Introduction
Table of Contents
Hydraulic presses have become an integral part of various industries due to their versatility and efficiency. These powerful machines utilize hydraulic systems to generate force, allowing them to perform a wide range of industrial applications effectively. From metalworking and plastics processing to woodworking, hydraulic presses play a crucial role in numerous industrial processes. They are capable of performing operations such as forging, punching, blanking, deep drawing, and forming with precision and consistency. With different variations available, including varying sizes, capacities, and configurations, hydraulic presses can be tailored to meet specific application requirements. Let's delve deeper into the world of hydraulic presses and explore their industrial applications.
Understanding Hydraulic Presses
Description of Hydraulic Presses
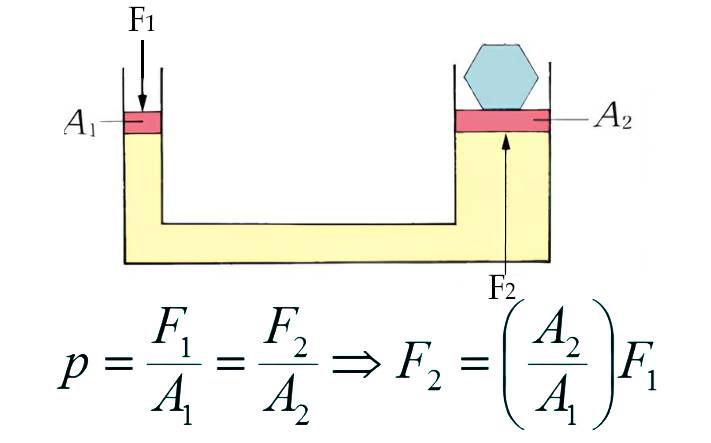
A hydraulic press is a machine that uses the pressure generated in a confined fluid to configure metals, plastics, rubber, and other materials. Its operation is governed by Pascal’s principle, which states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted unaltered throughout the fluid. In a hydraulic press, this pressure is transmitted to a piston that functions like a pump.
A hydraulic press incorporates a mainframe as well as control and power systems. Hydraulic fluid is forced into a small cylindrical piston (plunger cylinder), which drives the fluid into a larger piston (ram cylinder). As the larger piston moves, it forces the fluid back into the smaller piston. This continuous exchange generates varying degrees of mechanical pressure which is transmitted to an anvil that presses directly on the workpiece to be shaped.
Components of Hydraulic Presses
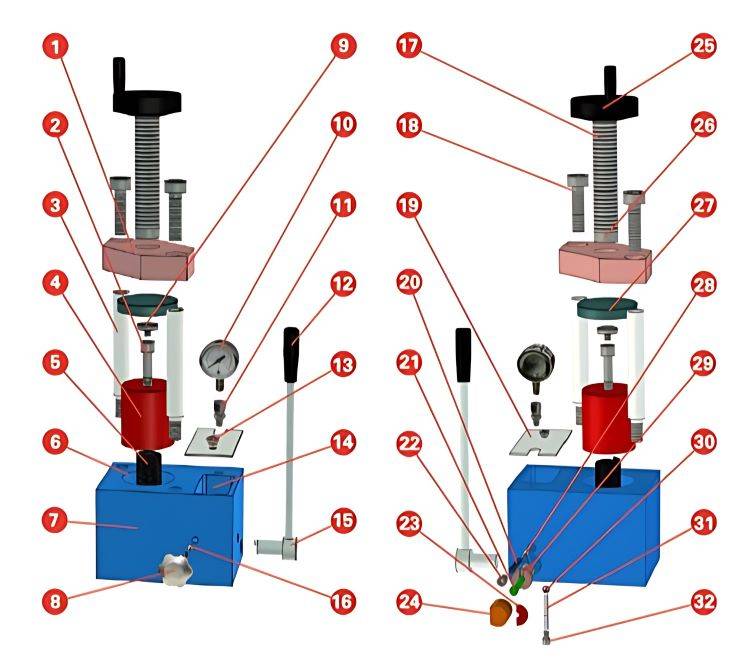
A hydraulic press contains three main components: the mainframe, power system, and hydraulic control system. The mainframe provides the structure and support for the press, while the power system generates the hydraulic force. The hydraulic control system regulates the flow of hydraulic fluid and controls the movement of the pistons.
