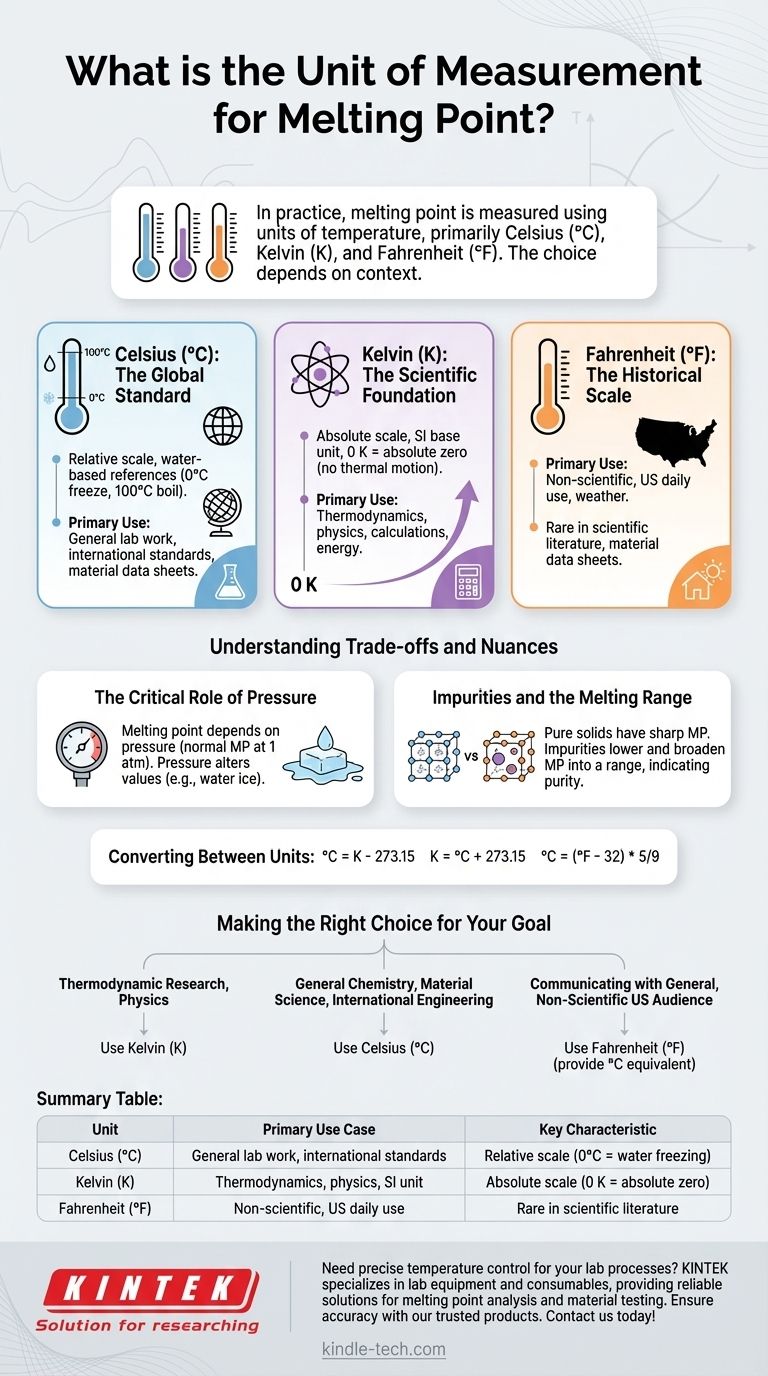
In practice, the melting point of a substance is measured and communicated using units of temperature. The most common units are Celsius (°C), Kelvin (K), and Fahrenheit (°F), with the specific choice depending heavily on the scientific or regional context.
The core issue is not which unit is "correct," but which is appropriate for the task. While Celsius is the global standard for most applications, Kelvin is the fundamental unit for scientific calculations because it is an absolute thermodynamic scale.

The Primary Scales of Temperature
Melting point is the specific temperature at which a substance changes state from a solid to a liquid. Because it is a measure of temperature, we use standard temperature scales to define it.
Celsius (°C): The Global Standard
The Celsius scale is the most widely used temperature scale in the world for both everyday and scientific purposes.
It is a relative scale defined by the freezing point (0°C) and boiling point (100°C) of water at standard atmospheric pressure. Its intuitive, water-based reference points make it practical for general laboratory work and international communication.
Kelvin (K): The Scientific Foundation
The Kelvin scale is the base unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI). It is an absolute scale, meaning its zero point, 0 K, represents absolute zero—the theoretical temperature at which all thermal motion ceases.
Because Kelvin is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of particles, it is the standard for thermodynamic calculations, physics, and physical chemistry. It avoids the negative values present in the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, simplifying mathematical formulas.
Fahrenheit (°F): The Historical Scale
The Fahrenheit scale is primarily used in the United States and a few other countries for daily weather and non-scientific applications.
While it is a valid unit, its use in a scientific or international context is rare. Most material data sheets and scientific literature will not use Fahrenheit as the primary unit for properties like melting point.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Simply stating a temperature is not enough. For a melting point to be a meaningful and reproducible value, other factors must be considered.
The Critical Role of Pressure
A substance's melting point is dependent on pressure. The value you typically see listed is the normal melting point, which is measured at a standard pressure of 1 atmosphere (atm) or 101.325 kilopascals (kPa).
For most substances, changes in ambient pressure have a negligible effect on the melting point. However, for substances like water ice, pressure can significantly alter it, which is why it's a critical parameter to note in precise scientific work.
Impurities and the Melting Range
A pure crystalline solid has a sharp, distinct melting point. However, the presence of impurities disrupts the crystal lattice, which both lowers and broadens the melting point.
Instead of a single temperature, an impure substance has a melting range. This phenomenon is a cornerstone of chemistry, often used to assess the purity of a synthesized compound.
Converting Between Units
Always ensure consistency within your calculations. If you need to convert, the standard formulas are:
°C = K - 273.15K = °C + 273.15°C = (°F - 32) * 5/9
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct unit is a matter of conforming to the standards of your specific field or audience.
- If your primary focus is thermodynamic research or fundamental physics: Use Kelvin (K), as it is the absolute SI standard required for calculations involving energy and entropy.
- If your primary focus is general chemistry, material science, or international engineering: Use Celsius (°C), as it is the most common and practical standard for lab work and data sheets.
- If your primary focus is communicating with a general, non-scientific audience in the United States: Use Fahrenheit (°F), but it is good practice to also provide the Celsius equivalent.
Ultimately, understanding the context behind the unit is more important than the unit itself.
Summary Table:
| Unit | Primary Use Case | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Celsius (°C) | General lab work, international standards | Relative scale (0°C = water freezing) |
| Kelvin (K) | Thermodynamics, physics, SI unit | Absolute scale (0 K = absolute zero) |
| Fahrenheit (°F) | Non-scientific, US daily use | Rare in scientific literature |
Need precise temperature control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for melting point analysis, material testing, and more. Ensure accuracy in your research with our trusted products. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing














