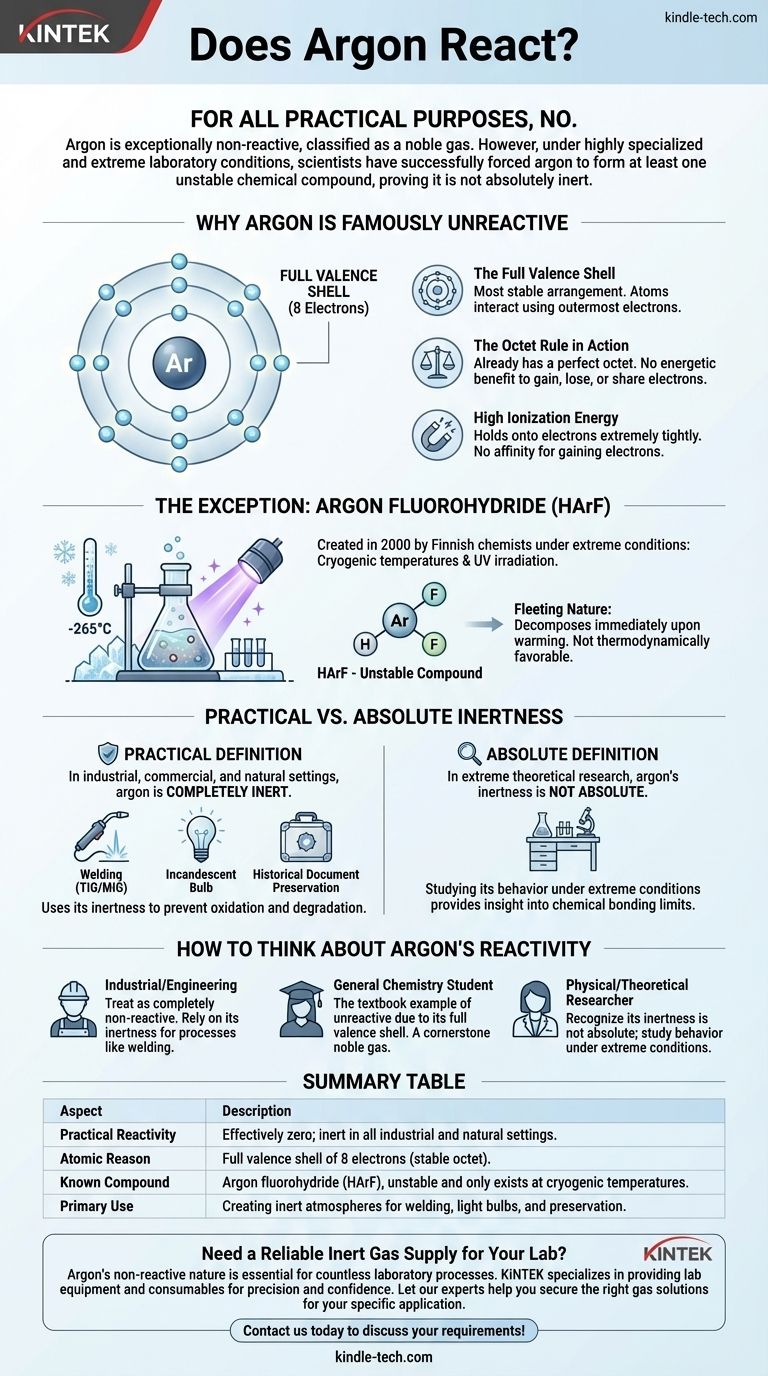
For all practical purposes, no. Argon is exceptionally non-reactive, which is why it is classified as a noble gas. However, under highly specialized and extreme laboratory conditions, scientists have successfully forced argon to form at least one unstable chemical compound, proving it is not absolutely inert.
The core takeaway is that an element's "reactivity" is not a simple yes-or-no question. While argon's perfect electron shell configuration makes it inert in any natural or industrial context, its non-reactivity can be overcome with enough energy under cryogenic conditions, revealing the subtle complexities of chemical bonding.

Why Argon Is Famously "Unreactive"
To understand why argon so strongly resists forming chemical bonds, we must look at its atomic structure. Its reputation for being inert is not arbitrary; it is a direct result of its electron configuration.
The Full Valence Shell
Atoms interact and form bonds using their outermost electrons, known as valence electrons.
Argon has eight valence electrons, which completely fills its outer electron shell. This is the most stable arrangement an atom can have.
