Yes, aluminum can be successfully brazed. It is a well-established joining process used across numerous high-performance industries, including aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing. The key to the process is not the aluminum itself, but the strategy used to manage the tough, invisible layer of oxide that instantly forms on its surface.
The success of brazing aluminum hinges entirely on one critical step: overcoming its natural, protective oxide layer. Every aspect of the process, from flux selection to furnace atmospheres, is designed to remove this barrier and allow the filler metal to form a true metallurgical bond with the base material.
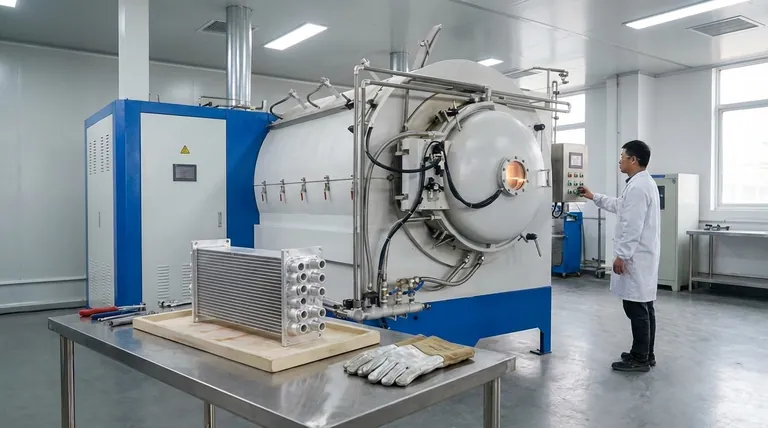

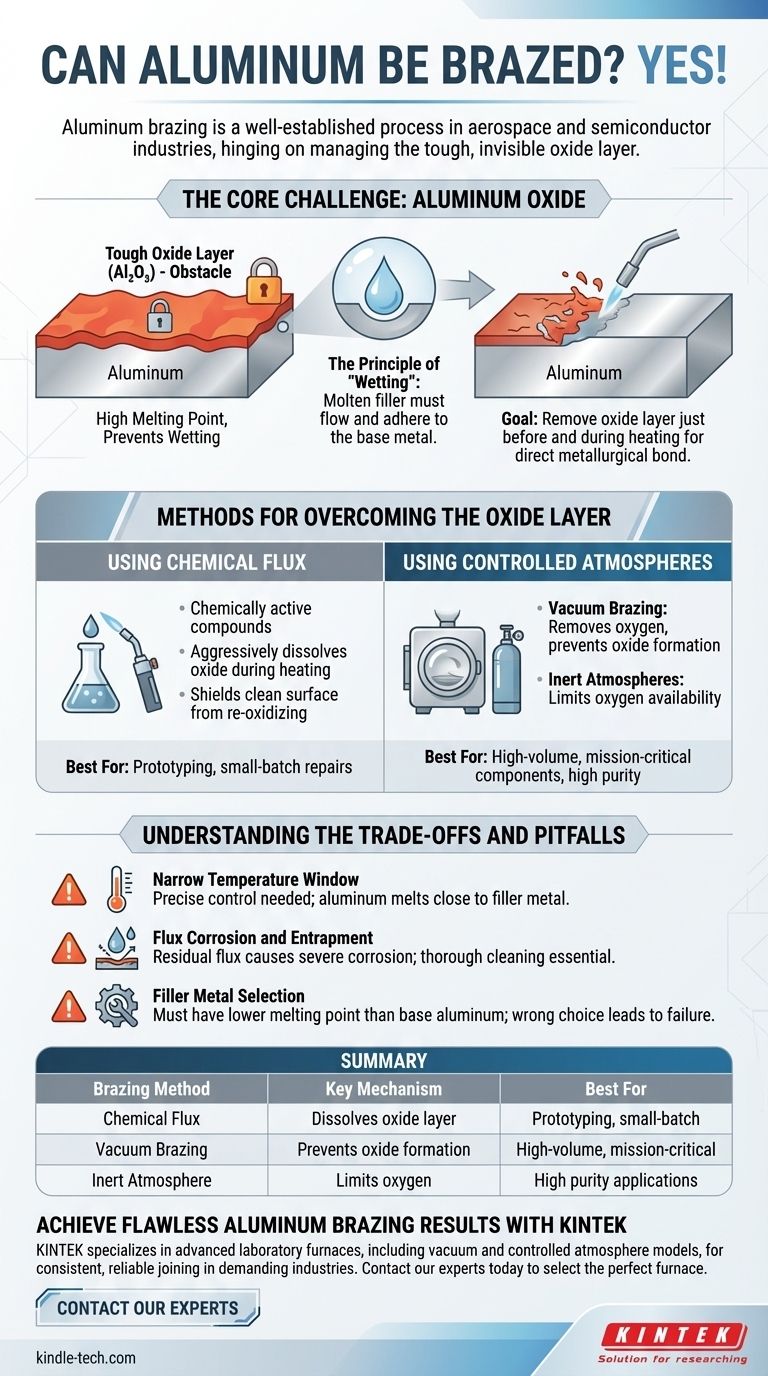
The Core Challenge: Aluminum Oxide
The primary difficulty in brazing aluminum is not a property of the metal but of its surface chemistry. Understanding this is the first principle of a successful braze.
