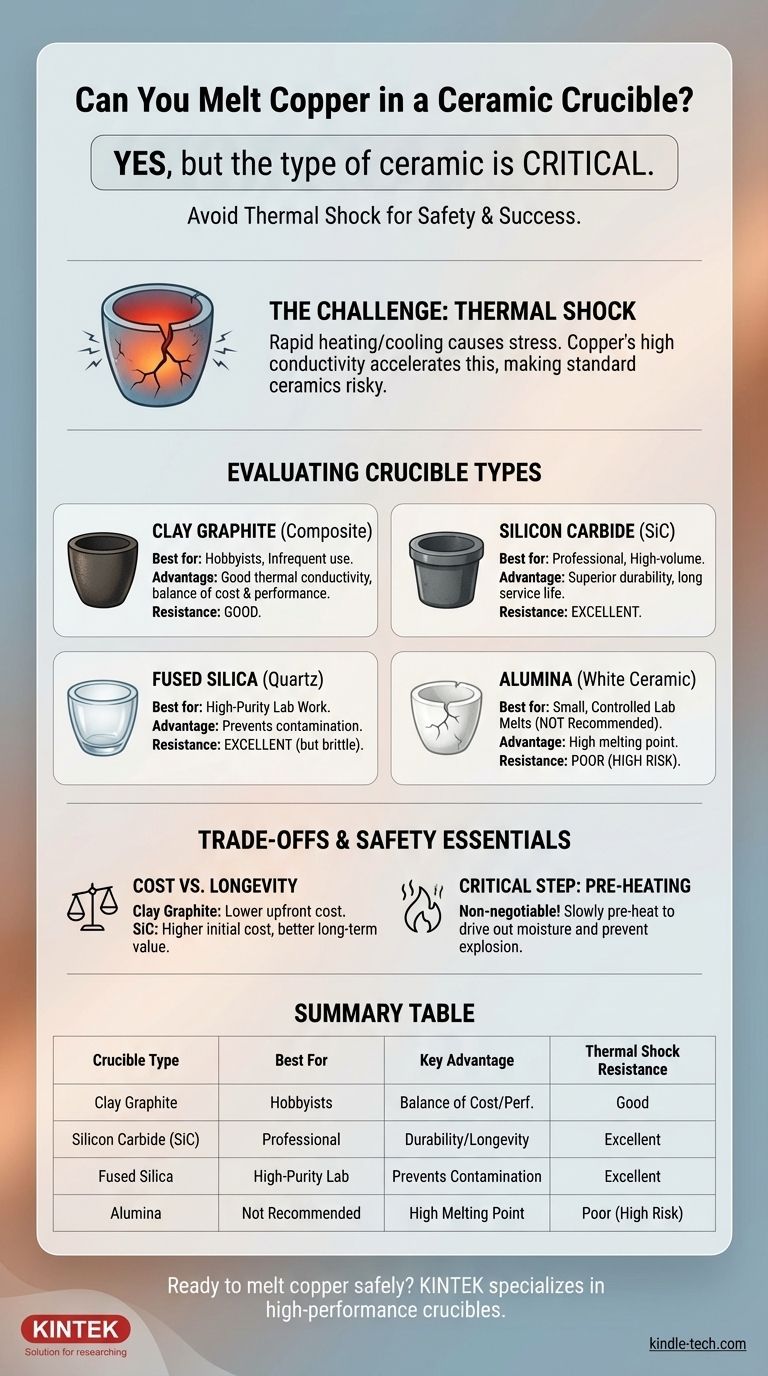
Yes, you absolutely can melt copper in a ceramic crucible, but the specific type of ceramic is the most critical factor for success and safety. While many ceramics can withstand copper's melting point of 1084°C (1983°F), not all can handle the intense thermal stress involved in the process. Using the wrong type can lead to catastrophic failure.
The central challenge isn't withstanding the heat, but surviving the rapid temperature change known as thermal shock. For this reason, specialized composite ceramics like clay graphite and silicon carbide are the industry standard, vastly outperforming common "white" ceramic crucibles like pure alumina.
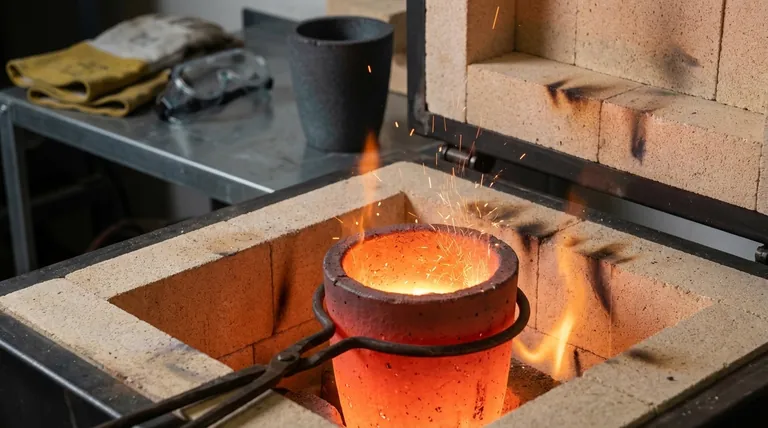

Why the Right Crucible is Critical for Copper
Melting copper places extreme demands on a crucible. The metal's high thermal conductivity and the rapid heating and cooling cycles create an environment where only specific materials can thrive.
