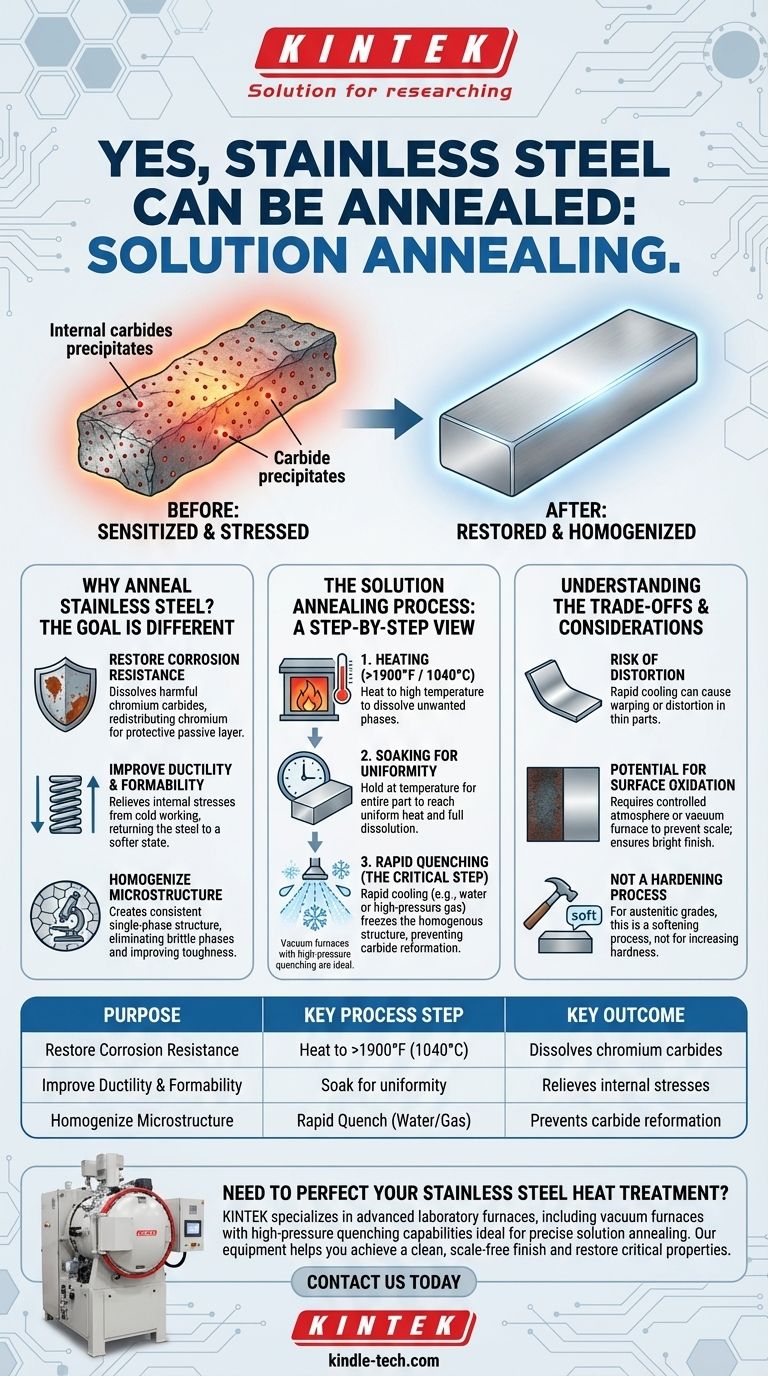
Yes, stainless steel can be annealed, but the process and its primary purpose differ significantly from the annealing of standard carbon steels. This heat treatment, most accurately called solution annealing, is a critical process designed to dissolve harmful precipitates, homogenize the metal's structure, and restore its inherent properties like corrosion resistance and ductility.
The core purpose of annealing stainless steel is not simply to soften it, but to reset its microstructure. By heating it to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it, you dissolve undesirable phases back into the steel, maximizing its performance, especially its resistance to corrosion.

Why Anneal Stainless Steel? The Goal is Different
For common steels, annealing is primarily used to reduce hardness and increase ductility. While stainless steel does become more ductile after annealing, the main objectives are metallurgical and are critical for performance in demanding environments.
Restoring Corrosion Resistance
During processes like welding, some stainless steels can become sensitized. This occurs when chromium atoms bond with carbon to form chromium carbides along the grain boundaries, depleting the surrounding areas of the chromium needed to form the protective passive layer. Solution annealing dissolves these carbides, redistributing the chromium uniformly and restoring maximum corrosion resistance.
Improving Ductility and Formability
Manufacturing processes like cold working, forming, or machining introduce significant internal stresses into the material. Annealing relieves these stresses, returning the steel to a softer, more ductile state, which makes it easier to work with and reduces the risk of stress-corrosion cracking during service.
Homogenizing the Microstructure
As mentioned for castings, the initial microstructure of stainless steel can be non-uniform. Solution annealing and homogenization create a consistent, single-phase structure. This eliminates brittle secondary phases that can act as initiation points for cracks, thereby improving the overall toughness and reliability of the component.
The Solution Annealing Process: A Step-by-Step View
The effectiveness of solution annealing hinges on a precise combination of high heat and, counterintuitively, rapid cooling.
Heating to a High Temperature
The stainless steel component is heated to a specific temperature, typically above 1900°F (1040°C) for common austenitic grades like 304 or 316. This temperature is high enough to cause the harmful chromium carbides and other unwanted phases to dissolve back into the steel's solid solution.
Soaking for Uniformity
The material is held at this high temperature for a calculated period. The goal of this "soaking" phase is to ensure the entire part, including its core, reaches a uniform temperature and that all the targeted precipitates have time to fully dissolve.
Rapid Quenching (The Critical Step)
Unlike the slow cooling of traditional annealing, stainless steel must be cooled very rapidly, a process called quenching. This is typically done with water, high-pressure gas, or other quenching media. This rapid cooling "freezes" the dissolved elements in place, preventing the chromium carbides from reforming and ensuring the homogenous structure is retained at room temperature. This is why vacuum furnaces with high-pressure quenching capabilities are so effective for this process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly beneficial, the solution annealing process is not without its challenges. Understanding these is key to achieving the desired outcome without introducing new problems.
Risk of Distortion
The combination of extreme heat followed by rapid cooling can introduce thermal stress. This can cause thin or complex parts to warp or distort, requiring careful planning and potentially post-treatment straightening.
Potential for Surface Oxidation
Heating steel to such high temperatures in the presence of oxygen will cause a thick, dark scale to form on the surface. To prevent this, the process is often performed in a controlled atmosphere or a vacuum furnace, which results in a clean, bright finish and avoids the need for aggressive post-process cleaning like acid pickling.
Not a Hardening Process
It is a common misconception that all heat treatments harden steel. For the most common types of stainless steel (austenitic grades), solution annealing is a softening process. It cannot be used to increase the hardness or strength of these alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying solution annealing correctly depends entirely on the material's condition and your final objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum corrosion resistance: Solution annealing is essential after welding or any thermal processing that could have sensitized the material, especially for parts used in chemical or food industries.
- If your primary focus is improving formability: Annealing is the correct step to relieve stresses from prior cold working, making the steel ductile and ready for subsequent forming operations.
- If your primary focus is ensuring reliability in a casting: A homogenization or solution anneal treatment is critical to refine the as-cast grain structure and ensure consistent mechanical properties throughout the part.
Ultimately, understanding solution annealing is key to unlocking the full potential of stainless steel in your application.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of Annealing Stainless Steel | Key Process Step | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Restore Corrosion Resistance | Heat to >1900°F (1040°C) | Dissolves chromium carbides |
| Improve Ductility & Formability | Soak for uniformity | Relieves internal stresses |
| Homogenize Microstructure | Rapid Quench (Water/Gas) | Prevents carbide reformation |
Need to perfect your stainless steel heat treatment?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory furnaces, including vacuum furnaces with high-pressure quenching capabilities ideal for precise solution annealing. Our equipment helps you achieve a clean, scale-free finish and restore the critical properties of your stainless steel components.
Contact us today to discuss how our lab equipment can enhance your process and ensure maximum corrosion resistance and reliability for your materials. Get in touch via our contact form.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















