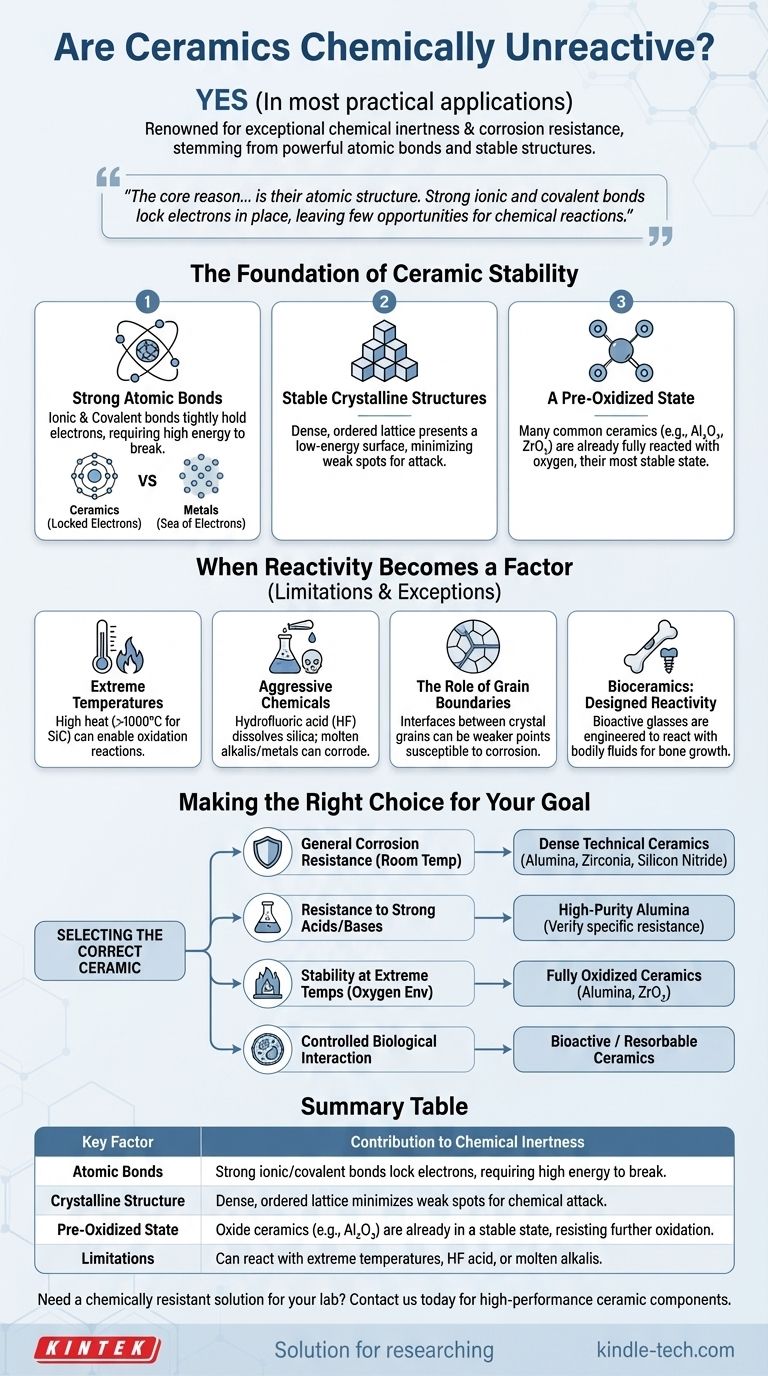
In most practical applications, yes. Ceramics are renowned for their exceptional chemical inertness and resistance to corrosion, which is a primary reason for their use in harsh environments. This stability stems directly from their powerful atomic bonds and stable crystalline structures, making them far less reactive than most metals.
The core reason for the chemical unreactivity of most ceramics is their atomic structure. Strong ionic and covalent bonds lock electrons in place, leaving few opportunities for the chemical reactions that cause corrosion and degradation in other materials.

The Foundation of Ceramic Stability
To understand why ceramics are so stable, we must look at their atomic and electronic structure. Their resistance isn't an accident; it's a fundamental property derived from their chemistry.
The Power of Strong Atomic Bonds
Unlike metals, which share a "sea" of free-floating electrons, ceramics are defined by very strong ionic and covalent bonds.
In these bonds, electrons are either transferred (ionic) or tightly shared (covalent) between specific atoms. This requires a significant amount of energy to break, making the material highly resistant to chemical attack.
Stable Crystalline Structures
The atoms in most ceramics are arranged in a rigid, densely packed crystalline lattice. This ordered structure presents a stable, low-energy surface to the outside world.
There are few "weak spots" or easily accessible electrons for chemical agents to interact with, effectively creating a chemical fortress at the molecular level.
A Pre-Oxidized State
Many of the most common technical ceramics, such as alumina (Al₂O₃) and zirconia (ZrO₂), are oxides.
This means they have already reacted fully with oxygen and are in their most stable thermodynamic state. They have no chemical tendency to oxidize further, which is the primary mechanism of corrosion for many metals.
When Reactivity Becomes a Factor
While highly stable, no material is completely inert under all possible conditions. Understanding the limits of a ceramic's chemical resistance is critical for proper material selection.
Extreme Temperatures
At very high temperatures, the increased atomic vibration can provide enough energy to enable reactions that would not occur at room temperature.
For example, non-oxide ceramics like silicon carbide (SiC) can begin to oxidize in air at temperatures exceeding 1000°C, forming a protective layer of silica (SiO₂).
Aggressive Chemical Environments
Certain powerful chemicals can attack specific ceramics. The most well-known example is hydrofluoric acid (HF), which is capable of dissolving silica-based ceramics and glasses.
Similarly, strong molten alkalis or certain molten metals can corrode even highly resistant ceramics over time.
The Role of Grain Boundaries
In most ceramic components, the material is not a perfect single crystal but a collection of tiny crystal grains. The grain boundaries—the interfaces where these crystals meet—can be sites of higher energy and impurity concentration.
These boundaries can be more susceptible to chemical corrosion than the bulk of the crystal grains, sometimes leading to a weakening of the material over time in harsh environments.
Bioceramics: Designed Reactivity
In medical applications, some ceramics are intentionally designed to be reactive. Bioactive glasses and certain calcium phosphates are engineered to slowly dissolve and react with bodily fluids to stimulate new bone growth. This is a case where controlled reactivity is a desired feature, not a failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct ceramic requires matching the material's specific chemical resistances to the demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is general corrosion resistance at room temperature: Almost any dense, technical ceramic like alumina, zirconia, or silicon nitride will provide excellent performance.
- If your primary focus is resistance to strong acids or bases: High-purity alumina is an exceptional choice, but always verify its resistance to your specific chemical, especially at high concentrations or temperatures.
- If your primary focus is stability at extreme temperatures in an oxygen environment: Fully oxidized ceramics like alumina or zirconia are often the best choice as they are already in their most stable state.
- If your primary focus is controlled interaction within a biological system: You must specifically choose a "bioactive" or "resorbable" ceramic designed for this purpose.
Understanding that ceramics are highly unreactive—but not infinitely so—is the key to leveraging their remarkable properties for challenging applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Contribution to Chemical Inertness |
|---|---|
| Atomic Bonds | Strong ionic/covalent bonds lock electrons, requiring high energy to break. |
| Crystalline Structure | Dense, ordered lattice minimizes weak spots for chemical attack. |
| Pre-Oxidized State | Oxide ceramics (e.g., Al₂O₃) are already in a stable state, resisting further oxidation. |
| Limitations | Can react with extreme temperatures, HF acid, or molten alkalis. |
Need a chemically resistant solution for your lab? The exceptional stability of ceramics makes them ideal for harsh environments, from high-temperature furnaces to corrosive chemical processes. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including ceramic components designed for maximum durability and inertness. Let our experts help you select the perfect material for your specific application. Contact us today to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with reliable, corrosion-resistant solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is ceramic insulation used for? Master High-Temperature Solutions for Industrial Efficiency
- What is the maximum temperature for ceramics? Find the Right Material for Your High-Temp Application
- Why are platinum electrode wires wrapped in oxidized zirconia coils? Ensure Signal Integrity in High-Temp Systems
- What are the applications of zirconia ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Can ceramic withstand high temperatures? Discover the Superior Materials for Extreme Heat



















