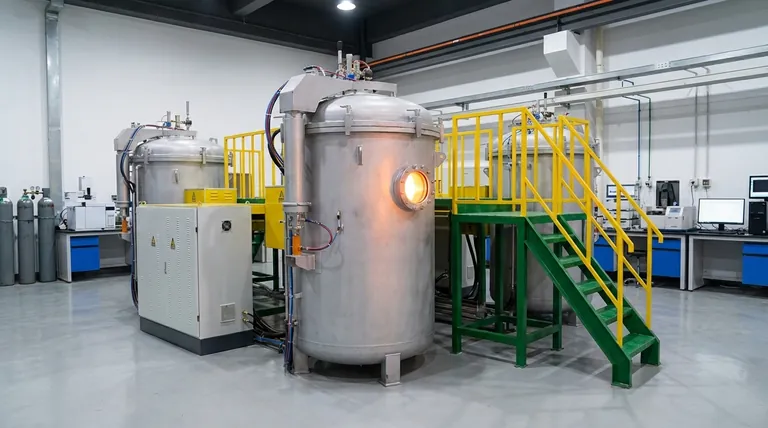
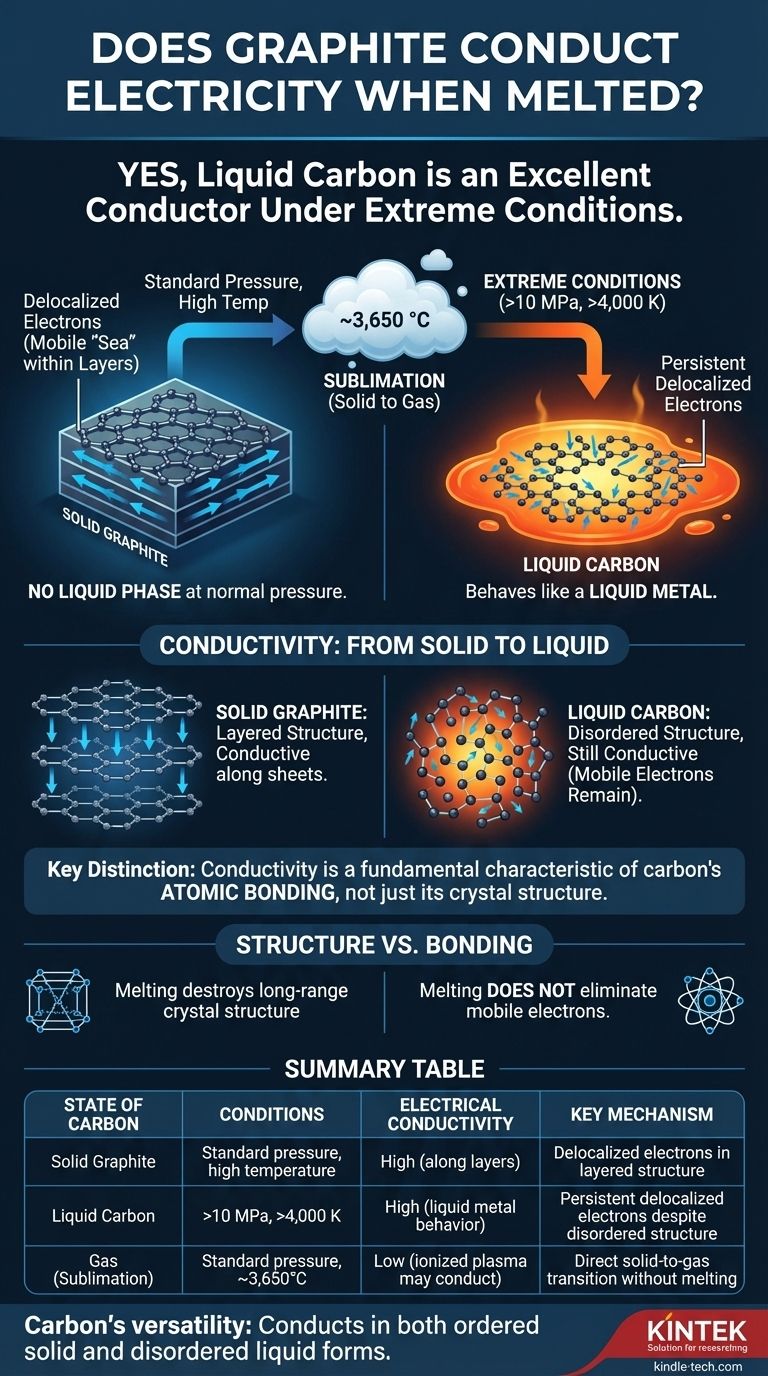
Yes, under the extreme conditions required to melt it, liquid carbon is an excellent electrical conductor. While graphite doesn't melt under normal atmospheric pressure, the liquid carbon that can be formed at very high pressures and temperatures behaves like a liquid metal, with electrons that are free to move and carry an electrical current.
The question isn't simply whether molten graphite conducts electricity—it does—but why. The answer reveals that conductivity is not solely a property of graphite's famous layered structure, but a more fundamental characteristic of carbon's atomic bonding that persists even in a disordered liquid state.

The Challenge of Melting Graphite
To understand conduction in liquid carbon, we must first appreciate how difficult it is to create. For most practical purposes, graphite does not have a liquid phase.
Sublimation, Not Melting
At standard atmospheric pressure, when you heat graphite to its limit, it does not turn into a liquid. Instead, it sublimes—transforming directly from a solid into a gas at temperatures around 3,650 °C (6,600 °F).
The Need for Extreme Conditions
To force carbon into a liquid state, you need to apply immense pressure and temperature simultaneously. Liquid carbon only exists at pressures above 10 megapascals (~100 times normal atmospheric pressure) and temperatures exceeding 4,000 K (~3,727 °C or 6,740 °F).
Conductivity: From Solid to Liquid
The reason both solid graphite and liquid carbon conduct electricity lies in the unique nature of carbon's electrons.
How Solid Graphite Conducts
In solid graphite, carbon atoms are arranged in flat, hexagonal sheets. Each carbon atom forms strong bonds with three neighbors, leaving its fourth outer electron delocalized.
These delocalized electrons are not tied to any single atom. Instead, they form a mobile "sea" of electrons within each sheet, which is why graphite is an excellent electrical conductor along its layers.
Conduction in the Liquid State
When graphite is forced to melt, its rigid, layered structure is destroyed. The atoms become disordered and can move freely, like in any liquid.
However, the local bonding environment still allows for delocalized electrons. The liquid is a complex, fluctuating mix of bonding types, but the presence of mobile electrons persists. This makes liquid carbon behave like a liquid metal, with high electrical conductivity.
Understanding the Key Distinction
It's easy to assume graphite's conductivity is purely a result of its sheet-like structure. The behavior of liquid carbon proves this is an incomplete picture.
Structure vs. Bonding
The key takeaway is the difference between structure and bonding. While melting destroys graphite's long-range crystal structure, it does not eliminate the fundamental atomic bonding that allows electrons to become mobile.
A Practical Limitation
This phenomenon is primarily of interest in extreme physics and materials science. In most engineering applications, such as in electric arc furnaces, you are dealing with a solid graphite electrode sublimating into a hot, ionized gas (a plasma), not a pool of liquid carbon.
Making Sense of Carbon's Properties
Your understanding of this topic depends on your goal. Use these points to frame the concept for your specific context.
- If your primary focus is fundamental chemistry: Liquid carbon's conductivity demonstrates that delocalized electrons, a feature of carbon's sp2 bonding, are not lost when the rigid lattice structure melts.
- If your primary focus is practical engineering: For virtually all applications, remember that graphite will sublimate into a gas far before it has a chance to melt, a critical factor for designing high-temperature systems.
Ultimately, carbon's ability to conduct electricity in both its ordered solid and disordered liquid forms reveals the remarkable versatility of its atomic bonds.
Summary Table:
| State of Carbon | Conditions Required | Electrical Conductivity | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Graphite | Standard pressure, high temperature | High (along layers) | Delocalized electrons in layered structure |
| Liquid Carbon | >10 MPa, >4,000 K | High (liquid metal behavior) | Persistent delocalized electrons despite disordered structure |
| Gas (Sublimation) | Standard pressure, ~3,650°C | Low (ionized plasma may conduct) | Direct solid-to-gas transition without melting |
Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Research with KINTEK
Understanding extreme material behaviors, like liquid carbon conductivity, requires reliable lab equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces, electrodes, and consumables designed for rigorous conditions. Whether you're exploring material science or developing advanced engineering systems, our products ensure accuracy and durability.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can support your high-temperature experiments and research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- Is graphite used as a refractory material? Discover Its Unmatched High-Temperature Performance
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- Is a graphite melting point high or low? Discover Its Extreme Thermal Resilience
- Why does graphite not melt? Unlocking the Secrets of Its Extreme Heat Resistance



















