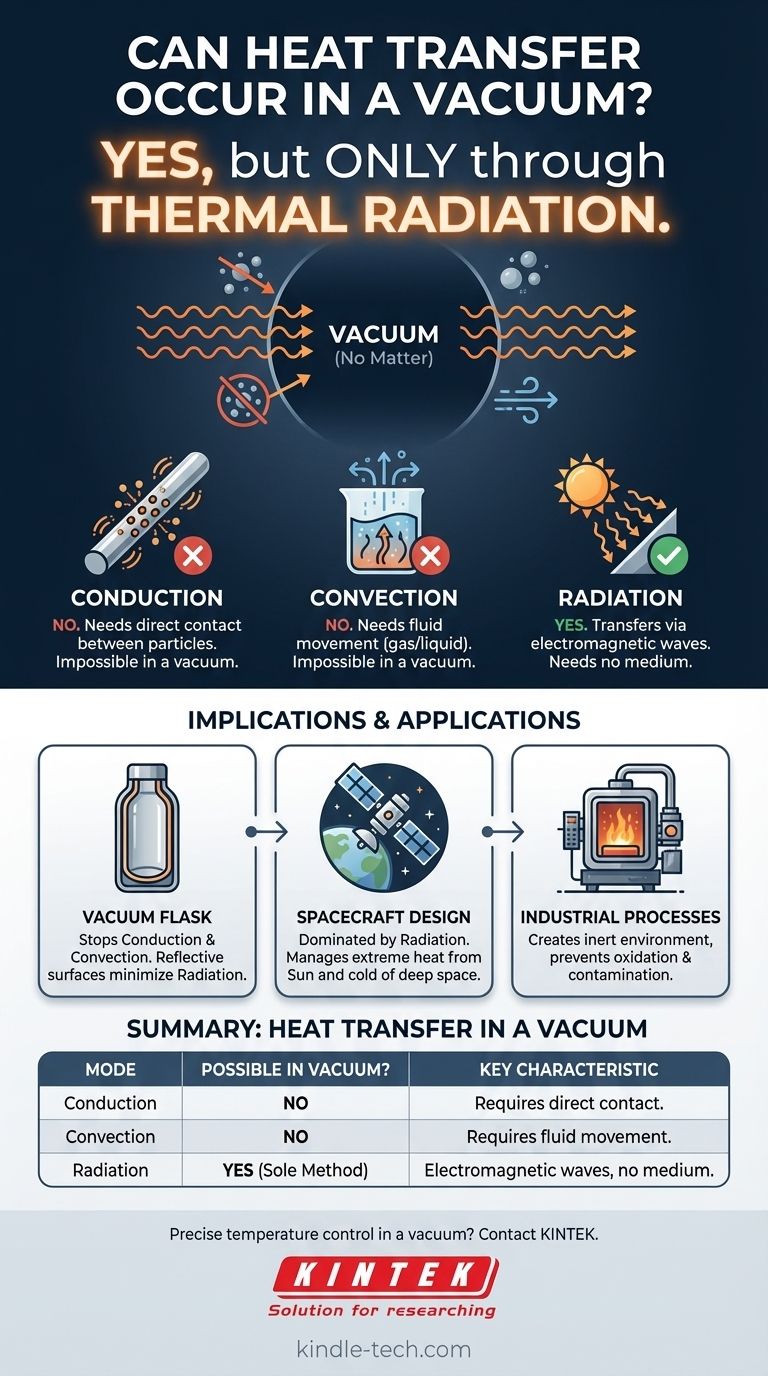
Yes, heat transfer can occur in a vacuum, but only through one specific mechanism: thermal radiation. A vacuum is defined by the absence of matter, which means it effectively stops the other two forms of heat transfer—conduction and convection—as they both require a physical medium to transport energy.
While a vacuum is an exceptional insulator because it eliminates heat transfer via physical contact (conduction) and fluid movement (convection), it is completely transparent to energy transfer through electromagnetic waves (radiation).
The Three Modes of Heat Transfer
To understand why a vacuum behaves this way, we must first distinguish between the three fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer.
Conduction: Transfer Through Direct Contact
Conduction is the transfer of heat through the vibration and collision of adjacent particles. Imagine a metal rod held over a flame; the heat travels from one end to the other as excited atoms jostle their neighbors in a chain reaction.
Because conduction relies on physical matter to propagate, it cannot occur across a perfect vacuum. There are no particles to vibrate or collide.
Convection: Transfer Through Fluid Motion
Convection is the transfer of heat through the bulk movement of fluids (liquids or gases). When a portion of a fluid is heated, it typically becomes less dense and rises, while the cooler, denser fluid sinks to take its place, creating a convection current.
This process inherently requires a fluid medium to move. Therefore, convection is also impossible in a vacuum.
Radiation: Transfer Through Electromagnetic Waves
Thermal radiation is fundamentally different. All objects with a temperature above absolute zero emit energy in the form of electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared spectrum.
These waves, like visible light, do not require any medium to travel. This is how the Sun’s heat travels 93 million miles through the vacuum of space to warm the Earth. In a vacuum, radiation is the sole method of heat transfer.
Understanding the Implications
The unique properties of a vacuum make it both a powerful tool for insulation and a unique challenge in certain environments.
The Principle Behind a Vacuum Flask
A vacuum flask (or Thermos) is a perfect practical example. It consists of two walls of glass or steel separated by a vacuum.
This vacuum gap almost completely stops conduction and convection from moving heat between the inner chamber and the outside environment. However, heat still slowly transfers via radiation, which is why the inner surfaces are often coated with a reflective, mirror-like layer to reflect thermal energy back to its source.
The Challenge of Spacecraft Design
Engineers designing satellites and spacecraft must contend with an environment dominated by radiation. Space is a near-perfect vacuum.
A satellite's surface facing the Sun can become incredibly hot due to intense solar radiation, while the side in shadow becomes extremely cold as it radiates its own heat away into deep space. Managing these extreme temperature swings without the help of convection or conduction is a primary challenge in aerospace engineering.
Harnessing Vacuums in Industry
In industrial processes like vacuum heat treating, the primary goal is often to prevent chemical reactions, not just to insulate.
By removing air and other gases, a vacuum furnace creates an environment free of particles like oxygen that would otherwise cause oxidation or contamination on a metal's surface at high temperatures.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Goal
Your approach to managing heat in a vacuum depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing insulation: Use a vacuum to eliminate conduction and convection, and add highly reflective surfaces to minimize thermal radiation.
- If your primary focus is operating in space: Design systems that can withstand extreme temperature changes and effectively radiate away excess heat generated by electronics.
- If your primary focus is ensuring material purity: Leverage a vacuum to create an inert environment, preventing unwanted particle-based chemical reactions during high-temperature processes.
By understanding precisely which forms of heat transfer a vacuum stops—and which one it doesn't—you can master its properties to solve a wide range of scientific and engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Mode | Possible in a Vacuum? | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | No | Requires direct contact between particles. |
| Convection | No | Requires the movement of a fluid (gas or liquid). |
| Radiation | Yes | Transfers energy via electromagnetic waves; needs no medium. |
Need to precisely control temperature in a vacuum environment? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum ovens and furnaces designed for optimal thermal management. Whether your goal is perfect insulation, material purity, or simulating space conditions, our solutions ensure accurate and reliable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory's unique challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- At what temperature does molybdenum evaporate? Understanding Its High-Temperature Limits
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.
- What is conduction in vacuum? Understanding Heat Transfer in the Absence of Matter
- What are the safety precautions for heat treatment process? A Guide to Managing Thermal, Atmospheric, and Equipment Risks



















