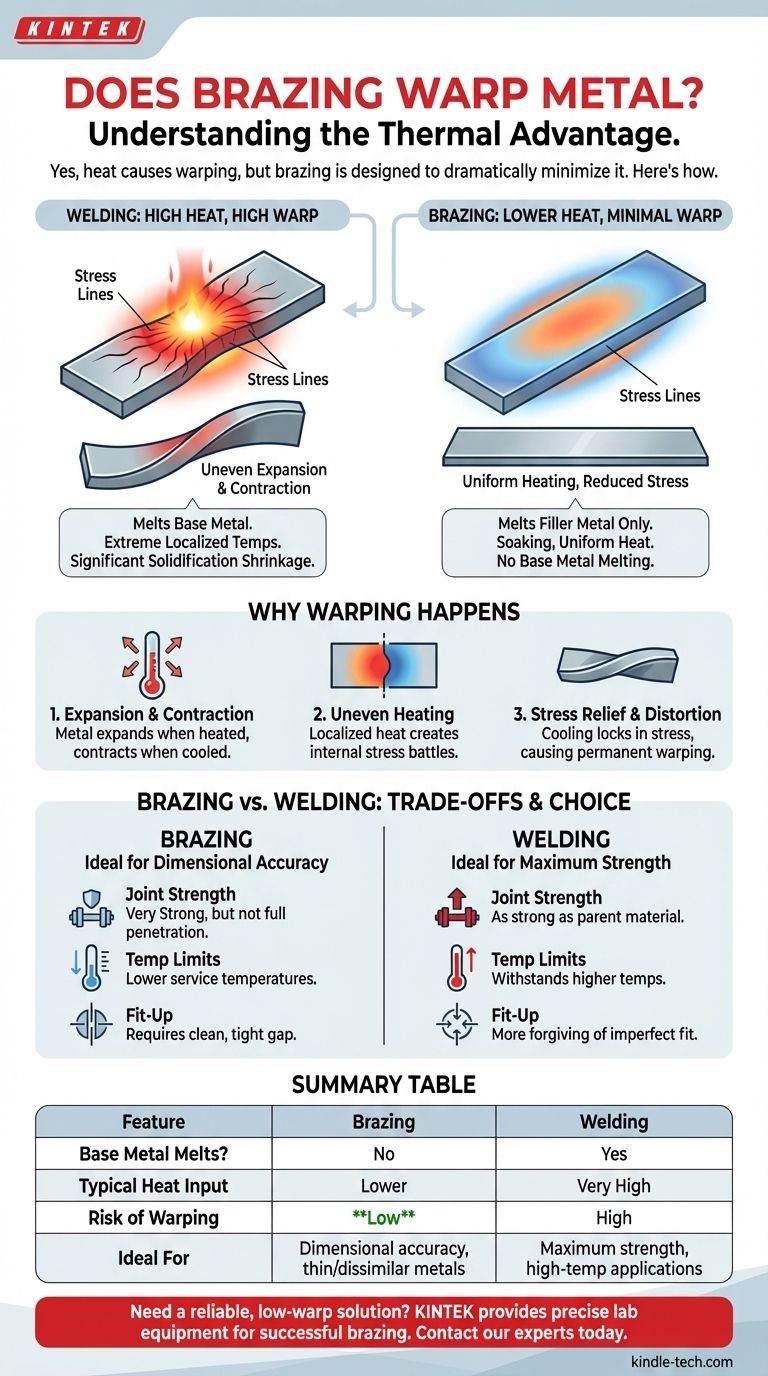
Yes, any process involving heat can cause metal to warp, but brazing is specifically designed and chosen to dramatically minimize this effect. Unlike welding, brazing heats metals to a much lower temperature and doesn't melt them, which is the primary reason it is preferred for applications where dimensional accuracy is critical.
The core reason brazing causes significantly less warping than welding is temperature. By operating below the melting point of the base metals, brazing introduces far less thermal stress, making it the superior method for maintaining the original shape and alignment of an assembly.

Why Heat Causes Warping: The Principle of Thermal Stress
Understanding why warping happens is key to preventing it. The entire issue comes down to how metal behaves when heated and cooled.
Expansion and Contraction
When you heat a piece of metal, it expands. When it cools, it contracts back to its original size. This physical property is unavoidable.
The Problem of Uneven Heating
Warping does not happen because of expansion alone. It happens because of uneven expansion and contraction.
If you heat one part of a metal sheet intensely while the rest remains cool, the hot section tries to expand but is constrained by the cold, rigid metal around it. This battle creates immense internal stress.
Stress Relief and Distortion
As the heated metal eventually cools and contracts, those locked-in stresses must be relieved. The metal relieves this stress by pulling and twisting itself into a new, distorted shape. This permanent change in shape is what we call warping.
How Brazing Mitigates Warpage
Brazing is fundamentally different from welding in ways that directly combat the root causes of warping.
The Critical Temperature Difference
This is the most important factor. Welding melts the base metals, requiring extremely high, localized temperatures (often thousands of degrees above the melting point).
Brazing works by melting a filler metal that flows between the base metals at a much lower temperature—always below the melting point of the parts being joined. Less heat input means less expansion, which means less internal stress.
Soaking Heat vs. Localized Heat
Many welding processes, like TIG or MIG, introduce a very intense, concentrated point of heat. This creates a severe temperature gradient between the weld zone and the surrounding metal, which is a perfect recipe for warping.
Brazing, especially with a torch or in a furnace, often involves heating a wider area more gently and uniformly. Bringing the entire joint area up to temperature together allows the parts to expand and contract more as a single unit, reducing stress.
No Melting, No Solidification Shrinkage
When a weld pool cools from a liquid to a solid, it undergoes significant shrinkage. This solidification shrinkage adds another powerful contracting force that pulls on the surrounding metal.
Because brazing never melts the base metals, it completely avoids this type of shrinkage, eliminating a major source of distortion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing brazing to avoid warping is an excellent strategy, but you must be aware of the trade-offs compared to welding.
Joint Strength
A properly executed weld fuses the parent metals, creating a joint that can be as strong as or stronger than the original material.
The strength of a brazed joint is determined by the shear strength of the filler metal and the design of the joint. While very strong, it is generally not as strong as a full-penetration weld in a structural, load-bearing application.
Temperature Limitations
A brazed joint cannot be used in an environment where service temperatures will approach the melting point of the filler alloy. The joint would simply fall apart. Welded joints can typically withstand much higher temperatures.
The Need for Cleanliness and Fit-Up
Brazing relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the tight gap between the parts. This action only works if the surfaces are exceptionally clean and the gap (clearance) between the parts is small and consistent. Welding can often be more forgiving of imperfect fit-up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Use your primary goal to guide your decision between brazing and welding.
- If your primary focus is preserving dimensional accuracy, especially on a complex frame or assembly: Brazing is an exceptional choice that minimizes the risk of distortion.
- If your primary focus is joining thin or delicate materials that would be destroyed by high-heat welding: Brazing is often the superior, and sometimes only, viable method.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength for heavy structural loads: A properly designed and executed weld is typically the stronger and more conventional choice.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals (like copper to steel): Brazing is one of the most effective and widely used methods, as welding these materials is often impossible.
By understanding the thermal principles at play, you can confidently choose and control the brazing process to achieve strong, precise joints with minimal distortion.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Base Metal Melts? | No | Yes |
| Typical Heat Input | Lower | Very High |
| Risk of Warping | Low | High |
| Ideal For | Dimensional accuracy, thin/dissimilar metals | Maximum strength, high-temp applications |
Need a reliable, low-warp solution for your metal joining projects? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for successful brazing processes. Our expertise ensures you achieve strong, dimensionally accurate joints every time. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