The "Octet Rule" in Action
The "octet rule" is a fundamental principle in chemistry stating that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell of eight electrons.
Because argon already has this perfect octet, there is no energetic benefit for it to gain, lose, or share electrons with other atoms. It is already in its ideal, low-energy state.
High Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. Argon has a very high ionization energy, meaning it holds onto its electrons extremely tightly.
Similarly, it has no affinity for gaining electrons. There is simply no chemical "motive" for argon to engage in a reaction under normal circumstances.
The Exception That Proves the Rule
For decades, argon was believed to be completely inert. This changed in the year 2000 when a team of Finnish chemists created the first known true argon compound.
Forcing a Reaction Under Extreme Conditions
The compound, argon fluorohydride (HArF), was not created in a typical lab beaker.
Scientists had to freeze a mixture of argon and hydrogen fluoride onto a surface at temperatures near absolute zero (around -265°C or -445°F) and then irradiate it with powerful ultraviolet light. This extreme energy input was enough to temporarily force the reluctant argon atom into a bond.
The Fleeting Nature of Argon Compounds
The resulting HArF compound is incredibly unstable. It only exists at these cryogenic temperatures.
If it is warmed even slightly, the weak bonds break, and it immediately decomposes back into separate argon and hydrogen fluoride. This highlights that the compound is not thermodynamically favorable and exists only because it is "trapped" by the extreme cold.
Practical Inertness vs. Absolute Inertness
This discovery forces us to distinguish between two concepts: what is true in a practical sense and what is true in an absolute, theoretical sense.
The Practical Definition of Inert
In any industrial, commercial, or natural setting, argon is completely inert. It does not react with air, water, metals, or any other substance it comes into contact with.
It's this practical inertness that makes it so valuable.
Why This Matters for Applications
Argon's non-reactivity is a feature, not a limitation. In welding (TIG/MIG), it creates an inert "shield" around the molten metal, preventing it from oxidizing or reacting with gases in the air, which ensures a clean, strong weld.
In incandescent light bulbs, an argon atmosphere prevents the hot tungsten filament from burning out. In historical document preservation, it provides an oxygen-free environment to stop degradation.
How to Think About Argon's Reactivity
Your context determines how you should view argon's chemical behavior. Understanding this distinction is key to applying chemical principles correctly.
- If you are working in an industrial or engineering setting: Treat argon as a completely non-reactive gas. Its inertness is its most valuable property and can be relied upon for processes like welding and manufacturing.
- If you are a student of general chemistry: Understand that argon is the textbook example of an unreactive element due to its full valence electron shell, making it a cornerstone of the noble gas group.
- If you are a researcher in physical or theoretical chemistry: Recognize that argon's inertness is not absolute, and studying its behavior under extreme conditions provides valuable insight into the limits of chemical bonding.
Ultimately, argon's extreme reluctance to react is a fundamental property that makes it both scientifically interesting and immensely useful in the real world.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Practical Reactivity | Effectively zero; inert in all industrial and natural settings. |
| Atomic Reason | Full valence shell of 8 electrons (stable octet). |
| Known Compound | Argon fluorohydride (HArF), unstable and only exists at cryogenic temperatures. |
| Primary Use | Creating inert atmospheres for welding, light bulbs, and preservation. |
Need a Reliable Inert Gas Supply for Your Lab?
Argon's non-reactive nature is essential for countless laboratory processes, from creating controlled atmospheres to sensitive material handling. Ensuring you have a consistent, high-purity supply is critical for your results.
KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need to operate with precision and confidence. Let our experts help you secure the right gas solutions for your specific application.
Contact us today via our form to discuss your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Grinding Bowl
People Also Ask
- Why is high-purity argon protection essential for titanium dioxide reduction? Ensure Peak Metal Purity
- Which type of furnace is used in annealing process? Choose the Right Controlled Atmosphere Furnace
- How do high-temperature atmosphere annealing furnaces ensure electrocatalytic activity? Optimize Your Metal Nitrides
- How do inert gas, airflow, and pressure work together in a furnace? Master Precise Atmosphere Control
- How does a hydrogen atmosphere control system influence the formation of pores in Cu-Ni microtubes? Expert Insights
- Why is a tube or box furnace with atmosphere protection required for VPO4 precursors? Achieve Pure Phase & Conductivity
- What is a controlled atmosphere temperature treatment system? Master Precision Heat Treatment
- Why are atmosphere-controlled furnaces used for solid electrolyte impurities? Optimize Your Battery Research Now














