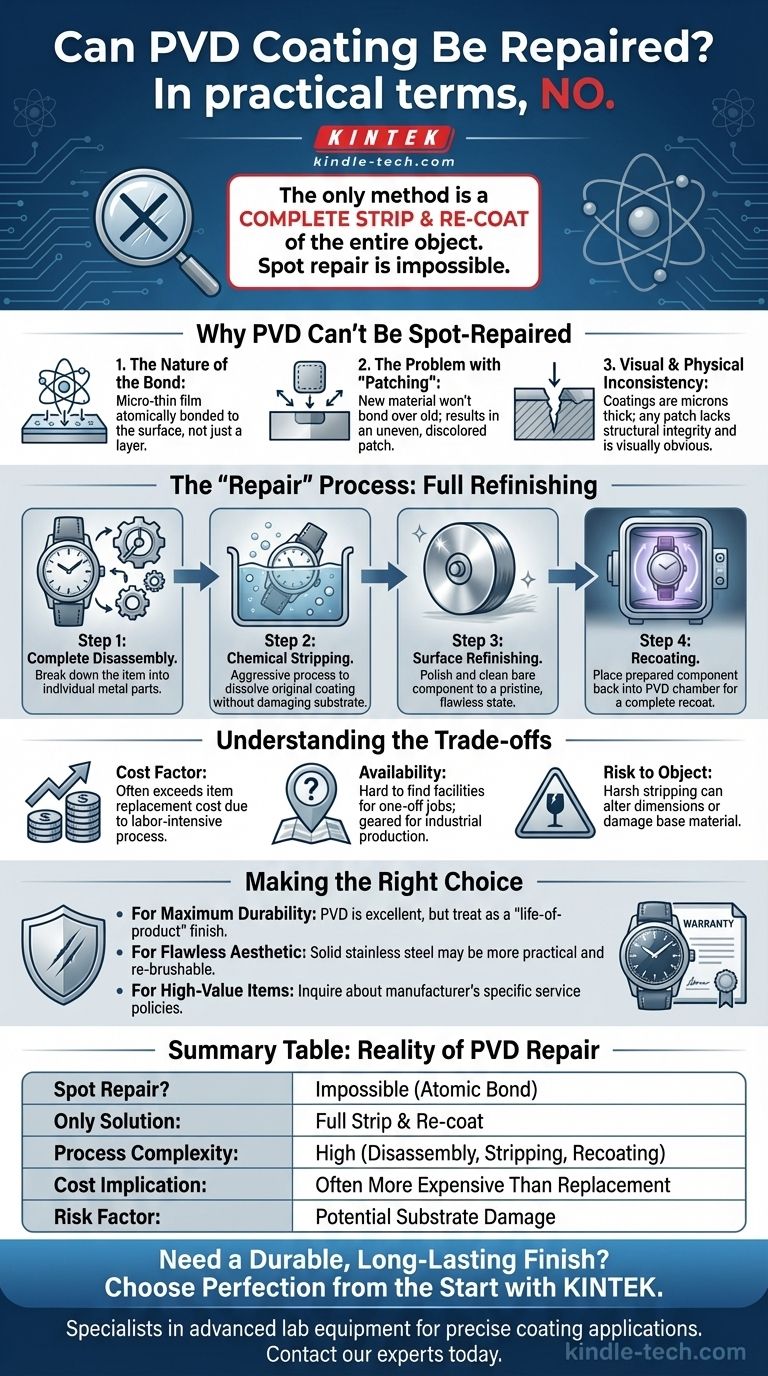
In practical terms, no. While Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is an exceptionally hard and durable finish, it cannot be spot-repaired or "touched up" if it is deeply scratched or damaged. The only method to restore a damaged PVD-coated item is to have the original coating completely stripped and then have the entire object re-coated, a process which is often complex and expensive.
The very properties that make PVD coatings incredibly durable—their atomic bond to the substrate and extreme thinness—are what make localized repairs impossible. Damage requires a full factory-level refinishing process, not a simple fix.

