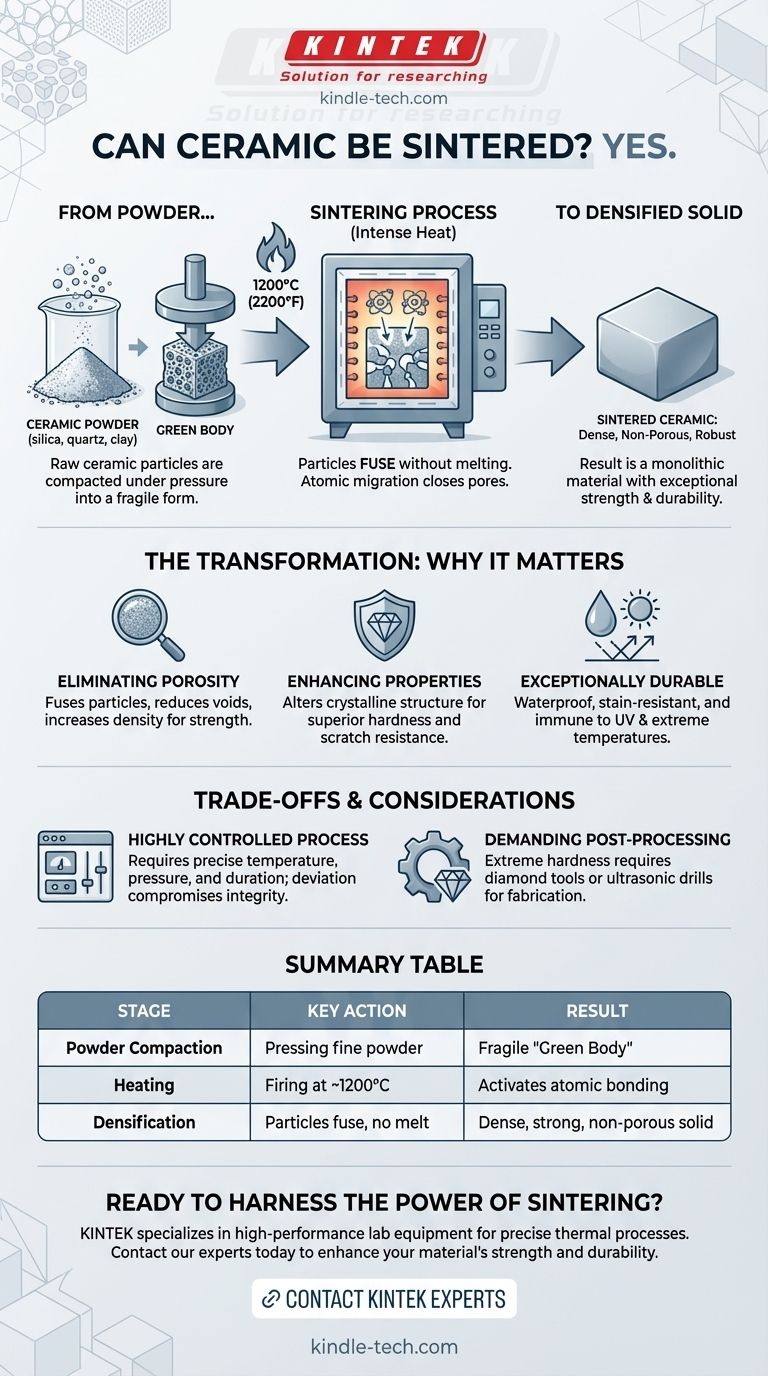
Yes, ceramic can be sintered. In fact, sintering is the fundamental industrial process that transforms a compacted ceramic powder into an incredibly dense, non-porous, and robust solid material. This is achieved by applying intense heat and pressure to fuse the material's particles together without melting them into a liquid state.
Sintering is not merely a method for hardening ceramic; it is a transformative process that re-engineers the material at a molecular level. It closes the gaps between raw particles, creating a monolithic structure with exceptional strength, durability, and resistance.
