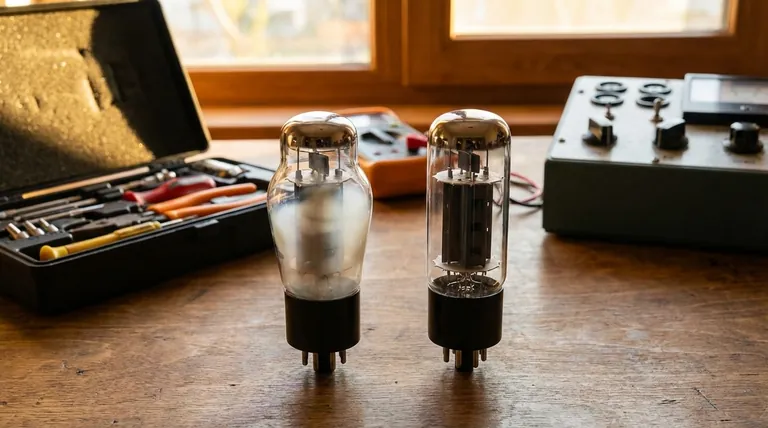
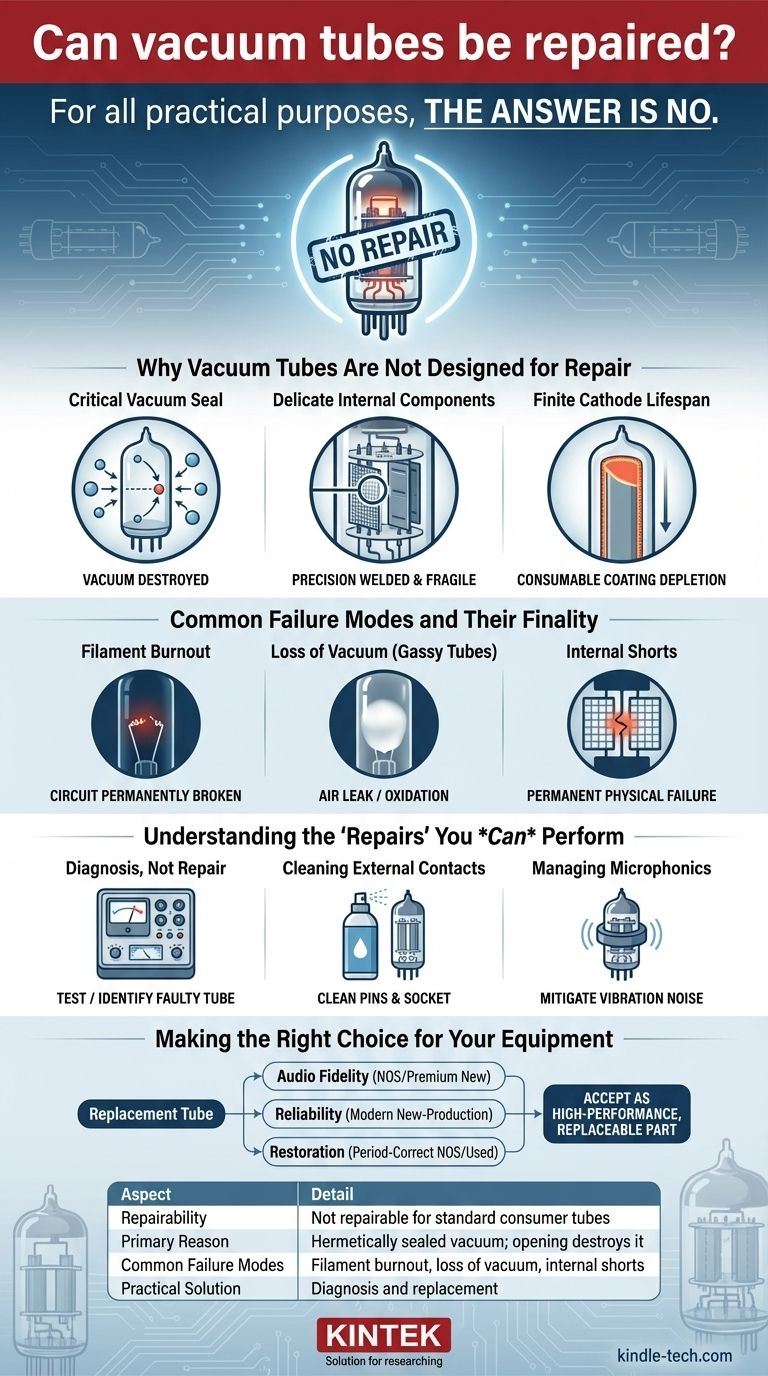
For all practical purposes, the answer is no. A standard vacuum tube used in consumer electronics like amplifiers or radios cannot be repaired. They are hermetically sealed, consumable components with a finite lifespan, much like an incandescent light bulb. Once a critical internal component fails, the entire tube must be replaced.
A vacuum tube is best understood as a disposable component, not a serviceable part. While theoretical repair exists for exceptionally rare, high-power industrial tubes, for 99.9% of applications, the correct and only practical course of action is diagnosis and replacement.

Why Vacuum Tubes Are Not Designed for Repair
Understanding the construction of a vacuum tube reveals why repair is impractical. The entire device is a delicate assembly of components housed within a precisely controlled environment.
The Critical Vacuum Seal
A tube's function depends on the flow of electrons in a near-perfect vacuum. This vacuum is created at the factory and sealed, usually in a glass or metal envelope.
Any attempt to open the tube would destroy this vacuum, allowing air to rush in and instantly contaminate the sensitive internal surfaces, rendering it useless.
Delicate Internal Components
Inside the tube, elements like the cathode, grids, and plate are positioned with extreme precision, often fractions of a millimeter apart.
These parts are fragile and welded in place. Even if you could get inside the tube, physically manipulating or replacing these parts without destroying their alignment is virtually impossible outside of a specialized manufacturing facility.
The Finite Lifespan of the Cathode
The cathode is coated with a material (like barium or strontium oxide) that emits electrons when heated. This emission process is what makes the tube work.
Over thousands of hours of use, this emissive coating is gradually depleted. This is a fundamental aging process, like a tire losing its tread, that cannot be reversed.
Common Failure Modes and Their Finality
When a tube "fails," it is almost always due to one of several terminal conditions.
Filament Burnout
The filament is a tiny wire that heats the cathode. Just like the filament in a light bulb, it can burn out and break. When this happens, the tube is "cold" and completely dead. The circuit is permanently broken.
Loss of Vacuum (Gassy Tubes)
If a microscopic crack develops in the glass or at a pin seal, air will leak in. This compromises the vacuum and interferes with electron flow, leading to poor performance or complete failure.
You can often spot a "gassy" tube by looking at the getter, a silvery patch on the inside of the glass. If it has turned white or milky, it has oxidized, indicating the presence of air.
Internal Shorts
Over time, heat and vibration can cause the delicate internal structures to warp or sag. If two elements touch, such as a grid and the plate, it creates an internal short circuit. This is a permanent physical failure.
Understanding the "Repairs" You Can Perform
While you cannot repair the tube itself, some issues that seem like tube failure can be resolved with simple maintenance. These steps address the tube's connection to the circuit, not the tube's internal function.
Diagnosis, Not Repair
A tube tester is a diagnostic tool. It does not repair tubes, but it is invaluable for confirming whether a tube is "good" or "bad." This helps you definitively identify the faulty component so it can be replaced.
Cleaning External Contacts
The pins on the bottom of a tube can become oxidized or dirty over time, leading to a poor electrical connection. This can cause crackling, noise, or signal loss.
Cleaning the pins with a specialized electronic contact cleaner can often solve these problems, making a tube seem "repaired" when the issue was only a dirty connection. Likewise, cleaning and re-tensioning the tube socket in the amplifier is a critical maintenance step.
Managing Microphonics
Some tubes are "microphonic," meaning they pick up physical vibrations and translate them into unwanted noise. This is due to internal parts vibrating. While you can't fix this internally, placing a silicone "tube damper" ring around the outside of the tube can reduce the vibrations and mitigate the symptom.
Making the Right Choice for Your Equipment
Your goal should be to find the right replacement tube. The market consists of New Old Stock (NOS) tubes—vintage tubes that were never used—and new-production tubes from modern factories.
- If your primary focus is audio fidelity in a high-end system: Seek out tested New Old Stock (NOS) or premium new-production tubes, as they are often considered to have superior sonic characteristics.
- If your primary focus is reliability for a working musician's amplifier: Modern, new-production tubes from reputable brands offer a dependable and cost-effective solution for consistent performance.
- If your primary focus is historically accurate restoration of a collectible: Sourcing a period-correct, tested used or NOS tube is the only way to maintain the equipment's originality.
Ultimately, accepting the vacuum tube as a high-performance, replaceable part is the key to confidently maintaining your equipment for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Repairability | Not repairable for standard consumer tubes |
| Primary Reason | Hermetically sealed vacuum; opening destroys it |
| Common Failure Modes | Filament burnout, loss of vacuum, internal shorts |
| Practical Solution | Diagnosis and replacement |
Keep your lab equipment running at peak performance with reliable components from KINTEK.
Just as a vacuum tube is a critical, consumable part of an amplifier, the equipment in your laboratory depends on high-quality consumables and replacement parts for consistent, accurate results. KINTEK specializes in supplying the lab equipment and consumables you need to maintain your workflow without interruption.
Contact our experts today to find the right replacement parts and consumables for your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- KF ISO Stainless Steel Vacuum Flange Blind Plate for High Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Cold Trap Chiller Indirect Cold Trap Chiller
- Laboratory Vertical Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What material are furnace tubes? Choosing the Right Material for High-Temperature Success
- Why are 304 or 430 stainless steel tubes used as canisters for ODS steel? Enhancing Corrosion Resistance via HIP
- What is the purpose of using high-temperature muffle or tube furnaces after incipient wetness impregnation of catalysts?
- What role does an industrial horizontal tube furnace play in Cr-Al-C coating? Master MAX Phase Transformation
- What is the feedstock for ethylene cracker? Choose the Right Hydrocarbon for Your Output
- What critical process conditions does a horizontal tube furnace provide during USP? Optimize Tungsten Oxide Production
- Why is annealing in a horizontal tube furnace using a quartz boat necessary for preparing mesoporous Nb-doped TiO2?
- What is the difference between a tube furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Heating Needs



















