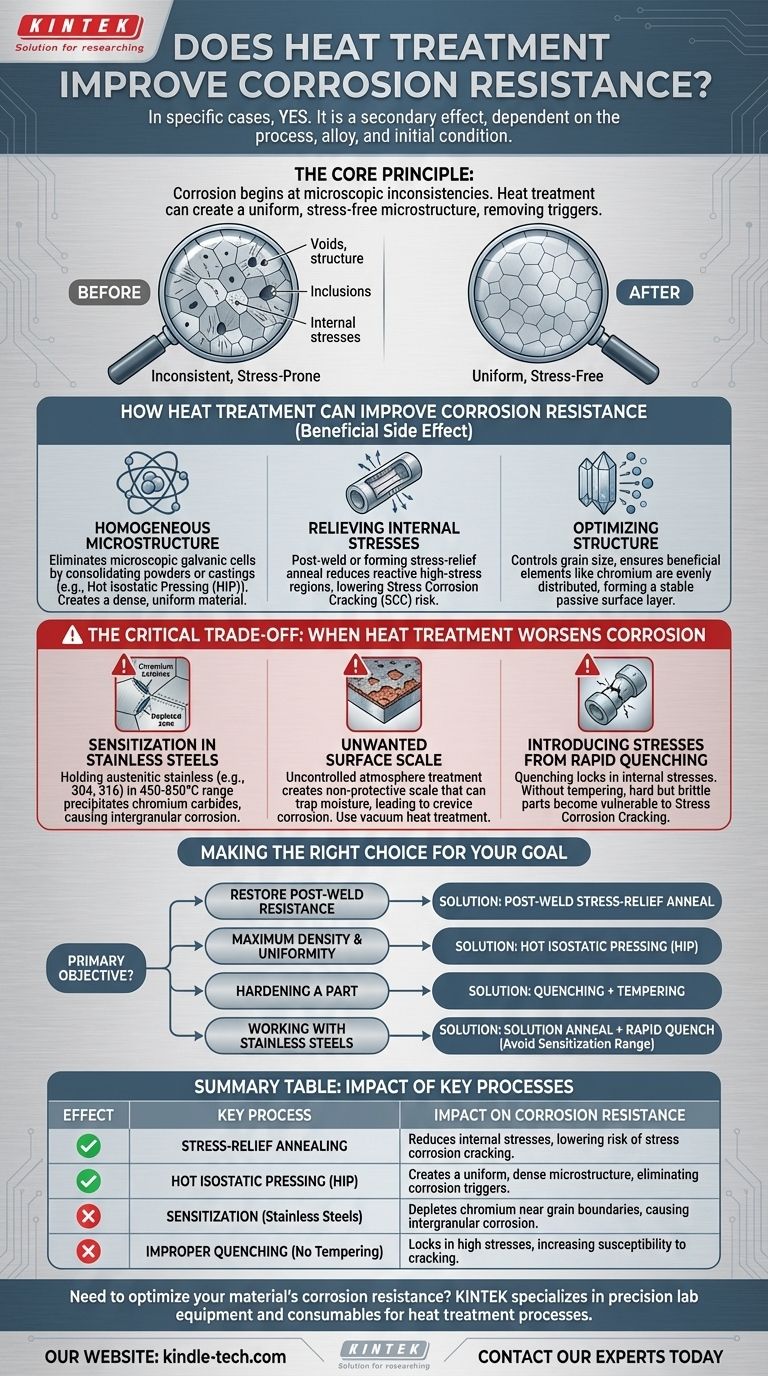
In certain, specific cases, yes—but it is not a universal guarantee. The effect of heat treatment on corrosion resistance is a secondary consequence of the primary goal, which is typically to alter a material's mechanical properties like hardness or ductility. Whether the treatment helps or hurts corrosion resistance depends entirely on the specific process, the type of alloy, and the material's condition before treatment.
The core principle is that corrosion often begins at microscopic inconsistencies within a material. Heat treatment improves corrosion resistance when it creates a more uniform, stress-free microstructure, thereby removing the trigger points for corrosion. Conversely, improper heat treatment can create new inconsistencies, making the material more susceptible to corrosion.

