which can eject molten metal from the furnace with violent force, posing an extreme danger to personnel and equipment. Modern furnaces have sophisticated leak detection systems to prevent this.
System Complexity and Maintenance
A water-cooling system adds complexity. It requires pumps, filters, heat exchangers, flow meters, and temperature sensors.
Each of these components requires regular inspection and maintenance to ensure the system is operating correctly. A failure in any part of the cooling loop can force a complete shutdown of the furnace.
Applying This Understanding to Your Operations
Grasping the role of the cooling system is fundamental to operating and maintaining an induction furnace safely and efficiently.
- If your primary focus is furnace operation: Treat the water cooling system as being just as critical as the power supply. Never ignore a low-flow or high-temperature alarm, as it is often the first warning of an impending failure.
- If your primary focus is maintenance: Your goal is to ensure maximum heat transfer. Regularly check for internal scale buildup, ensure water purity is within specification, and inspect for leaks to prevent both inefficiency and catastrophic accidents.
- If your primary focus is system design or procurement: A robust, well-engineered cooling system with reliable leak detection is a non-negotiable investment in safety, uptime, and the long-term health of the furnace.
Ultimately, water acts as the silent guardian that enables the controlled and efficient power of induction melting.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Critical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Coil Cooling | Prevents copper coil from melting due to electrical resistance | Uses deionized water to prevent short circuits |
| Heat Removal | High heat capacity efficiently transfers waste heat away | Requires constant circulation via pumps and heat exchangers |
| Safety Management | Prevents catastrophic steam explosions from water-molten metal contact | Modern systems include leak detection for safety |
| Operational Efficiency | Enables continuous high-power furnace operation | Regular maintenance prevents scale buildup and system failure |
Ensure your lab's induction furnace operates safely and efficiently with KINTEK's expert support.
As specialists in lab equipment and consumables, we understand the critical role of proper cooling systems in your melting operations. Our team can help you:
- Select the right water purification systems to maintain cooling efficiency
- Implement maintenance protocols to prevent scale buildup and leaks
- Source reliable components for your furnace's cooling loop
Don't risk equipment failure or safety hazards – contact our experts today to optimize your induction furnace cooling system and protect your valuable laboratory investments.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression



















