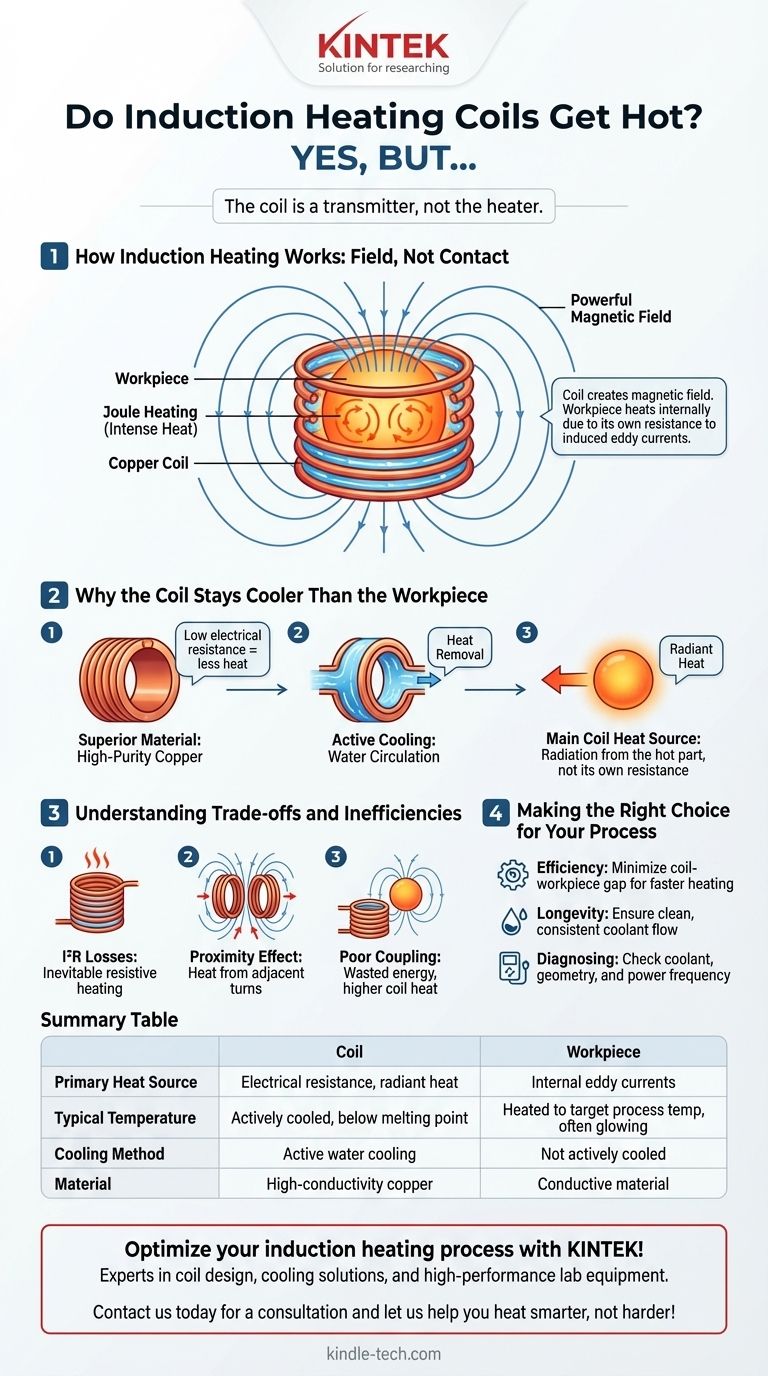
Yes, induction heating coils get hot, but they are designed to stay significantly cooler than the workpiece being heated. The heat in the coil is an undesirable byproduct, whereas the intense heat in the workpiece is the entire point of the process.
The core principle of induction heating is that the coil's job is to create a powerful magnetic field, not to generate heat itself. The workpiece heats up internally due to its own resistance to the electrical currents induced by this field. While the coil does heat up from its own electrical resistance and radiation from the hot part, it is almost always actively cooled to prevent it from melting.