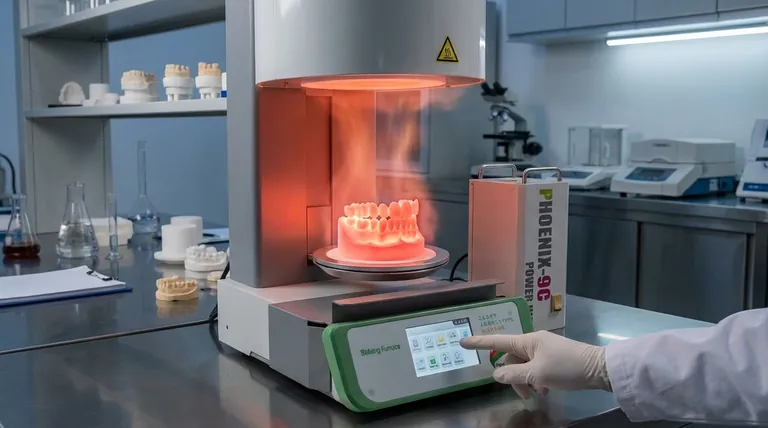

What is Sintering? A Look at the Core Process
Sintering is a highly controlled manufacturing technique that turns loose, raw materials into a finished, high-performance product. The process involves several distinct stages.
From Powder to a "Green" Body
The journey begins with natural materials like silica, quartz, feldspars, and clay. These are ground into a very fine, calibrated powder. This powder is then compacted under immense pressure to form a coherent shape, often called a "green body," which is solid but still porous and relatively fragile.
The Role of Intense Heat
The green body is fired in a kiln at extreme temperatures, typically around 1200°C (2200°F). This intense heat provides the energy needed to activate the bonding process between the ceramic particles.
Fusing Particles at the Atomic Level
Crucially, the material is heated to a point where the particles fuse together, but it does not melt into a liquid. Under this heat, atoms migrate across the boundaries of the particles, closing the microscopic pores between them. This process, known as densification, results in a solid, virtually pore-free slab.
The Transformation: Why Sintering Matters
Sintering is what gives advanced ceramics, also known as sintered stone or ultra-compact surfaces, their remarkable characteristics. The change from a porous powder to a dense solid fundamentally enhances the material's physical properties.
Eliminating Porosity and Increasing Density
The primary goal of sintering is to reduce porosity. By fusing the particles and eliminating the voids between them, the process creates a material with extremely high density. This density is the foundation for its strength and impermeability.
Enhancing Physical Properties
This structural transformation dramatically improves the material's performance. For example, in materials like zirconia, sintering alters the crystalline structure itself, making it exceptionally hard and strong. This process is key to unlocking properties like superior scratch resistance, impact resistance, and rigidity.
Creating an Exceptionally Durable Final Product
Because the sintered material is non-porous and chemically inert, it becomes highly resistant to a wide range of environmental factors. It is waterproof and immune to staining, UV rays, extreme temperatures, and graffiti. This is why sintered ceramic is valued for its superior durability in high-traffic or demanding applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While the results are impressive, the sintering process has specific requirements and implications that are important to understand.
A Highly Controlled Process
Sintering is not simple baking. The final physical properties of the ceramic are entirely dependent on an optimized and precisely controlled sintering process. Any deviation in temperature, pressure, or duration can compromise the integrity and performance of the final product.
Post-Processing is Demanding
The extreme hardness that makes sintered ceramic so desirable is also a manufacturing challenge. Once sintered, the material can only be machined or cut with highly specialized equipment, such as diamond tools or ultrasonic drills. This adds complexity and cost to fabrication.
Not a "One-Size-Fits-All" Method
Different ceramic compositions require different sintering parameters. The specific temperatures, pressures, and atmospheric conditions must be carefully tailored to the raw materials being used to achieve the desired outcome.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding sintering helps you evaluate if this type of material is right for your objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and performance: Sintered ceramic is an ideal choice for applications like countertops, building facades, or high-traffic flooring where resistance to scratching, heat, and stains is critical.
- If your primary focus is material science: The key principle to grasp is densification without liquefaction, where atomic migration creates a new, superior material structure from a simple powder.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing: Recognize that sintering is the value-adding step that creates the material's core properties, but budget for the specialized and costly fabrication required for the finished product.
Ultimately, sintering is the transformative process that turns fine ceramic powders into some of the most robust and high-performance materials available today.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Compaction | Pressing fine powder into a shape | Forms a fragile "green body" |
| Heating | Firing at ~1200°C (2200°F) | Activates atomic migration and bonding |
| Densification | Particles fuse without melting | Creates a dense, strong, non-porous solid |
Ready to harness the power of sintering for your lab or production needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the high-performance lab equipment required for precise thermal processes like sintering. Whether you are developing new ceramic materials or manufacturing durable components, our expertise and solutions can help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how KINTEK's sintering furnaces and consumables can enhance your material's strength, density, and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations



