Why Oxide is the Obstacle
When exposed to air, aluminum instantly forms a thin, tough, and chemically stable layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃). This layer has a very high melting point, far higher than the aluminum base metal itself.
The Principle of "Wetting"
For a braze to work, the molten filler metal must "wet" the surfaces of the parts being joined. This means it needs to flow across and adhere to the base metal. The aluminum oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the filler metal from making direct contact and forming a bond.
The Goal of the Brazing Process
Therefore, the central technical goal of any aluminum brazing operation is to remove this oxide layer just before and during the heating process. This allows the filler metal to flow into the joint and bond directly with the pure aluminum underneath.
Methods for Overcoming the Oxide Layer
Two primary strategies are employed to defeat the oxide layer, each suited to different applications and scales of production.
Using Chemical Flux
Fluxes are chemically active compounds applied to the joint before heating. As the assembly is heated, the flux melts and aggressively dissolves the aluminum oxide layer. It also shields the cleaned surface from re-oxidizing, allowing the braze filler to wet the joint properly.
Using Controlled Atmospheres
For high-volume or high-purity applications, furnace brazing is often used. This process manages the oxide layer by controlling the environment itself.
- Vacuum Brazing: By performing the process in a high vacuum, oxygen is removed from the environment. This prevents the oxide layer from forming in the first place, allowing for an exceptionally clean and strong joint without the need for chemical flux.
- Inert Atmospheres: Using an inert gas atmosphere can also limit the amount of oxygen available, though a vacuum is generally more effective for reactive metals like aluminum.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While effective, brazing aluminum requires careful process control to avoid common issues.
Narrow Temperature Window
Aluminum alloys have a relatively low melting point which can be very close to the melting temperature of the braze filler metal. This creates a narrow process window, demanding highly precise temperature control to melt the filler without melting or distorting the parent parts.
Flux Corrosion and Entrapment
If a flux-based method is used, it is critical to remove all residual flux after brazing. Leftover flux can absorb moisture from the air and cause severe, aggressive corrosion at the joint. Proper post-braze cleaning is not optional; it is essential for the long-term integrity of the part.
Filler Metal Selection
Choosing the right filler metal is paramount. These are typically aluminum-silicon alloys specifically designed to have a melting point lower than the base aluminum alloy being joined. The wrong choice can easily lead to part failure during the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your approach to brazing aluminum should be dictated by your component's complexity, required performance, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is on prototyping or small-batch repairs: Flux-based methods like torch brazing are often the most accessible and cost-effective approach.
- If your primary focus is on high-volume production with complex geometries: Controlled atmosphere or vacuum furnace brazing provides unmatched consistency and joint quality.
- If your primary focus is on mission-critical components and maximum joint integrity: Vacuum brazing is the superior choice, as it eliminates the risk of flux entrapment and corrosion.
Successfully brazing aluminum is fundamentally a matter of precise control over its surface chemistry and thermal environment.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Key Mechanism | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Flux | Dissolves the oxide layer during heating | Prototyping, small-batch repairs |
| Vacuum Brazing | Prevents oxide formation by removing oxygen | High-volume production, mission-critical components |
| Inert Atmosphere | Limits oxygen to manage oxide layer | Applications requiring high purity |
Achieve flawless aluminum brazing results with KINTEK.
Brazing aluminum requires precise control over temperature and atmosphere to manage its challenging oxide layer. Whether you are developing prototypes or scaling up for high-volume production, the right equipment is critical for success.
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory furnaces, including vacuum and controlled atmosphere models, designed specifically for high-performance joining processes like aluminum brazing. Our solutions provide the consistent, reliable environment needed to create strong, corrosion-free joints for aerospace, semiconductor, and other demanding industries.
Let us help you select the perfect furnace for your application. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure your brazing process is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond



















