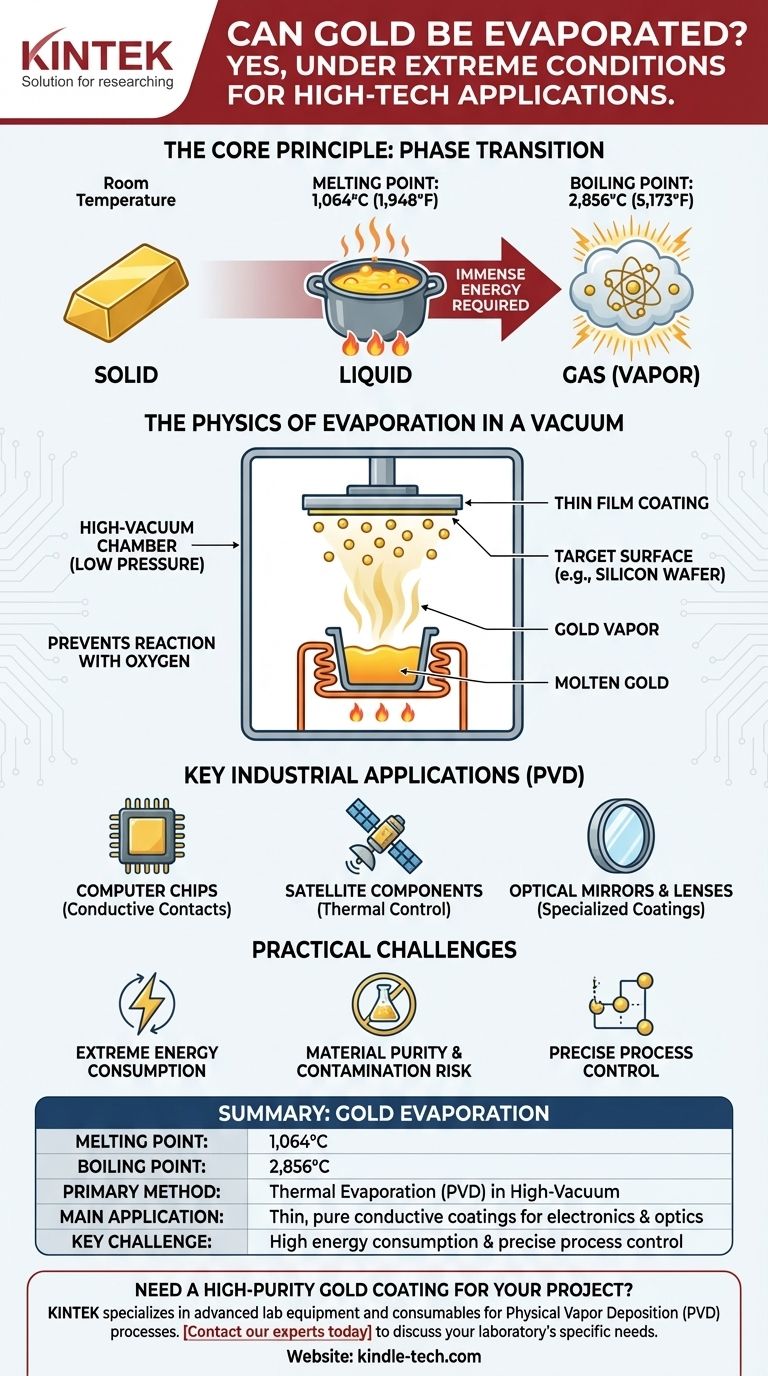
Yes, gold can be evaporated and turned into a gas. However, this process occurs under extreme conditions far beyond everyday experience, requiring temperatures of thousands of degrees Celsius, typically within a high-vacuum chamber. This isn't like boiling water on a stove; it's a highly controlled industrial or scientific process.
The core principle is that gold, like nearly all matter, can exist as a solid, liquid, or gas. Transitioning it to a gaseous state requires immense energy to overcome the strong metallic bonds holding its atoms together, a process leveraged for creating ultra-thin gold coatings in high-tech applications.

The Physics of Vaporizing a Metal
To understand how a dense metal like gold can become a vapor, we need to look beyond its familiar solid form and examine the fundamental principles of phase transition.
From Solid to Gas
Every element has a melting point and a boiling point. Gold first melts into a liquid at 1,064°C (1,948°F). To turn this liquid into a gas, you must continue adding energy until it reaches its boiling point of 2,856°C (5,173°F).
At this temperature, the atoms gain so much kinetic energy that they overcome the forces holding them together in a liquid state and escape into the air as a metallic vapor.
The Critical Need for a Vacuum
In practice, evaporating gold is almost exclusively done in a high-vacuum chamber. This serves two critical purposes.
First, removing air molecules dramatically lowers the pressure. Think of it as removing an atmospheric "lid" that's pushing down on the liquid gold. With less pressure, the gold atoms can escape into a gaseous state more easily and at a slightly lower temperature.
Second, the vacuum prevents the extremely hot gold vapor from reacting with oxygen or other gases in the air. This is crucial for ensuring the purity of the final gold coating.
How Gold Evaporation is Used in Practice
The ability to vaporize gold is not just a scientific curiosity; it is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing in a process called Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Creating Thin Films
The primary application is thin film deposition. In a vacuum chamber, evaporated gold atoms travel in a straight line until they strike a cooler surface, such as a silicon wafer, a glass lens, or a piece of plastic.
Upon impact, the gold atoms rapidly cool and condense back into a solid, forming an exceptionally thin, uniform, and pure layer of gold. This coating can be mere nanometers thick.
Key Industrial Applications
This process is vital for creating the highly conductive gold contacts on computer chips and other electronic components. It's also used to coat satellite components for thermal control and to create specialized coatings for high-performance optical mirrors and lenses.
Understanding the Practical Challenges
While effective, thermal evaporation of gold is a demanding process with significant operational hurdles.
Extreme Energy Consumption
Heating a crucible containing gold to over 2,500°C requires a tremendous amount of electrical energy. This makes the process expensive and is a major factor in the cost of the final product.
Material Purity and Contamination
The crucible holding the molten gold must be made of a material with an even higher melting point, such as tungsten or molybdenum. There is always a risk that microscopic particles from the crucible itself can evaporate and contaminate the gold film.
Precise Process Control
Maintaining a stable high vacuum while managing extreme temperatures requires sophisticated and expensive equipment. Any fluctuation in temperature or pressure can ruin the uniformity and quality of the gold coating.
Applying This to Your Goal
Choosing to use or specify an evaporated gold process depends entirely on your technical requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-purity electronic conductivity: Thermal evaporation in a high vacuum is a superior method for creating the clean, dense conductive layers required for microelectronics.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex shape uniformly: You may want to consider an alternative PVD method called sputtering, which offers better coverage on non-flat surfaces, though often at a slower deposition rate.
- If your primary focus is a decorative or protective finish: Thicker, less pure coatings applied through electroplating are often far more cost-effective than vapor deposition for non-critical applications.
Ultimately, turning solid gold into a gas is a powerful technique for engineering materials at the atomic scale.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 1,064°C (1,948°F) |
| Boiling Point | 2,856°C (5,173°F) |
| Primary Method | Thermal Evaporation (PVD) in High-Vacuum |
| Main Application | Thin, pure conductive coatings for electronics & optics |
| Key Challenge | High energy consumption and precise process control |
Need a high-purity gold coating for your project?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes. Whether you are developing next-generation microchips, high-performance optical components, or specialized sensors, our expertise and reliable equipment can help you achieve the precise, uniform thin films your research or production demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs with the right tools and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- At what temperature does molybdenum evaporate? Understanding Its High-Temperature Limits
- What is the critical temperature of heat treatment? Unlock the Key to Steel's Hardness and Performance
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing



