How Heat Treatment Can Improve Corrosion Resistance
The improvement is not a direct feature but a beneficial side effect of achieving specific metallurgical goals. The key mechanisms involve refining the material's internal structure.
Creating a Homogeneous Microstructure
Corrosion is an electrochemical process. In a non-uniform microstructure, different areas can have slightly different electrical potentials, creating microscopic galvanic cells that accelerate localized corrosion.
Processes like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) consolidate powders or castings under high heat and pressure, resulting in an extremely uniform and dense material, free of the voids and inconsistencies that invite corrosion.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Mechanical processes like welding, forming, or even aggressive machining introduce high levels of internal stress into a part. These high-stress regions are more chemically reactive and thus more vulnerable to corrosion, particularly a failure mode called Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC).
A stress-relief anneal is a heat treatment specifically designed to reduce these internal stresses without significantly changing other properties, thereby restoring or improving the material's inherent corrosion resistance.
Optimizing Crystalline and Phase Structure
Heat treatments are used to control a material's grain size and ensure the desired metallurgical phases are present. For some alloys, a finer, more uniform grain structure can lead to the formation of a more stable and protective passive layer on the surface.
Furthermore, some treatments ensure that beneficial elements (like chromium in stainless steel) are evenly distributed throughout the material, rather than being locked away in undesirable phases.
The Critical Trade-off: When Heat Treatment Worsens Corrosion
It is crucial to understand that the wrong heat treatment is often worse than no treatment at all. Several common scenarios can severely degrade a material's ability to resist corrosion.
The Danger of Sensitization in Stainless Steels
This is the classic example of heat treatment gone wrong. If austenitic stainless steels (like 304 or 316) are held for too long within a specific temperature range (roughly 450-850°C), chromium atoms will combine with carbon and precipitate as chromium carbides along the grain boundaries.
This process depletes the areas adjacent to the grain boundaries of the chromium needed for corrosion resistance, making the material "sensitized" and extremely susceptible to intergranular corrosion.
Creating Unwanted Surface Scale
Heat treating in an uncontrolled atmosphere (i.e., with oxygen present) will create an oxide layer, or "scale," on the material's surface. This scale can be porous, flaky, and non-protective.
Worse, it can trap moisture against the metal surface, creating a perfect environment for crevice corrosion to begin underneath the scale. This is why processes like vacuum heat treatment are often preferred, as they produce a clean, scale-free surface.
Introducing Stresses from Rapid Quenching
While rapid cooling (quenching) is essential for achieving high hardness in many steels, it can also lock in significant internal stresses.
If not followed by a proper tempering treatment to relieve these stresses, the hard but brittle and highly-stressed part becomes much more vulnerable to Stress Corrosion Cracking, even if its surface hardness is high.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use heat treatment must be driven by a clear understanding of your primary objective and the material you are working with.
- If your primary focus is restoring corrosion resistance after welding: A post-weld stress-relief anneal is often the correct choice to reduce internal stresses and homogenize the heat-affected zone.
- If your primary focus is maximum material density and uniformity: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is an advanced process that inherently produces a superior, corrosion-resistant microstructure.
- If your primary focus is hardening a part: You must pair quenching with a subsequent tempering cycle to reduce the risk of stress corrosion cracking.
- If you are working with stainless steels: You must use a proper solution anneal and rapid quench to avoid the sensitization temperature range and keep chromium in solution where it can protect the material.
Ultimately, leveraging heat treatment for corrosion control requires a precise understanding of your material's metallurgy and the demands of its service environment.
Summary Table:
| Effect of Heat Treatment | Key Process | Impact on Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ Improves | Stress-Relief Annealing | Reduces internal stresses, lowering risk of stress corrosion cracking. |
| ✅ Improves | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Creates a uniform, dense microstructure, eliminating corrosion triggers. |
| ❌ Worsens | Sensitization (in stainless steels) | Depletes chromium near grain boundaries, causing intergranular corrosion. |
| ❌ Worsens | Improper Quenching (without tempering) | Locks in high stresses, increasing susceptibility to cracking. |
Need to optimize your material's corrosion resistance? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for heat treatment processes, including furnaces and controlled atmosphere systems. Whether you're working with stainless steels, alloys, or specialized materials, our solutions help you achieve the right microstructure for superior performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision



