The main parts of a hydraulic press include:
-
Hydraulic Cylinder: This is the part of the press that generates the force. It consists of a piston and a cylinder that are connected by hydraulic fluid. When the fluid is pressurized, it pushes the piston, creating a force that can be used to shape or deform materials.
-
Pump: The pump is responsible for generating the hydraulic pressure. It forces hydraulic fluid into the hydraulic cylinder, creating the force needed to operate the press.
-
Control System: The control system regulates the flow of hydraulic fluid and controls the movement of the pistons. It allows the operator to adjust the pressure and speed of the press, ensuring precise and accurate results.
Hydraulic presses are widely used across various industries for fabrication, assembly, and maintenance purposes. They are versatile and efficient machines that can be used for shaping, forging, stamping, and other processes. Depending on the specific requirements of the application, hydraulic presses are available in different sizes, capacities, and configurations.
Role of Hydraulic Presses in Industrial Processes
Metalworking
Hydraulic presses are widely used in the metalworking industry for various processes such as sheet metal forming, stamping, punching, blanking, bending, and coining. These presses are particularly beneficial in large volume production, helping the automotive industry manage labor costs. For example, deep-drawing is a common sheet metal forming process that greatly benefits from the use of hydraulic presses. The precise control over speed and force provided by hydraulic presses ensures consistency and accuracy in high production environments like the automotive industry.
Plastics Processing
Hydraulic presses also play a vital role in plastics processing. They are used to assemble, bend, crush, and alter the shapes of plastic materials. The use of hydraulic presses in the plastics industry enables efficient production processes such as molding, blanking, and deep drawing. With the increasing importance of lightweighting in industries like aerospace and automotive, hydraulic presses are being utilized in the processing of thermoplastics, composites, SMC sheet molded composites, RTM resin transfer molding, GMT glass mat transfer, and carbon fiber molding. These applications require precise control and repeatability, which hydraulic presses provide.

Woodworking
In the woodworking industry, hydraulic presses are essential for tasks like forging, clinching, molding, and forming. They are particularly useful in the making of swords and general blacksmithing. Hydraulic presses provide the necessary even pressure and slow, steady rate required to flatten the blade of a sword or knife. Additionally, hydraulic presses find applications in the production of powder products. Food manufacturers use them to produce fat-free cocoa powder by pressing chocolate liquor to remove the fat. Cosmetic manufacturers use hydraulic presses for producing face powders, and in medicine, special presses are used for the powder in pills.
Hydraulic presses are versatile and efficient machines that are widely used in various industries. They offer precise control, repeatability, and the ability to generate high compressive forces. Whether it's in metalworking, plastics processing, or woodworking, hydraulic presses play a crucial role in enhancing productivity and achieving desired outcomes.
Operations Performed by Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic presses are versatile and efficient machines that play a crucial role in many industrial processes, including metalworking, plastics processing, and woodworking. They can be used to perform various operations such as forging, punching, blanking, deep drawing, and forming. Let's take a closer look at each of these operations:
Forging
Forging is one of the oldest metalworking processes, historically performed by blacksmiths using a hammer and anvil. However, with the advancement of technology, forging is now done using hydraulic presses, resulting in superior part quality and higher production rates. Hydraulic forging presses are widely used in foundries, forging facilities, job shops, and more. They offer versatility, allowing for the production of parts with superior strength, custom shapes and sizes, and unique performance specifications.
Punching
Hydraulic presses are also commonly used for punching operations. Punching involves creating holes or indentations in a material using a punch and die set. Hydraulic presses provide the necessary force to drive the punch through the material, creating precise and clean holes. Punching is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Blanking
Blanking is a process that involves cutting out a flat shape from a sheet of material. Hydraulic presses can be used for blanking operations, providing the required force to cut through the material. This process is commonly used in the production of metal components for various industries, including automotive, electronics, and appliances.
Deep Drawing
Deep drawing is a metal forming process used to create hollow, three-dimensional shapes from sheet metal. Hydraulic presses are used to apply force to the sheet metal, causing it to deform and take on the desired shape. Deep drawing is commonly used in the production of automotive parts, kitchenware, and other consumer products.
Forming
Hydraulic presses are also widely used for forming operations. Forming involves bending, shaping, or molding a material into a desired shape. Hydraulic presses provide the necessary force and control to shape the material accurately. This process is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, construction, and furniture manufacturing.
In addition to the operations mentioned above, hydraulic presses have various other applications. They are used in powder compacting, concrete compression testing, scrap baling, ceramics manufacturing, laboratory testing, and sample preparation. Hydraulic presses offer precise control, repeatability, and versatility, making them an essential tool in many industries.
Whether it's forging, punching, blanking, deep drawing, or forming, hydraulic presses provide the necessary force and control to carry out these operations efficiently and effectively. With their ability to create intricate shapes while being economical with materials, hydraulic presses are a valuable asset in modern manufacturing processes.
Variations in Hydraulic Presses
Differing Sizes and Capacities
Hydraulic presses come in a variety of sizes and capacities to suit different applications. The size and capacity of a hydraulic press will depend on the intended use and the requirements of the laboratory.
One type of hydraulic press is the manual hydraulic press, which uses a hand-operated lever to apply load to a sample. It requires physical effort to operate and may not be suitable for frequent use. However, for infrequent use, a manual press can be a cost-effective option.
On the other hand, an automatic hydraulic press uses an electric motor to drive the pump and electric switches to control the pressure. This type of press offers high accuracy and repeatability, making it ideal for applications that require precise control.
Configurations Based on Application Requirements
Each application has unique requirements for clamping force, dwelling time, temperature, and other factors. Therefore, it is crucial to select a hydraulic press that is suitable for the specific application to achieve the best results.
Kin-Tech, with its extensive experience in the field, can help make this choice easier. They offer a range of hydraulic presses to suit various applications and can provide standard presses or custom options to fit unique needs.
If your laboratory staff needs to produce pressed samples recurrently, an automatic hydraulic press will likely be more convenient and enable a quicker pace of work.

Complexity of Control Systems
Different types of hydraulic presses have different control systems. Manual hydraulic presses have a mechanical lever that controls a piston, while automatic hydraulic presses have a switch or automated controller to control the piston.
Manual hydraulic presses are often cheaper than their automatic counterparts but require more physical effort to use. They are also harder to use consistently for each task, as there is a chance that samples may be pressurized to slightly different loads by the operator.
On the other hand, automatic hydraulic presses offer precise application of force and can be controlled to a high accuracy and repeatability. They are ideal for applications that require consistent and repeatable results.
In conclusion, selecting the right hydraulic press for your laboratory application is essential to ensure accurate and repeatable results. Kin-Tech offers a range of hydraulic presses to suit various applications and can help guide you in choosing the ideal press for your needs.
Please note that the content provided is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydraulic presses are a versatile and efficient tool that play a crucial role in various industrial processes. Whether it's metalworking, plastics processing, or woodworking, hydraulic presses offer the power and precision needed to perform a range of operations like forging, punching, blanking, deep drawing, and forming. With variations in sizes, capacities, and configurations, hydraulic presses can be tailored to meet specific application requirements. The complexity of control systems ensures seamless operation and optimal performance. Overall, hydraulic presses are a valuable asset in the manufacturing world, providing reliability and productivity to businesses across industries.
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
Related Articles
- Automatic Hydraulic Press: The Ultimate Guide for Efficient Sample Preparation and Industrial Processes
- Applications and Importance of Hydraulic Press in Laboratories
- The Science Behind Hydraulic Presses and Their Applications
- Comprehensive Guide to Hydraulic Hot Press: Function, Features and Applications
- What is lab hydraulic press