Why PVD Can't Be Spot-Repaired
Understanding the nature of PVD reveals why simple repairs are not feasible. It is fundamentally different from paint or powder coating.
The Nature of the Bond
PVD is not a layer of material sitting on the surface; it is a micro-thin film that is atomically bonded to the surface in a vacuum. This creates a finish that is part of the object itself.
The Problem with "Patching"
You cannot "fill in" a scratch on a PVD coating. Attempting to apply new PVD material over a damaged area would result in an uneven, discolored patch that would not bond correctly. The process requires a pristine, perfectly prepared surface that is impossible to achieve in a small, damaged area.
Visual and Physical Inconsistency
A PVD coating is measured in microns (thousandths of a millimeter). Any scratch deep enough to be noticeable has likely penetrated the entire coating to the substrate below. A "patch" would be visually obvious and lack the structural integrity of the original, uniform coating.
The "Repair" Process: Stripping and Recoating
While a scratch can't be patched, an object can be restored through a multi-step industrial process. This is not a repair but a complete refinishing.
Step 1: Complete Disassembly
The item must be fully disassembled. Only the single component to be coated can go into the PVD chamber. For a watch or a faucet, this means breaking it down into its individual metal parts.
Step 2: Chemical Stripping
The original PVD coating must be chemically stripped away. This is an aggressive process using specialized agents that dissolve the coating without, ideally, damaging the base metal (the substrate).
Step 3: Surface Refinishing
Once stripped, the bare component must be polished and cleaned to a flawless state, identical to how it was before its very first coating. Any remaining imperfections on the substrate will be visible through the new PVD layer.
Step 4: Recoating
Finally, the perfectly prepared component is placed back into a PVD vacuum chamber, and the entire coating process is performed again from scratch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
This refinishing process has significant practical and economic implications that you must consider.
The Cost Factor
Stripping and recoating a single item is labor-intensive. It is often significantly more expensive than the original PVD application, which is typically done in large, efficient batches. For many consumer goods, the cost of refinishing can easily exceed the replacement cost of the item itself.
The Availability of Service
Finding a facility willing to take on a one-off refinishing job for a consumer product can be difficult. Most PVD coating companies are geared toward industrial-scale production runs, not individual service requests.
The Risk to the Object
The chemical stripping process is harsh. If not performed with extreme care, it can minutely alter the dimensions or texture of the underlying material. There is always a small risk of damaging the original part during the refinishing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PVD is an excellent technology, but you must align its characteristics with your long-term expectations.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and scratch resistance: PVD is an outstanding choice. You should, however, treat it as a "life-of-product" finish and accept that minor cosmetic damage may be permanent.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a flawless aesthetic over time: A simpler material like solid stainless steel may be more practical. It scratches more easily but can be re-brushed or polished to a new condition with relative ease.
- If you are buying a high-value PVD item (like a luxury watch): Inquire about the manufacturer's specific service policy. Some high-end brands offer case replacement or refinishing as a (costly) service, while others do not.
Ultimately, you should view PVD as a high-performance, semi-permanent finish, not as a surface that can be easily maintained or repaired.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Reality of PVD Repair |
|---|---|
| Spot Repair? | Impossible due to atomic-level bonding. |
| Only Solution | Full strip and re-coat of the entire object. |
| Process Complexity | High; requires disassembly, chemical stripping, and recoating. |
| Cost Implication | Often more expensive than replacing the item. |
| Risk Factor | Potential damage to the underlying substrate during stripping. |
Need a Durable, Long-Lasting Finish for Your Components?
Understanding the permanence of PVD coating is key to selecting the right surface treatment for your products. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise coating applications. Whether you are developing high-wear components or luxury goods, our solutions ensure a flawless, durable finish from the start.
Let us help you achieve perfection the first time. Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can meet your laboratory's coating and material science needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum hot-pressing furnace preferred over a standard atmospheric pressure sintering furnace for fabricating Carbon Fiber/Silicon Nitride (C_fiber/Si3N4) composites?
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials
- Why is a heated laboratory hydraulic press necessary for preparing composite laminates with specific fiber orientations?



















