Yes, absolutely. Gold can be heated, melted, and even vaporized using induction. As an electrically conductive metal, it responds directly to the principles of induction heating, making this a common and highly effective method in professional settings like refining and jewelry manufacturing.
While gold is an excellent candidate for induction heating, its high conductivity and low electrical resistance present a unique challenge. This means successful heating depends entirely on using a high-frequency induction system specifically designed to work with such materials.

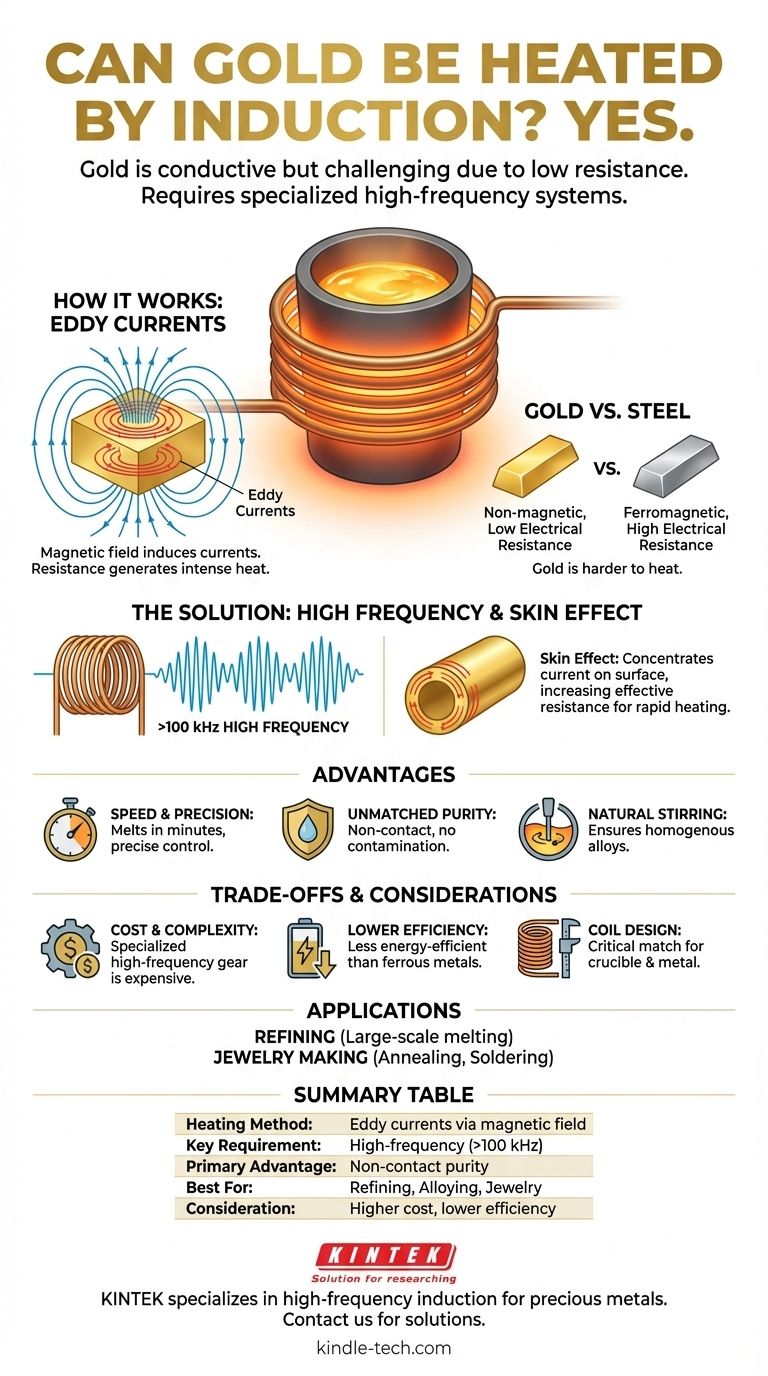
How Induction Heating Works on a Metal Like Gold
Induction does not heat gold through thermal conduction, like a flame. Instead, it turns the gold itself into the source of the heat.
The Principle: Eddy Currents
An induction heater uses a coil of wire to generate a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field. When gold is placed within this field, the magnetic field induces small, circular electrical currents within the metal. These are called eddy currents.
The Role of Electrical Resistance
All metals resist the flow of electricity to some degree. As these eddy currents swirl through the gold, the metal's own internal resistance creates friction, which generates intense, rapid heat. This is the same principle (I²R heating) that makes an electric stovetop get hot.
Why Gold is Different from Steel
Heating gold is not the same as heating a piece of iron or steel. Steel is a ferromagnetic material with high electrical resistance, making it extremely easy to heat with induction, even at lower frequencies.
Gold, in contrast, is non-magnetic and has extremely low electrical resistance. This makes it a "more difficult" material to heat, as less heat is generated for a given amount of electrical current.
The Critical Factor: Matching Frequency to the Metal
To overcome gold's low resistance, induction systems must be engineered with a specific characteristic in mind: frequency.
The Need for High Frequency
For materials with low resistance like gold, silver, and copper, a high-frequency (typically 100 kHz and above) magnetic field is required. This high frequency compensates for the low resistance, inducing stronger eddy currents and enabling rapid heating.
The "Skin Effect" Explained
Higher frequencies also cause a phenomenon called the "skin effect." This forces the eddy currents to flow only in a thin layer near the surface of the metal. By concentrating the current in a smaller area, the effective resistance increases, dramatically improving the heating efficiency for a low-resistance metal like gold.
Understanding the Practical Advantages
Despite the need for specialized equipment, induction offers several key advantages for working with gold.
Speed and Precision
Induction heating is incredibly fast, capable of melting gold in minutes. The heat is generated directly within the metal, allowing for precise control that is difficult to achieve with traditional furnaces or torches.
Unmatched Purity
Because induction is a non-contact heating method, the gold never touches a flame or heating element. This eliminates the risk of contamination, which is critical when working with a high-value material.
Natural Stirring for Homogenous Alloys
As mentioned in metallurgical research, the eddy currents create a natural stirring motion within the molten metal. This is a significant benefit when creating gold alloys (e.g., mixing gold with copper to make 18k rose gold), as it ensures the final product is perfectly homogenous.
Key Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, induction heating for gold is not without its specific requirements and limitations.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
High-frequency induction heaters are more complex and generally more expensive than the low-frequency units used for steel. The investment is significant and typically reserved for commercial or serious professional applications.
Lower Efficiency Compared to Ferrous Metals
Even with the correct frequency, the laws of physics dictate that more energy is required to heat a mass of gold to its melting point than is required for the same mass of steel. The process is simply less energy-efficient due to gold's fundamental properties.
Coil Design is Crucial
The induction coil (the copper tube that generates the magnetic field) must be carefully designed and matched to the crucible holding the gold. The distance between the coil and the metal is critical for efficient energy transfer.
Applying Induction for Your Gold-Related Task
Your choice of heating method should align with your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale melting or refining: Induction is the industry standard due to its speed, control, and the self-stirring action that guarantees consistent alloy quality.
- If your primary focus is jewelry making (annealing or soldering): The precision, speed, and cleanliness of induction are ideal for localized heating without damaging delicate components or contaminating the piece.
- If you are simply exploring metal heating: Understand that heating gold effectively requires different, higher-frequency equipment than what is used for common metals like steel.
By matching the right induction frequency to the metal, you can leverage a process that offers an unparalleled combination of speed, purity, and control for working with gold.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Detail for Gold |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Eddy currents induced by a magnetic field |
| Key Requirement | High-frequency system (typically >100 kHz) |
| Primary Advantage | Non-contact heating ensures high purity |
| Best For | Refining, alloying, and jewelry manufacturing |
| Consideration | Higher equipment cost and lower energy efficiency vs. ferrous metals |
Ready to achieve precise, pure, and efficient gold heating?
KINTEK specializes in high-frequency induction heating systems designed specifically for precious metals like gold. Our equipment delivers the speed, control, and contamination-free environment essential for refining, alloying, and jewelry making.
Contact us today to find the perfect induction heating solution for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















