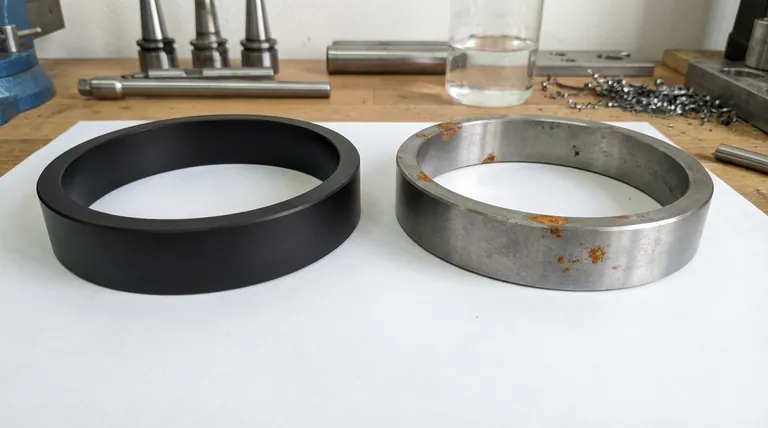
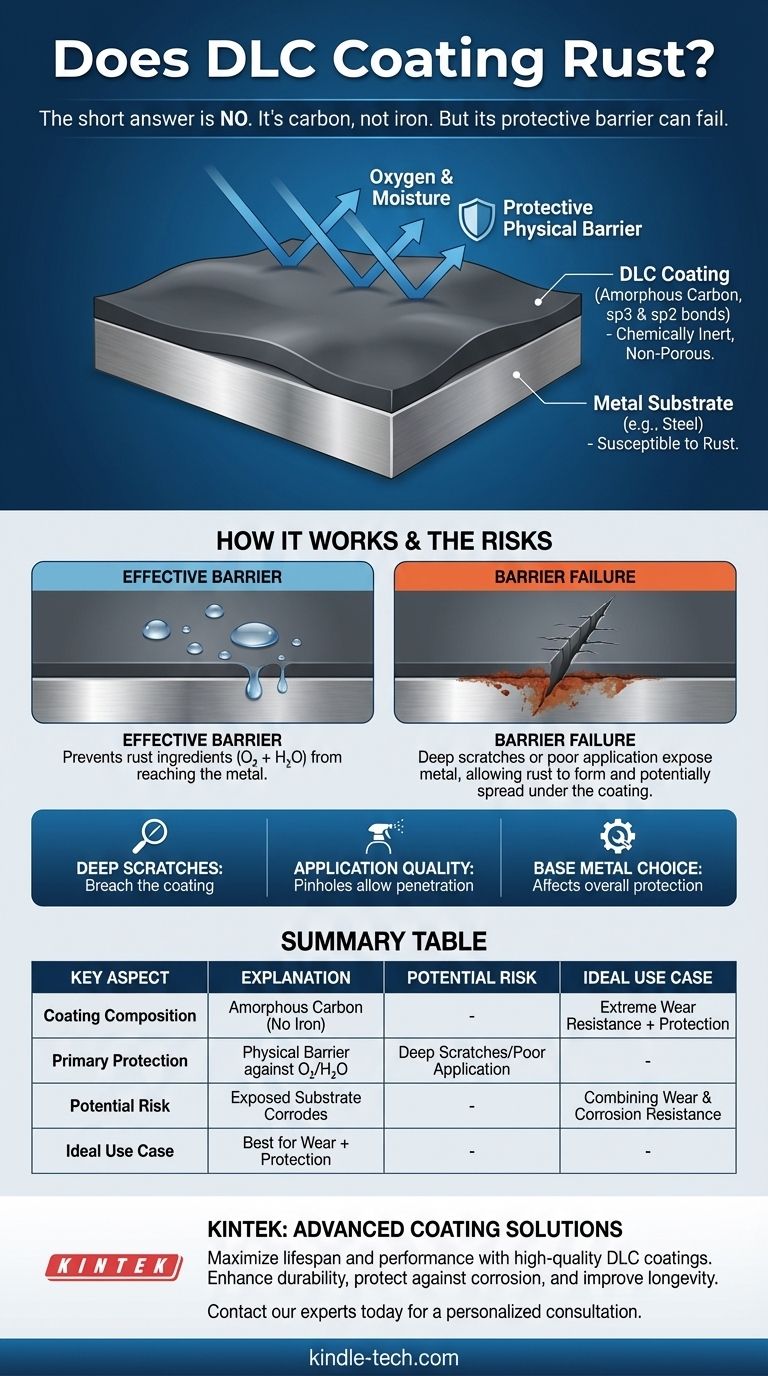
No, a Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating itself does not rust. Rust is the common term for iron oxide, which forms when iron or steel corrodes. As a form of carbon, DLC contains no iron and is chemically inert, making it incapable of rusting.
