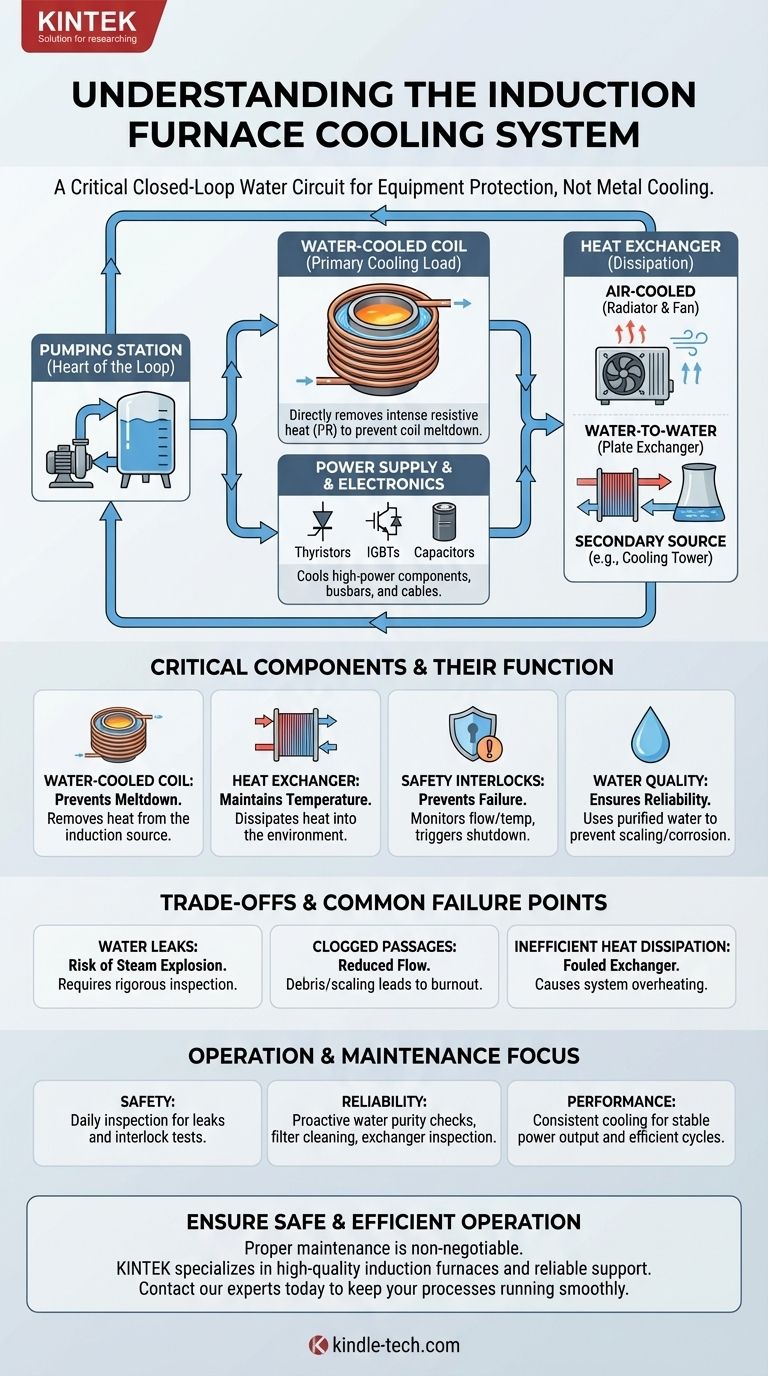
At its core, the cooling system of an induction furnace is a closed-loop water circuit designed to remove waste heat from the high-power electrical components. This system is not for cooling the metal being melted, but is absolutely essential for preventing the furnace's own components—primarily its powerful induction coil—from melting down under the massive electrical load.
The central challenge is not managing the heat of the molten metal, but managing the immense heat generated within the electrical coil itself. Therefore, the cooling system is the lifeblood of the furnace, protecting the equipment that generates the magnetic field, not the crucible or its contents.

Why Cooling is a Critical System, Not an Accessory
An induction furnace works by passing an enormous alternating current through a copper coil. While the resulting magnetic field is what heats the metal charge, the coil itself is subject to intense resistive heating (I²R heating). Without an active cooling system, this heat would destroy the coil in seconds.
The Heart of the System: The Water-Cooled Coil
The primary component requiring cooling is the induction coil. This coil is constructed from hollow copper tubing specifically so that coolant—almost always water—can be circulated directly through it. This allows for the most efficient possible heat transfer, removing heat at the precise point it is generated.
Protecting the Entire Power Supply Chain
The cooling requirement extends beyond the coil. The high-power electronics that convert mains electricity into the high-frequency current needed for induction also generate significant heat. A comprehensive cooling circuit will typically service:
- The Induction Coil: The primary and most critical cooling load.
- The Power Supply: Components like thyristors, IGBTs, and capacitors.
- Busbars and Cables: The heavy copper connections that carry current from the power supply to the coil.
Components of a Typical Water-Cooling Circuit
A complete cooling system is a dedicated subsystem with several key parts working in unison to ensure the furnace operates safely.
The Pumping Station
This is the heart of the cooling loop. It consists of a pump to circulate the water and a reservoir or tank. The system is typically a closed loop to maintain the quality and purity of the cooling water.
The Heat Exchanger
The heat absorbed by the water from the furnace components must be dissipated into the environment. This is the job of the heat exchanger. Common types include:
- Air-Cooled: A radiator and fan system (like a car's radiator) that transfers heat from the water to the ambient air.
- Water-to-Water: A plate-style exchanger that transfers heat from the closed-loop furnace water to a secondary source, such as city water or a large cooling tower.
Water Quality and Treatment
The quality of the water is critical. Using untreated tap water would lead to mineral scaling inside the hollow coil, creating insulating hotspots that cause the coil to fail. Therefore, systems use distilled or deionized water with specific additives to prevent corrosion and biological growth.
Safety Interlocks
Modern furnaces are protected by a series of sensors that monitor the cooling circuit. Flow switches and temperature sensors are wired into the furnace's control system. If the water flow drops or the temperature rises above a safe limit, the system triggers an immediate shutdown of the power supply to prevent catastrophic equipment failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Failure Points
While robust, the water-cooling system is also the furnace's primary vulnerability. Understanding its failure modes is key to safe operation.
The Risk of Water Leaks
A water leak is the most significant hazard. Any leak that allows water to come into contact with the molten metal inside the crucible can cause a dangerous steam explosion. Rigorous inspection and maintenance of all hoses, fittings, and the coil itself are paramount.
Clogged Passages and Reduced Flow
This is the most common cause of component failure. Debris or mineral buildup can restrict water flow in the narrow passages of the coil or power supply. This leads to localized overheating and burnout, even if the overall system temperature appears normal. This reinforces the critical need for high-purity water and proper filtration.
Inefficient Heat Dissipation
If the heat exchanger becomes fouled with dust (in an air-cooled system) or scale (in a water-cooled system), its ability to remove heat from the circuit is compromised. The entire loop temperature will begin to rise, eventually triggering a high-temperature fault and shutdown.
Making the Right Choice for Operation and Maintenance
Understanding the cooling system's function directly informs how you should approach furnace operation and maintenance.
- If your primary focus is safety: Your highest priority is daily inspection of the entire water circuit for leaks and ensuring all safety interlocks for flow and temperature are tested and functional.
- If your primary focus is reliability and uptime: Emphasize proactive maintenance, including regular checks of water purity, cleaning of filters, and inspection of the heat exchanger to ensure unrestricted flow and heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is performance: Recognize that consistent and correct cooling ensures the electrical components operate in their optimal temperature range, providing stable power output and efficient, predictable melt cycles.
Ultimately, viewing the cooling system as the lifeblood of the furnace—not an afterthought—is the key to safe, reliable, and efficient operation.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Critical for |
|---|---|---|
| Water-Cooled Coil | Removes heat directly from the induction source | Preventing coil meltdown |
| Heat Exchanger | Dissipates absorbed heat into the environment | Maintaining system temperature |
| Safety Interlocks (Flow/Temp Sensors) | Monitors system and triggers shutdown if unsafe | Preventing catastrophic failure |
| Water Treatment | Uses purified water to prevent scaling/corrosion | Ensuring long-term component reliability |
Ensure your lab's induction furnace operates safely and efficiently. The cooling system is the lifeblood of your equipment, and proper maintenance is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with high-quality induction furnaces and reliable support. Don't risk downtime or safety hazards—contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and keep your melting processes running smoothly.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to equip corn cob hydrolysis systems with rapid cooling? Maximize Glucose and Xylose Yield
- What is the purpose of using a cooling water system after wheat straw pretreatment? Optimize Sugar Yield and Safety
- Why is a high-performance cooling circulator necessary in silica membrane desalination? Boost Your Permeate Mass Transfer
- Why is a high-precision chiller core in natural gas hydrate synthesis? Master Thermal Stability for Lab Success
- What is the importance of a Recirculating Cooling Water System? Protect Your Lab and Master Reaction Control



