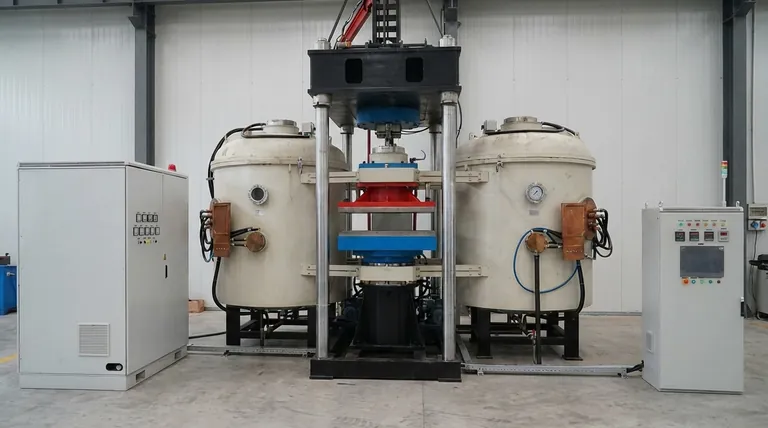

How Induction Heating Works: Field, Not Contact
To understand why the coil doesn't melt, you must first understand that it is not the primary source of heat. It is a transmitter that tells the workpiece to heat itself.
Creating the Magnetic Field
An induction heater passes a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through a copper coil. According to the laws of electromagnetism, this flow of current generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
Inducing Currents in the Workpiece
When a conductive material (like a piece of steel) is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents within the metal. These are called eddy currents.
The Source of Intense Heat
The workpiece has a natural electrical resistance. As these strong eddy currents are forced to flow through the material, they encounter this resistance, which generates immense friction and thus, intense heat. This is known as Joule heating. The workpiece effectively heats itself from the inside out.
Why the Coil Stays Cooler Than the Workpiece
The entire system is engineered to focus heat in the workpiece and remove it from the coil. This is achieved through three key factors.
Superior Material and Design
Induction coils are made from high-purity, high-conductivity copper tubing. Copper has a very low electrical resistance, which means it generates far less heat for the same amount of current compared to a material like steel.
The Critical Role of Active Cooling
The copper tubing used for the coil is hollow. During operation, a coolant—most often water—is continuously pumped through the inside of the coil. This cooling circuit actively pulls heat out of the copper, keeping its temperature well below its melting point.
The Primary Source of Coil Heat: Radiation
In a well-designed system, the most significant source of heat in the coil is not its own electrical resistance. Instead, it's the radiant heat being absorbed from the glowing-hot workpiece placed just millimeters away. The cooling system's main job is often to combat this radiated heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Inefficiencies
While the goal is a cool coil and a hot part, some coil heating is unavoidable and represents an energy loss in the system.
Inevitable I²R Losses
Even low-resistance copper will generate some heat when massive currents are passed through it. This resistive heating (known as I²R loss) is a fundamental property of physics and represents a direct loss of efficiency.
The Proximity Effect
The turns of the coil are close to each other. The magnetic field from one turn of the coil can induce small, unwanted eddy currents in the adjacent turns. This phenomenon, known as the proximity effect, generates additional heat within the coil itself.
Poor Coupling
If the coil is too far from the workpiece or its geometry is a poor match, the magnetic field cannot efficiently induce currents in the part. The system may need to run at much higher power to achieve the target temperature, increasing the resistive heating in the coil and wasting energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding why a coil gets hot is key to diagnosing problems and optimizing your induction heating application.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Ensure the gap between the coil and the workpiece is as small as is safely possible. A well-coupled part requires less power and heats faster.
- If your primary focus is coil longevity: Prioritize a clean, consistent, and adequate flow of coolant. Overheating due to a coolant blockage is the most common cause of coil failure.
- If you are diagnosing an overheating coil: First, check the coolant flow. Then, verify that the coil's geometry is appropriate for the part and that the power supply frequency is tuned correctly for the application.
Mastering induction heating begins with recognizing that the coil is a precision tool, not a simple heating element.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Coil | Workpiece |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Heat Source | Electrical resistance (I²R loss) and radiant heat from the part | Internal eddy currents (Joule heating) |
| Typical Temperature | Actively cooled, stays well below melting point | Heated to target process temperature (often glowing red hot) |
| Cooling Method | Active cooling (water flowing through copper tubing) | Not actively cooled during heating |
| Material | High-conductivity copper | Conductive material like steel, aluminum, etc. |
Optimize your induction heating process with KINTEK!
Is your coil overheating or underperforming? Our experts can help you select the right coil design and cooling solutions to maximize efficiency, extend equipment life, and achieve precise, repeatable results.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including induction heating systems tailored to your specific laboratory or industrial needs.
Contact us today for a consultation and let us help you heat smarter, not harder!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve Superior Lithium Niobate Piezoelectric Density
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace address structural defects in as-cast CoCrPtB alloy ingots? Optimize Your Density
- How does axial pressure in vacuum hot-press furnaces influence diamond/aluminum composites? Optimize Microstructure



















