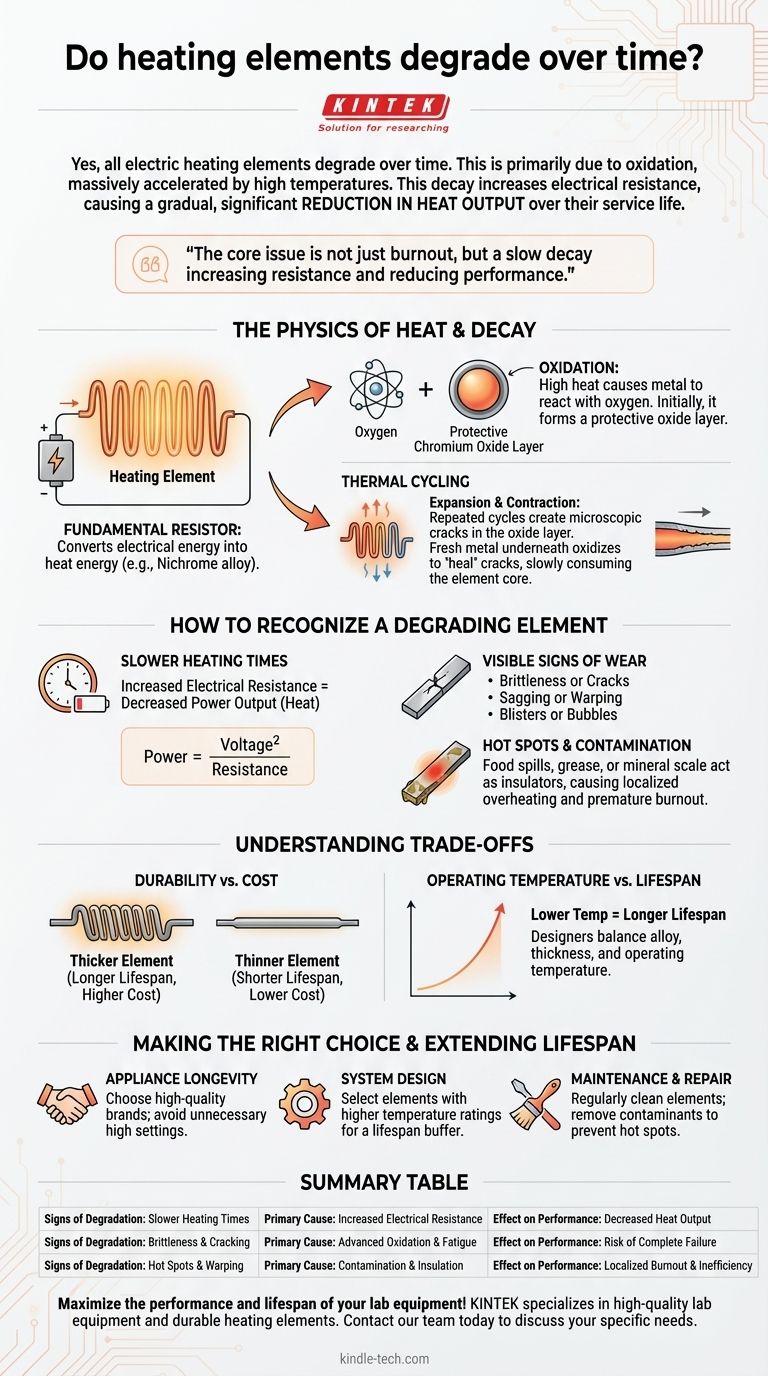
Yes, all electric heating elements degrade over time. This degradation is an unavoidable consequence of their operation, primarily driven by a process called oxidation, which is massively accelerated by the high temperatures at which they run. This process gradually alters the element's physical and electrical properties, leading to reduced performance long before it fails completely.
The core issue is not that heating elements simply "burn out," but that they undergo a slow decay. This decay increases their electrical resistance, which, contrary to intuition, causes a gradual but significant reduction in heat output over their service life.

The Physics of Heat and Decay
To understand why elements fail, you must first understand how they work. The process is a combination of material science and basic electrical principles.
How a Heating Element Works
A heating element is fundamentally a resistor. When electrical current flows through it, the resistance of the material converts electrical energy into heat energy.
This is why they glow red-hot. The material is specifically chosen for its high electrical resistance and its ability to withstand extreme temperatures without melting. The most common material is an alloy called Nichrome (nickel-chromium).
The Primary Culprit: Oxidation
At high temperatures, the metal in the element reacts with oxygen in the air. For Nichrome, this is initially a benefit, as it forms a stable, protective outer layer of chromium oxide.
This oxide layer prevents the underlying metal from oxidizing further and failing quickly. However, the protection isn't permanent.
The Role of Thermal Cycling
Every time an appliance is turned on and off, the heating element expands as it heats and contracts as it cools. This constant movement, known as thermal cycling, creates microscopic cracks in the protective oxide layer.
When the element heats up again, oxygen enters these new cracks, consuming a tiny amount of the fresh metal underneath to "heal" the protective layer. Over thousands of cycles, this repeated process slowly consumes the core metal, making the element thinner.
How to Recognize a Degrading Element
The signs of degradation are often subtle and can be mistaken for other problems. The most telling symptom is a change in performance.
Slower Heating Times
This is the most common and misunderstood symptom. As the element thins from oxidation, its cross-sectional area decreases. This increases its electrical resistance.
According to Ohm's Law for power (Power = Voltage² / Resistance), if the voltage from your wall outlet is constant, an increase in resistance leads directly to a decrease in power output (heat). An oven takes longer to preheat, a water heater can't keep up with demand, and a stove burner seems weaker.
Visible Signs of Wear
A visual inspection can often confirm degradation. Look for:
- Brittleness or cracks: A sign of advanced material fatigue.
- Sagging or warping: The element loses structural integrity at high temperatures.
- Blisters or bubbles: These indicate localized hot spots where the element is close to failing completely.
Hot Spots and Contamination
Contaminants are a major accelerator of failure. Food spills in an oven, grease on a stove burner, or mineral scale on a water heater element act as insulators.
This insulation traps heat, causing the spot underneath to get much hotter than the rest of the element. This extreme localized temperature dramatically accelerates oxidation and leads to a burnout at that specific point.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No heating element lasts forever. Their design is a careful balance of cost, performance, and longevity.
Durability vs. Cost
Thicker, heavier-gauge elements have more material to sacrifice to oxidation and will last significantly longer than thinner elements. They are also more expensive. Manufacturers of lower-cost appliances often use thinner elements to save on material costs, which directly translates to a shorter service life.
Operating Temperature vs. Lifespan
The relationship between temperature and lifespan is not linear; it's exponential. A heating element run at 1400°F may last thousands of hours longer than the exact same element run at 1500°F. Designers must choose an element alloy and thickness that provides a safety margin above the appliance's normal operating temperature.
The Impact of Environment
The operating environment is a critical factor. An element in a convection oven with constant airflow will behave differently than one submerged in hard water, which is prone to mineral scaling. The design must account for the specific application to ensure a reasonable lifespan.
Making the Right Choice and Extending Lifespan
You can actively manage the lifespan of heating elements by understanding the forces working against them.
- If your primary focus is appliance longevity: Choose high-quality appliances from reputable brands, as they are more likely to use heavier-gauge elements, and avoid running them on the highest possible settings unless necessary.
- If your primary focus is system design or engineering: Select an element alloy and diameter rated for a temperature significantly higher than your target operating point to build in a substantial lifespan buffer.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and repair: Regularly clean elements exposed to contaminants, such as in ovens or water heaters, to prevent insulating hot spots that lead to premature failure.
Understanding these principles of material decay allows you to move from simply using a product to intelligently managing its performance and lifespan.
Summary Table:
| Signs of Degradation | Primary Cause | Effect on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Slower Heating Times | Increased Electrical Resistance | Decreased Heat Output |
| Brittleness & Cracking | Advanced Oxidation & Fatigue | Risk of Complete Failure |
| Hot Spots & Warping | Contamination & Insulation | Localized Burnout & Inefficiency |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your lab equipment! KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable heating elements designed for rigorous use. Our experts can help you select the right components to ensure reliability and efficiency in your laboratory. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
People Also Ask
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C









