Introduction to Reference Electrodes
Ideal Conditions for Reference Electrodes
For accurate electrochemical measurements, reference electrodes must quickly establish and maintain a stable thermodynamic equilibrium potential. This stability is crucial for ensuring the precision of the measurements. The reference electrode should exhibit minimal drift over time, which can be influenced by factors such as temperature, solution composition, and mechanical stress.
Common types of reference electrodes include calomel and silver-silver chloride electrodes. These electrodes are preferred due to their ability to achieve and sustain a stable potential under various conditions. Calomel electrodes, for instance, are known for their reliability in aqueous environments, while silver-silver chloride electrodes are particularly robust in both acidic and basic solutions.
To maintain optimal performance, reference electrodes should be regularly checked and maintained. This includes ensuring that the internal resistance remains below 10KΩ, as higher resistance can indicate blockages that may affect the electrode's performance. Additionally, the electrode potential should be monitored regularly by comparing it with a known good reference electrode in a KCl solution. Any potential difference greater than 3mV or a change greater than 1mV may necessitate replacement or regeneration of the electrode.

In summary, the ideal conditions for reference electrodes involve rapid establishment of thermodynamic equilibrium potential and sustained stability over time. Regular maintenance and checks are essential to ensure these conditions are met, thereby guaranteeing accurate and reliable electrochemical measurements.
Use and Maintenance of Reference Electrodes
Operational Guidelines
To ensure the proper functioning of your reference electrode during electrochemical measurements, several operational guidelines must be followed meticulously.
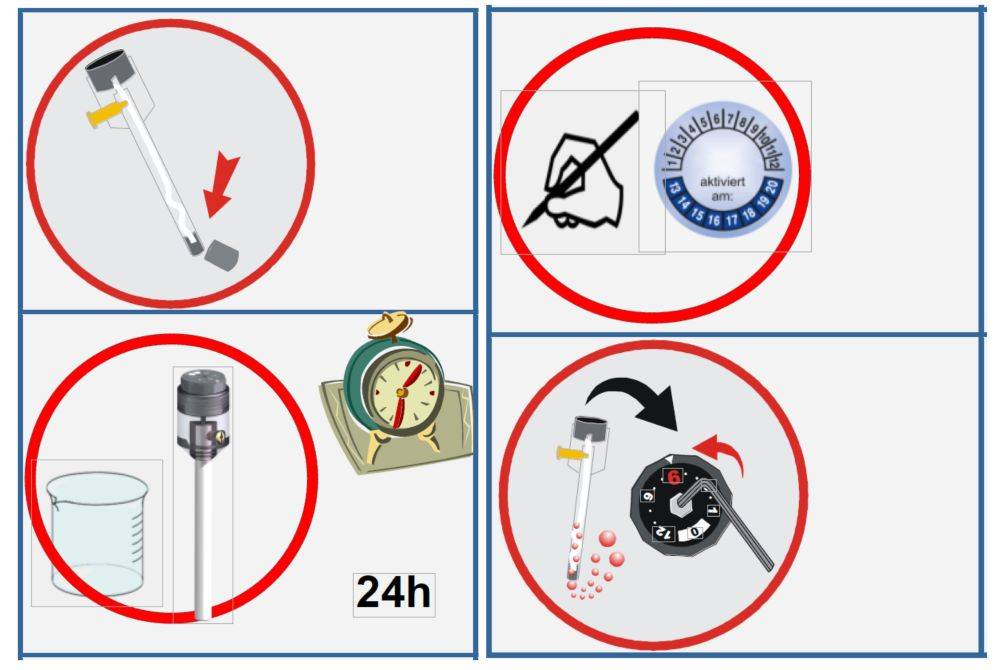
Firstly, removing the rubber plug from the filling port is crucial. This action facilitates an unobstructed flow of the electrode solution, which is essential for maintaining a consistent and accurate potential reading. Without this step, the flow rate may be compromised, leading to potential inaccuracies in your measurements.
Secondly, maintaining the salt bridge level above the interface to be measured is a critical precaution. This positioning prevents the reference electrode from drawing in external solutions, thereby safeguarding the integrity of the measurement environment. It’s akin to setting a protective barrier that ensures the electrode only interacts with the intended solution.
Lastly, preventing air bubbles in the electrode solution is non-negotiable. Air bubbles can introduce significant errors by altering the electrical contact between the electrode and the solution. To eliminate this risk, ensure that the solution is free of any trapped air by gently agitating the electrode or by using a degassing process if necessary.
| Guideline | Importance |
|---|---|
| Remove rubber plug | Ensures flow rate consistency |
| Maintain salt bridge level | Prevents external solution contamination |
| Prevent air bubbles | Avoids measurement errors |
By adhering to these operational guidelines, you can significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of your electrochemical measurements.
Replenishment and Temperature Control
Maintaining the reference electrode solution at the correct concentration is crucial for ensuring accurate electrochemical measurements. Regular replenishment of the solution is essential to prevent depletion, which can lead to unstable potentials and erroneous readings. The frequency of replenishment depends on the usage rate and the specific requirements outlined in the electrode's manual. It is recommended to check the solution level before each measurement session and top it up as necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Temperature control during measurements is equally important. Temperature fluctuations can significantly affect the potential stability of the reference electrode. To mitigate this, it is advisable to conduct measurements in a controlled environment where temperature variations are minimal. If this is not feasible, consider using a temperature-controlled chamber or a thermostat to regulate the ambient temperature around the electrode. Additionally, ensure that the electrode solution is at room temperature before use to avoid thermal shock, which can cause transient changes in potential.
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Solution Replenishment | Check and replenish solution before each session; follow manual guidelines. |
| Temperature Control | Conduct measurements in a controlled environment; use a thermostat if necessary. |
By adhering to these practices, you can ensure that your reference electrode remains in optimal condition, providing reliable and accurate measurements.
Handling Liquid Connection Blockages
When dealing with reference electrodes, one of the most critical aspects of maintenance is ensuring that the liquid connection remains unobstructed. Blockages in the liquid connection can lead to inaccurate measurements and instability in the electrode's potential. Here are the steps to effectively handle such blockages:
-
Scraping Off Blockages: If the blockage is minor, you can attempt to scrape it off gently. Use a clean, soft tool to avoid damaging the delicate parts of the electrode. This method is particularly useful for removing superficial deposits that have accumulated over time.
-
Replacing the Liquid Connection Part: In cases where the blockage is severe or recurring, it may be necessary to replace the entire liquid connection part. This ensures that the electrode functions correctly and maintains its accuracy. Replacement parts are typically available from the manufacturer and should be installed according to the provided guidelines.
-
Preventive Measures: To avoid future blockages, regularly inspect the liquid connection part. Ensure that the solution is free from contaminants and that the flow rate is maintained as per the operational guidelines. Additionally, keep the salt bridge level higher than the interface to be measured, which helps prevent blockages from forming.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your reference electrode remains in optimal condition, providing reliable and accurate measurements.
Temperature Limitations and Light Sensitivity
Glymercury electrodes, while highly effective in many electrochemical applications, have specific operational constraints that must be strictly adhered to. The primary limitation is temperature; these electrodes should not be used at temperatures exceeding 70°C. Exposing glymercury electrodes to such high temperatures can lead to degradation of the electrode material, compromising its performance and accuracy.
In addition to temperature constraints, light sensitivity is another critical factor to consider. Glymercury electrodes are particularly sensitive to light, which can cause photochemical reactions that alter the electrode's potential. To mitigate this issue, it is essential to shield the electrode from light exposure. A practical solution is to apply a black polyethylene tube to the electrode rod. This simple yet effective measure ensures that the electrode remains stable and maintains its intended potential, even in environments where light exposure is unavoidable.
By adhering to these guidelines, users can ensure the longevity and accuracy of their glymercury electrodes, thereby optimizing their performance in various electrochemical measurements.
Storage and Pre-use Preparation
When storing solid reference electrodes, it is crucial to keep them submerged in a potassium chloride (KCl) solution. This solution acts as a protective medium that helps maintain the electrode's integrity and performance over time. Before using the reference electrode, it is recommended to immerse it in a container filled with KCl solution for several hours. This pre-use preparation ensures that the electrode reaches a stable and consistent potential, which is essential for accurate electrochemical measurements.
In addition to the immersion process, it is also important to ensure that the KCl solution is at the appropriate concentration as specified by the manufacturer. This helps in preventing any potential issues related to concentration gradients that could affect the electrode's performance. Proper storage and pre-use preparation are key steps in ensuring that the reference electrode functions optimally, thereby enhancing the reliability of the electrochemical measurements.
| Preparation Step | Details |
|---|---|
| Storage | Keep solid reference electrodes in KCl solution to maintain their integrity. |
| Pre-use Immersion | Immerse the electrode in a container of KCl solution for several hours before use. |
| Solution Concentration | Ensure the KCl solution is at the appropriate concentration as per manufacturer guidelines. |
By following these steps, you can ensure that your reference electrode is ready for use, providing stable and accurate potential readings in your electrochemical experiments.
Methods of Checking Reference Electrodes
Internal Resistance Check
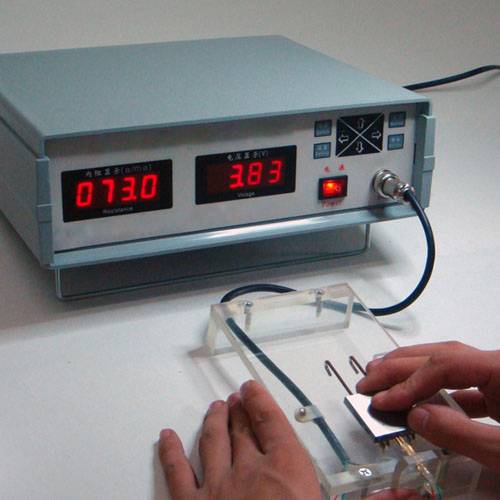
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of your reference electrode, it is crucial to perform regular internal resistance checks using a conductivity meter. The internal resistance of the electrode should ideally be below 10KΩ. Conductivity meters are designed to measure the ease with which electric current flows through the electrode, providing a direct indication of its operational efficiency.
High internal resistance typically signifies a blockage within the electrode, which can severely compromise its ability to maintain a stable potential. This blockage often occurs in the liquid junction or the filling solution, hindering the free movement of ions and thus increasing the resistance.

| Resistance Level | Indication | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Below 10KΩ | Normal | No immediate action |
| Above 10KΩ | Blockage | Investigate and clear blockage |
When the resistance exceeds the recommended threshold, it is imperative to address the issue promptly. Common methods to clear blockages include mechanical removal, vacuum treatment, or soaking in specific solutions. Each method has its own set of guidelines and potential risks, so it is advisable to consult the electrode's manual or a professional for the most appropriate course of action.
By maintaining an internal resistance below 10KΩ, you can ensure that your reference electrode continues to provide accurate and stable measurements, essential for reliable electrochemical experiments and applications.
Electrode Potential Check
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of your electrochemical measurements, it is crucial to periodically check the potential of your reference electrodes. This process involves comparing the potential of a known good reference electrode with a suspected poor one, both immersed in a potassium chloride (KCl) solution. The potential difference between these two electrodes should be meticulously observed.
| Potential Difference | Action Required |
|---|---|
| Greater than 3mV | Replace or regenerate the suspect electrode |
| Change greater than 1mV | Replace or regenerate the suspect electrode |
A potential difference exceeding 3mV or a change greater than 1mV indicates that the suspect electrode is no longer functioning within acceptable parameters. In such cases, immediate action is necessary to either replace the electrode or undergo a regeneration process to restore its functionality. This proactive approach ensures that your measurements remain accurate and your experiments are not compromised by faulty equipment.
Appearance Check
During the inspection of reference electrodes, particularly the mercury core and the silver-silver chloride (Ag-AgCl) electrode, it is crucial to observe both the interfaces and the colors of these components. A clear interface signifies that the electrode is functioning correctly, allowing for accurate potential measurements. Conversely, any cloudiness or irregularities at the interface can indicate potential issues that may affect the electrode's performance.
The color of the Ag-AgCl electrode is another critical indicator of its condition. Ideally, the Ag-AgCl electrode should maintain its characteristic silver hue. However, if an off-white coloration is observed, this is a clear sign of decomposition. This change in color typically results from the breakdown of the silver chloride layer, which can occur due to exposure to light, temperature fluctuations, or improper storage conditions. Such decomposition can lead to an unstable electrode potential, thereby compromising the accuracy of electrochemical measurements.
To summarize, a thorough visual inspection of the mercury core and Ag-AgCl electrode should be conducted regularly. Ensure that the interfaces remain clear and that the Ag-AgCl electrode retains its proper silver color. Any deviations from these standards should prompt further investigation or corrective action to maintain the integrity and reliability of the reference electrode.
Regeneration Methods for Reference Electrodes
Soaking and Ammonia Immersion
To rejuvenate the liquid junction part of reference electrodes, it is essential to soak it in a carefully prepared solution. This solution consists of a hot mixture containing 10% saturated potassium chloride (KCl) and 90% deionized water. This step is crucial for restoring the electrode's functionality by removing any accumulated contaminants.
For specific types of electrodes, such as Ag-AgCl electrodes, an additional step is required. These electrodes should be immersed in concentrated ammonia. The ammonia acts as a powerful solvent, effectively dissolving any silver chloride (AgCl) deposits that may have formed on the electrode surface. This process not only cleans the electrode but also restores its optimal performance, ensuring accurate and reliable measurements.

| Electrode Type | Restoration Method |
|---|---|
| General | Soak in hot 10% KCl and 90% deionized water |
| Ag-AgCl | Immersion in concentrated ammonia |
By following these precise regeneration methods, the longevity and accuracy of reference electrodes can be significantly enhanced, ensuring they remain in optimal condition for extended periods.
Vacuum Treatment and Boiling
To ensure the smooth operation of reference electrodes, it is crucial to address any mechanical blockages that may impede the functionality of the liquid junction. One effective method for this is vacuum treatment. By employing a suction pump, you can create a vacuum that helps dislodge any obstructions within the liquid junction. This process is particularly useful for removing particulate matter or small deposits that can hinder the proper flow of the electrolyte.
Following vacuum treatment, the liquid junction part of the electrode should undergo boiling. This step involves immersing the liquid junction in water and heating it to a boil for a brief period. Boiling helps to loosen and remove any remaining blockages, ensuring that the electrode can function optimally. It is essential to monitor the duration of boiling to prevent overheating, which could damage the electrode. After boiling, allow the electrode to cool down completely before proceeding with further treatments or measurements.
| Treatment Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Treatment | Use a suction pump to create a vacuum, dislodging mechanical blockages. |
| Boiling | Immerse the liquid junction in boiling water for a short duration. |
| Cooling | Ensure the electrode cools down fully before any subsequent treatments. |
These combined methods of vacuum treatment and boiling are critical for maintaining the integrity and accuracy of reference electrodes, ensuring they remain reliable for electrochemical measurements.
Mechanical Removal of Blockages
When dealing with blockages in the liquid junction part of reference electrodes, one common method involves gently grinding the affected area using gauze paper. This technique can effectively remove superficial obstructions, restoring the electrode's functionality temporarily. However, it is important to note that this method carries a significant risk of causing permanent damage to the electrode. The abrasive action of the gauze paper can wear away essential components, leading to long-term clogging or even structural degradation of the electrode.
For more severe blockages, alternative methods such as vacuum treatment or boiling the liquid junction part may be more appropriate. These techniques avoid the physical abrasion that can cause permanent damage and are often more effective in clearing substantial obstructions. It is crucial to weigh the potential benefits of mechanical removal against the risk of irreversible damage to ensure the longevity and accuracy of the reference electrode.
Storage of Reference Electrodes
Optimal Storage Solutions
Proper storage of reference electrodes is crucial for maintaining their performance and longevity. For Ag-AgCl electrodes, it is essential to store them in a potassium chloride (KCl) solution. This prevents the precipitation of AgCl, which can lead to potential instability and inaccuracies in measurements. The KCl solution acts as a protective medium, ensuring that the electrode remains in optimal condition.
For calomel electrodes, the storage requirements are equally critical. The filled solution level should always be maintained higher than the calomel core. This ensures that the electrode remains submerged, preventing exposure to air and potential contamination. Maintaining the correct solution level helps in preserving the electrode's integrity and ensuring accurate potential readings.
| Electrode Type | Storage Solution | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Ag-AgCl | KCl Solution | Prevent AgCl precipitation |
| Calomel | Filled Solution | Solution level above calomel core |
By adhering to these storage guidelines, users can significantly extend the lifespan of their reference electrodes and ensure consistent, reliable performance in electrochemical measurements.
Applications of Reference Electrodes
Telemetry and Cathodic Protection
Reference electrodes play a crucial role in telemetry systems designed for pipeline cathodic protection. These electrodes serve as the primary signal source, transmitting critical data about the cathodic protection status. This data is essential for maintaining the integrity of pipelines, ensuring they remain free from corrosion and damage.
In the context of cathodic protection, reference electrodes provide precise measurements that help in monitoring the effectiveness of the protective measures. They are often used in conjunction with telemetry systems to relay real-time data to control centers, allowing for immediate adjustments if necessary. This continuous monitoring ensures that the cathodic protection system operates optimally, thereby extending the lifespan of the pipelines.
Moreover, the stability and accuracy of reference electrodes are paramount in these applications. Any deviation in the electrode's potential can lead to incorrect readings, potentially compromising the entire cathodic protection system. Therefore, regular checks and maintenance of reference electrodes are vital to guarantee the reliability of the telemetry data.
In summary, reference electrodes are indispensable in telemetry and cathodic protection applications, offering a reliable means to monitor and maintain the protective measures for pipelines.
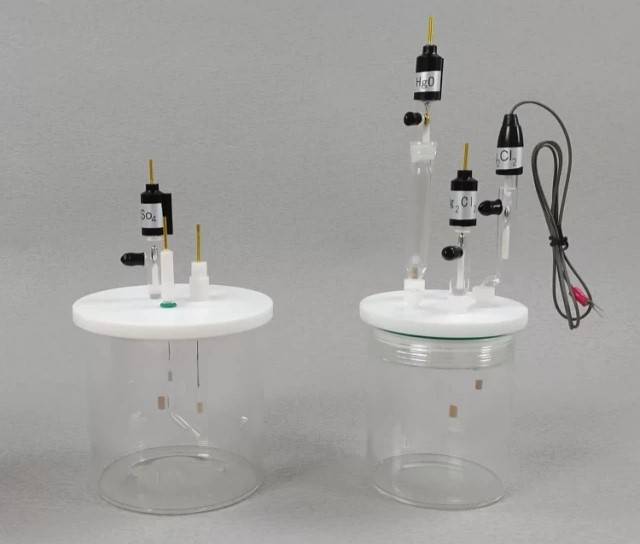

Inaccessible Monitoring Positions
Reference electrodes can be strategically pre-buried in locations that are otherwise difficult to access, such as the heart of large industrial containers or deep within underground fuel depots. These placements ensure continuous, long-term monitoring without the need for frequent human intervention. The durability and stability of reference electrodes make them ideal for such demanding environments, where other monitoring solutions might fail due to harsh conditions or limited accessibility.
For instance, in large storage tanks used for petroleum products, the center of the tank is often the most critical yet challenging area to monitor. By embedding a reference electrode during construction, engineers can achieve real-time data collection on the electrochemical conditions within the tank, providing invaluable insights for maintenance and safety protocols. Similarly, in underground fuel depots, the reference electrode can be installed during the initial setup, allowing for ongoing monitoring of the electrochemical environment without the need for excavation or intrusive inspections.
This method of deployment is particularly advantageous in scenarios where frequent access is impractical or hazardous. The ability to monitor these critical areas remotely and continuously ensures that any potential issues can be detected and addressed promptly, thereby enhancing the overall safety and efficiency of the operation.
Automatic Control in Cathodic Protection
In the context of cathodic protection for buried pipelines and underground metal structures, reference electrodes play a crucial role as stable signal sources for automatic control systems. These systems rely on the consistent and accurate readings provided by reference electrodes to ensure the continuous and effective protection of these structures from corrosion.
The stability of the signal from reference electrodes is paramount. For instance, in a typical cathodic protection setup, the reference electrode's potential is continuously monitored to adjust the current applied to the protected structure. Any fluctuations or inconsistencies in the electrode's potential can lead to improper current application, potentially exposing the structure to corrosion.
To maintain this stability, reference electrodes must be carefully maintained and regularly checked. This includes ensuring that the internal resistance remains below 10KΩ, as higher resistance can indicate blockages that could affect the electrode's performance. Additionally, the electrode's potential should be compared with a known good reference electrode in a KCL solution. A potential difference greater than 3mV or a change greater than 1mV necessitates immediate attention, either through replacement or regeneration.
Moreover, the operational guidelines for reference electrodes, such as maintaining a flow rate by removing the rubber plug from the filling port and ensuring the salt bridge level is higher than the interface to be measured, are critical to their effective functioning. These practices help prevent issues such as air bubbles in the electrode solution, which can disrupt the readings.
In summary, reference electrodes are indispensable components in the automatic control systems of cathodic protection projects. Their stability and accuracy are maintained through rigorous maintenance and checking protocols, ensuring the long-term protection of buried pipelines and underground metal structures.
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Electrode Fixture for Electrochemical Experiments
- Gold Disc Electrode
Related Articles
- AgAgCl Reference Electrode Working Principle and Applications
- Electrolytes and Electrochemical Electrodes
- Understanding Saturated Calomel Reference Electrodes: Composition, Uses, and Considerations
- How to Make Your Own Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode for Electrochemical Experiments
- How to Choose the Right Reference Electrode for Your Application
















