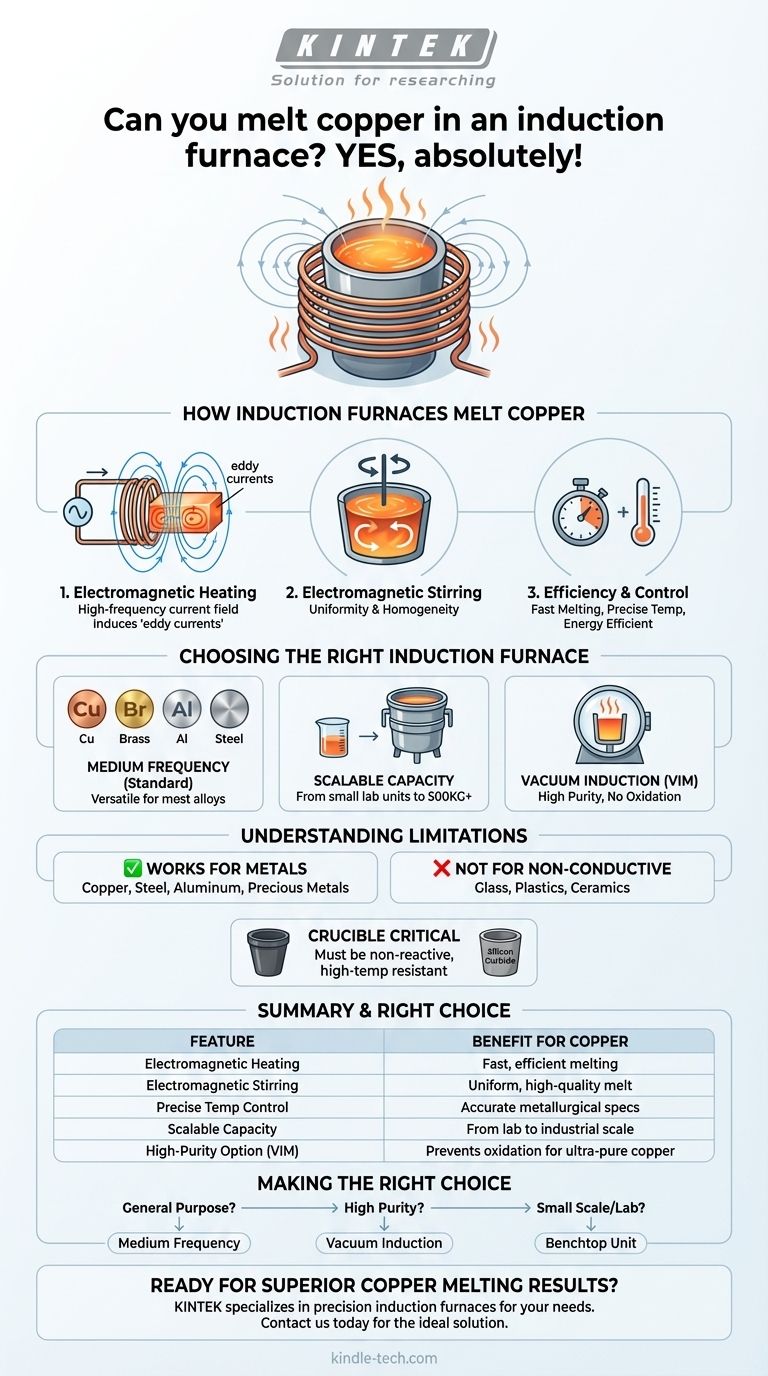
Yes, you can absolutely melt copper in an induction furnace. In fact, induction furnaces are one of the most common and effective technologies used for melting copper, its alloys like brass and bronze, and a wide range of other non-ferrous and ferrous metals. Their ability to generate intense heat directly within the copper itself makes them highly efficient and precise for this purpose.
An induction furnace is an ideal tool for melting copper due to its speed, efficiency, and the electromagnetic stirring action that ensures a high-quality, homogeneous final product. The key is understanding that different furnace types are optimized for different scales and purity requirements.
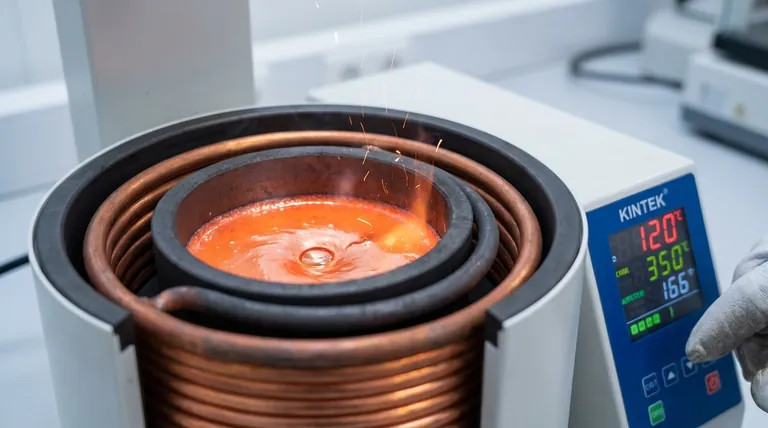

How Induction Furnaces Melt Copper
The Principle of Electromagnetic Heating
An induction furnace does not use an external flame or heating element to melt the metal. Instead, a high-frequency electrical current is passed through a copper coil that surrounds a non-conductive container, or crucible, holding the metal charge.