While the DLC coating is inherently immune to rust, its true value lies in acting as a protective barrier. The overall corrosion resistance of a DLC-coated part depends entirely on how well this barrier protects the underlying metal from exposure to the elements.

How DLC Provides Corrosion Resistance
The Nature of a DLC Coating
A DLC coating is a unique material known as amorphous carbon, meaning its atoms lack long-range order. It is composed of both sp3 bonds, which are found in diamond and provide extreme hardness, and sp2 bonds, found in graphite, which provide lubricity.
This combination of bonds makes the coating not only incredibly hard and slick but also chemically stable and resistant to environmental factors.
Acting as a Physical Barrier
The primary way DLC prevents rust is by creating a non-porous, sealed layer over the base metal, which is often a type of steel susceptible to rust. This barrier shields the steel from oxygen and moisture, the two key ingredients required for rust to form.
Because of its high performance in corrosive environments, DLC is valued as much for its protective qualities as its wear resistance.
The Real Risk: When the Barrier Fails
The Impact of Deep Scratches
While DLC is exceptionally hard, it is not indestructible. A sufficiently deep scratch or a significant impact can breach the coating, exposing a small area of the underlying steel.
If this exposed steel comes into contact with moisture, it will begin to rust. This rust can then potentially creep underneath the edges of the coating, causing it to bubble or flake over time.
The Role of Application Quality
The effectiveness of the corrosion protection is highly dependent on the quality of the coating application process. A flawless application ensures a complete, uniform seal over the base metal.
However, a poor application can leave microscopic pinholes or imperfections. These tiny openings are enough to allow moisture to penetrate and initiate corrosion on the substrate, even with no visible damage to the coating itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you get the performance you expect, consider the primary goal for your coated item.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear and corrosion resistance: Choose a product with a high-quality DLC coating applied over an already corrosion-resistant base metal, such as stainless steel.
- If you are maintaining a carbon steel item with a DLC coat: Regularly inspect it for deep scratches or chips, and ensure the surface is kept clean and dry to prevent moisture from compromising any exposed areas.
- If your primary focus is solely rust prevention in a harsh marine environment: You may want to consider specialized coatings designed exclusively for corrosion resistance, as DLC's chief advantages are hardness and low friction.
Ultimately, a DLC coating is an exceptional protective layer, but its ability to prevent rust is only as good as the integrity of the barrier it maintains.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Coating Composition | Amorphous carbon (sp3/sp2 bonds); contains no iron, so it cannot rust. |
| Primary Protection | Acts as a hard, non-porous physical barrier against oxygen and moisture. |
| Potential Risk | Deep scratches or poor application can expose the substrate to corrosion. |
| Ideal Use Case | Best for combining extreme wear resistance with a high level of corrosion protection. |
Maximize the lifespan and performance of your components with a high-quality DLC coating.
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced coating solutions for laboratory and industrial equipment. Our precision DLC coating services provide an unparalleled combination of hardness, lubricity, and corrosion resistance to protect your valuable metal parts.
Let us help you:
- Enhance durability and reduce wear
- Protect against corrosive environments
- Improve component performance and longevity
Ready to elevate your equipment's capabilities? Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation to see if DLC coating is the right solution for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance









