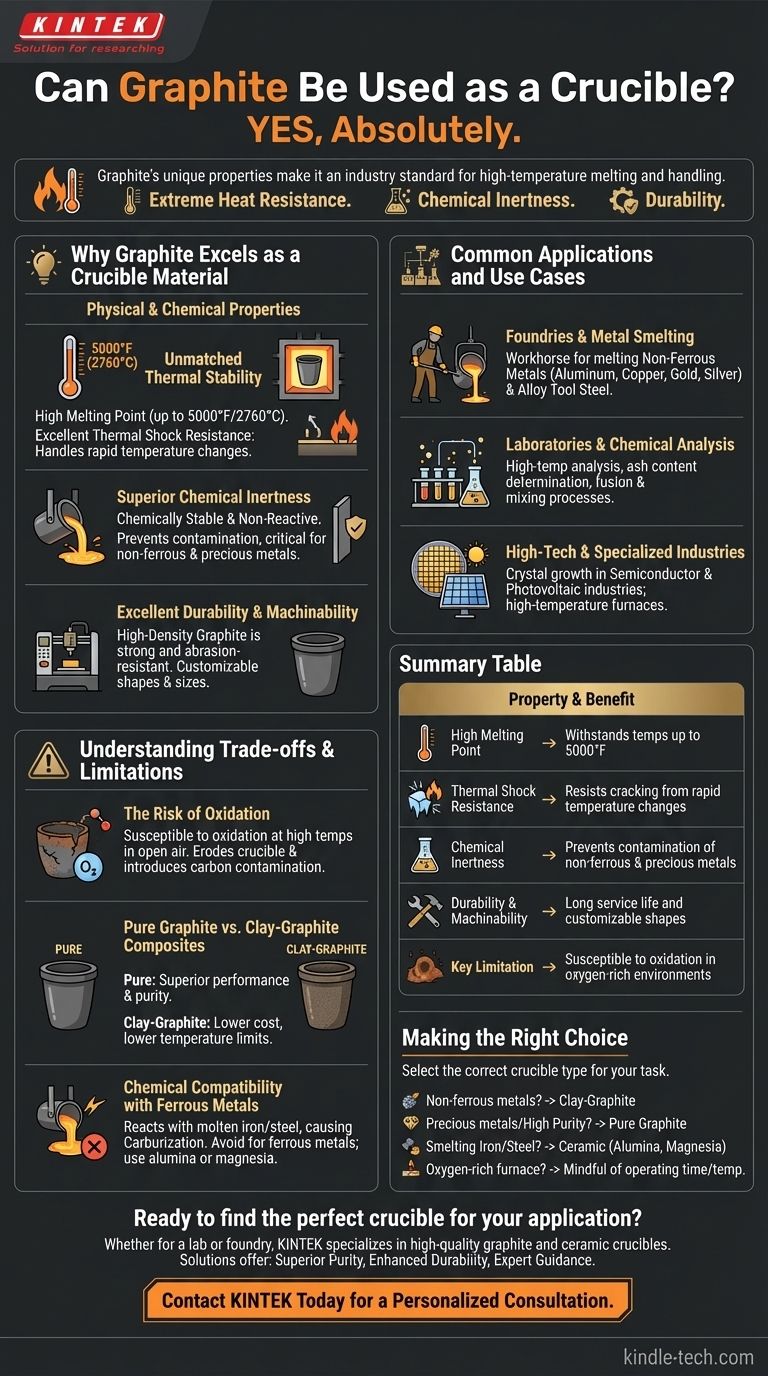
Yes, absolutely. Graphite is one of the most widely used and effective materials for crucibles, especially for high-temperature applications. Its unique combination of extreme heat resistance, chemical inertness, and durability makes it an industry standard for melting and handling a wide range of materials.
Graphite's value as a crucible material stems from its ability to withstand temperatures up to 5000°F without melting or deforming. However, the key to using it successfully lies in understanding the difference between pure graphite and clay-graphite composites and managing the risk of oxidation.

Why Graphite Excels as a Crucible Material
Graphite's physical and chemical properties make it uniquely suited for containing molten materials in extreme environments.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Graphite has an exceptionally high melting point, maintaining its structural integrity at temperatures as high as 5000°F (approx. 2760°C).
It also has excellent thermal shock resistance. This means it can handle rapid changes in temperature without cracking, making it suitable for processes where the crucible is heated or cooled quickly.
Superior Chemical Inertness
For most applications, graphite is chemically stable and non-reactive. It will not dissolve into or contaminate the molten materials it holds, which is critical for maintaining the purity of metals and alloys.
This inertness is especially valuable when melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, and precious metals.
Excellent Durability and Machinability
High-density graphite is strong and resists abrasion. This ensures a longer service life compared to more fragile ceramic materials.
Furthermore, graphite is relatively easy to machine. This allows for the creation of crucibles in precise, custom sizes and shapes tailored to specific industrial or laboratory needs.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Graphite crucibles are indispensable across numerous industries, from heavy manufacturing to delicate laboratory work.
Foundries and Metal Smelting
This is the most common use. Graphite crucibles are the workhorse in foundries for melting alloy tool steel and non-ferrous metals and their alloys, including aluminum, copper, brass, gold, and silver.
Laboratories and Chemical Analysis
In laboratory settings, graphite crucibles are used for high-temperature chemical analysis, determining the ash content of samples, and for storing materials during fusion and mixing processes.
High-Tech and Specialized Industries
The unique properties of graphite make it essential in advanced fields. It is used in the semiconductor and photovoltaic industries for crystal growth and in high-temperature furnaces for various specialized processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While graphite is highly effective, it is not without its operational considerations. Understanding these limitations is key to using it properly.
The Risk of Oxidation
Graphite's primary weakness is its susceptibility to oxidation at high temperatures in the presence of oxygen.
If a graphite crucible is held at a high temperature in an open-air furnace for too long, it can begin to erode and burn away. This not only weakens the crucible but can also introduce carbon contamination into the melt.
Pure Graphite vs. Clay-Graphite Composites
Many commercially available "graphite" crucibles are actually a composite made by mixing graphite powder with refractory clay and other binders.
These clay-graphite crucibles are less expensive but have lower temperature limits and are less durable than crucibles made from pure, machined graphite. Pure graphite offers superior performance and purity for the most demanding applications.
Chemical Compatibility with Ferrous Metals
While graphite is inert with most non-ferrous metals, it can react with molten iron and steel. The carbon from the crucible can dissolve into the iron, a process known as carburization, which alters the properties of the final steel alloy. For this reason, other materials like alumina or magnesia are often preferred for melting ferrous metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Selecting the correct crucible type is critical for the success and purity of your work.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals (like aluminum or copper): A clay-graphite crucible is an excellent, cost-effective, industry-standard choice.
- If your primary focus is melting precious metals or requires maximum purity: Invest in a pure, machined graphite crucible to avoid contamination from clay binders.
- If your primary focus is smelting iron or steel: Avoid graphite and choose a ceramic crucible (like alumina or magnesia) to prevent carbon from dissolving into your melt.
- If you are working in an oxygen-rich furnace: Be mindful of the operating time and temperature to minimize crucible oxidation and extend its service life.
By understanding these properties and trade-offs, you can confidently leverage graphite as a powerful tool in your high-temperature processes.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Crucible Use |
|---|---|
| High Melting Point | Withstands temperatures up to 5000°F (2760°C) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Resists cracking from rapid temperature changes |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination of non-ferrous & precious metals |
| Durability & Machinability | Long service life and customizable shapes |
| Key Limitation | Susceptible to oxidation in oxygen-rich environments |
Ready to find the perfect crucible for your application?
Whether you're melting precious metals in a lab or non-ferrous alloys in a foundry, selecting the right crucible is critical for purity and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including a range of graphite and ceramic crucibles tailored to your specific needs.
We provide solutions that offer:
- Superior Purity: Ideal for sensitive applications like precious metal melting.
- Enhanced Durability: Withstand extreme temperatures and thermal cycling.
- Expert Guidance: Help you choose between pure graphite, clay-graphite composites, and other ceramics.
Let our experts help you enhance your process efficiency and material integrity. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the right crucible solution for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What precautions should be taken when using a crucible? Essential Steps for Safety and Accuracy
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- Why are alumina crucibles selected for wood-plastic composite tests? Ensure Precision at 1000°C



