This current generates a powerful and rapidly alternating magnetic field. The magnetic field penetrates the copper inside the crucible and induces strong electrical currents within it, known as eddy currents. The inherent electrical resistance of the copper causes these eddy currents to generate immense heat, melting the metal from the inside out.
The Benefit of Electromagnetic Stirring
A significant advantage of induction melting is the natural stirring action created by the magnetic forces. This constant, gentle motion ensures that the molten copper is uniform in temperature.
This is especially critical when creating alloys. The stirring action guarantees that additions like zinc (for brass) or tin (for bronze) are thoroughly mixed, resulting in a completely homogeneous and high-quality melt.
Efficiency and Control
Because the heat is generated directly within the copper charge, the process is extremely fast and energy-efficient. There is very little waste heat lost to the environment compared to fuel-fired furnaces. This also allows for highly precise temperature control, which is vital for meeting metallurgical specifications.
Choosing the Right Induction Furnace
Medium Frequency Furnaces are the Standard
For most copper and non-ferrous metal applications, medium frequency induction furnaces are the industry standard. As noted in foundry specifications, these systems are specifically designed to efficiently melt materials like copper, brass, aluminum, gold, and silver.
Matching Capacity to Your Needs
Induction technology is highly scalable. Furnaces are available in a vast range of sizes, from small benchtop units with a capacity of a few kilograms for labs or jewelers, all the way up to industrial units capable of melting 500KG or more per batch.
Vacuum Induction for High Purity
For applications demanding the highest purity, such as in electronics or aerospace, a vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace is used. This specialized furnace operates under a vacuum to prevent the molten copper from reacting with oxygen or nitrogen in the air, which can introduce impurities.
Understanding the Limitations
A Broad Spectrum of Metals
The versatility of an induction furnace is a primary strength. The same furnace used for copper can typically be used to melt steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and precious metals. It simply requires adjusting the power settings and ensuring you have the correct crucible for the target temperature.
Not for Non-Conductive Materials
The core principle of induction heating relies on the material being an electrical conductor. Therefore, it is completely unsuitable for melting non-metallic materials like glass, plastics, or ceramics. These materials require different technologies, such as a muffle furnace, which relies on radiant heat.
Crucible Selection is Critical
The crucible that holds the molten copper must be able to withstand extreme temperatures without reacting with the metal. It must also be an electrical insulator so that it does not heat up itself. Materials like graphite, silicon carbide, or clay-graphite are common choices for melting copper.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct furnace comes down to the specific goals of your project.
- If your primary focus is versatile, general-purpose melting: A standard medium-frequency induction furnace provides the best balance of efficiency and flexibility for copper, brass, aluminum, and steel.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity copper or reactive alloys: A vacuum induction furnace is necessary to prevent contamination from atmospheric gases.
- If your primary focus is small-scale casting or lab research: A small-capacity (3-15KG) benchtop induction furnace is a cost-effective and highly capable solution.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently select the right induction technology for your specific copper melting needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Copper Melting |
|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Heating | Heat is generated directly within the copper for fast, efficient melting. |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Creates a uniform, homogeneous melt, essential for quality alloys. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Allows for accurate metallurgical specifications to be met. |
| Scalable Capacity | Available from small benchtop units to large industrial furnaces (500KG+). |
| High-Purity Option (VIM) | Vacuum induction melting prevents oxidation for ultra-pure copper. |
Ready to achieve superior copper melting results?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including induction furnaces perfectly suited for melting copper, brass, bronze, and other non-ferrous metals. Whether you need a versatile benchtop unit for R&D or a high-capacity system for production, our solutions deliver the efficiency, control, and quality you require.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal induction furnace for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do you melt metal in an induction furnace? A Guide to Fast, Clean & Efficient Melting
- What is the effect of frequency in induction furnace? Unlock Optimal Melting Efficiency & Control
- Is induction heating efficient? Achieve Over 90% Energy Efficiency with Direct Internal Heating
- What is the difference between blast furnace and induction furnace? Choosing the Right Metal Melting Solution
- Who invented induction furnace? Discover the Pioneers Behind Modern Metallurgy
- Can you melt Aluminium in an induction furnace? Yes, and here's how to do it efficiently.
- What is the role of a high-frequency induction melting furnace in super duplex stainless steel prep? Achieve Precision
- How does induction melting work? Harness Electromagnetic Energy for Clean, Efficient Metal Processing



