The Primary Challenge: Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is the stress that builds up in a material when different parts of it expand or contract at different rates due to rapid temperature changes.
Because copper is an excellent thermal conductor, it draws heat from the furnace and into itself very quickly. This can cause the crucible's inner wall to get extremely hot while the outer wall is still much cooler, leading to immense stress that can crack or shatter it.
This is the number one cause of crucible failure in small-scale metal melting.
The Need for Chemical Stability
At over 1000°C, molten copper can be chemically reactive. The crucible material must be inert and not react with the copper, which would contaminate your melt and degrade the crucible itself over time.
Evaluating Common Crucible Types
Not all "ceramics" are created equal. The material's composition dictates its performance, especially its resistance to thermal shock.
Clay Graphite Crucibles
These are a composite material made from refractory clays and graphite flakes. They are the most common and versatile choice for hobbyists and many small foundries.
The graphite provides excellent thermal conductivity, allowing the crucible to heat more evenly and reducing the internal stress. The clay provides the structural form. They offer a great balance of performance, durability, and cost.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
Often considered the professional-grade standard, silicon carbide crucibles offer superior performance. They are manufactured by bonding SiC grains together, sometimes with added graphite.
SiC has exceptional thermal shock resistance and very high thermal conductivity, even better than clay graphite. This makes them extremely durable and resistant to cracking, allowing for a much longer service life.
Fused Silica (Quartz) Crucibles
Fused silica is a type of high-purity glass with a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, giving it excellent thermal shock resistance.
These crucibles are primarily used in laboratory settings or for melting high-purity metals where avoiding contamination from a graphite-based crucible is the top priority. They tend to be more brittle and less suited for rough foundry use.
Alumina Crucibles (The "White Ceramic" Risk)
When people think of a generic "ceramic" crucible, they often picture a white, porcelain-like alumina vessel. While pure alumina has an extremely high melting point, it generally has poor thermal shock resistance.
Using a standard alumina crucible for melting a large mass of copper is very risky. It is highly susceptible to cracking upon heating or cooling and is not recommended for this application outside of very small, controlled laboratory melts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a crucible involves balancing cost, durability, and the specific needs of your project.
Cost vs. Longevity
A clay graphite crucible offers the lowest upfront cost, making it an excellent starting point. However, a silicon carbide crucible, while more expensive initially, will typically last for many more melts, making it more cost-effective in the long run for frequent use.
The Critical Step: Pre-heating is Non-Negotiable
No matter which crucible you choose, it is vital to pre-heat it properly before its first use and before every subsequent melt. Any absorbed moisture in the crucible walls will turn to steam instantly, causing it to crack or explode.
Always heat the empty crucible slowly to a few hundred degrees (e.g., 200°C / 400°F) and hold it there to ensure all moisture is driven out. This step is essential for both safety and the longevity of your crucible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your crucible based on your specific application and frequency of use.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist casting or infrequent melting: A clay graphite crucible is the ideal choice, offering the best balance of performance and affordability.
- If your primary focus is professional, high-volume, or demanding foundry work: Invest in a silicon carbide (SiC) crucible for its superior durability and long-term value.
- If your primary focus is high-purity laboratory work: A fused silica crucible is the correct tool when preventing any contamination is your highest priority.
Choosing the correct crucible is the foundation for a safe and successful metal casting practice.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Thermal Shock Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay Graphite | Hobbyists, Infrequent Melting | Excellent balance of cost & performance | Good |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Professional, High-Volume Work | Superior durability & longevity | Excellent |
| Fused Silica | High-Purity Laboratory Work | Prevents contamination from graphite | Excellent |
| Alumina (White Ceramic) | Small, Controlled Lab Melts (Not Recommended) | High melting point | Poor (High Risk) |
Ready to melt copper safely and efficiently?
Choosing the right crucible is critical for your project's success and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including durable crucibles designed for demanding applications like copper melting.
Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible—whether it's cost-effective clay graphite for your hobby foundry or robust silicon carbide for professional use—ensuring you get the performance and longevity you need.
Don't risk a failed melt. Contact our team today to find the ideal crucible solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- How are carbon crucibles made? Discover the Engineering Behind High-Performance Crucibles
- What is the role of high-purity alumina crucibles in LBE corrosion experiments? Ensure Data Integrity and Accuracy
- Why is a platinum (Pt) sample crucible preferred for TGA of LCLA composite materials? Ensure Superior Data Integrity
- Can crucibles withstand very high temperatures? Yes, if you choose the right material for your application.
- What is the function of crucible with cover in laboratory? Master High-Temperature Reactions
- What is the function of a por4 grade filtering crucible in the recovery of hydrothermal liquefaction products?
- What is the temperature range of a carbon crucible? Maximize Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for molten FLiNaK? Ensure Peak Purity in Corrosive Salt Environments



















