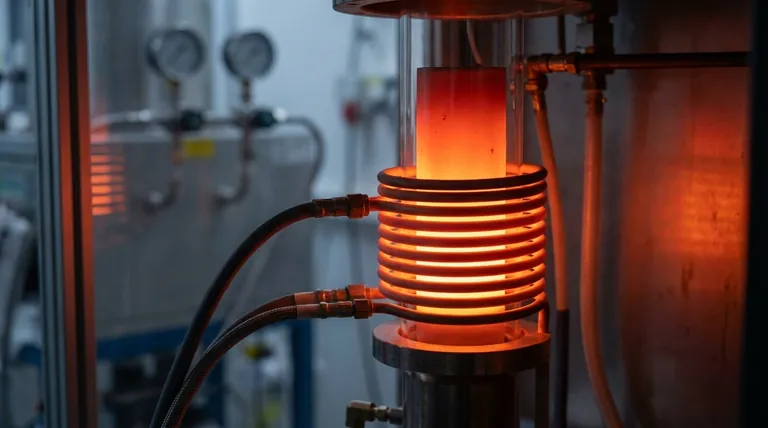
Yes, induction heating works exceptionally well on graphite. While often associated with metals, the core principle of induction heating applies to any electrically conductive material, and graphite is an effective conductor of electricity. It is widely used for applications like graphite crucibles and heating elements in high-temperature furnaces.
The key to understanding this is to separate the idea of "metal" from "electrically conductive." Induction heating induces electrical currents in a material; graphite's conductivity allows these currents to form, and its natural resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and efficiently.

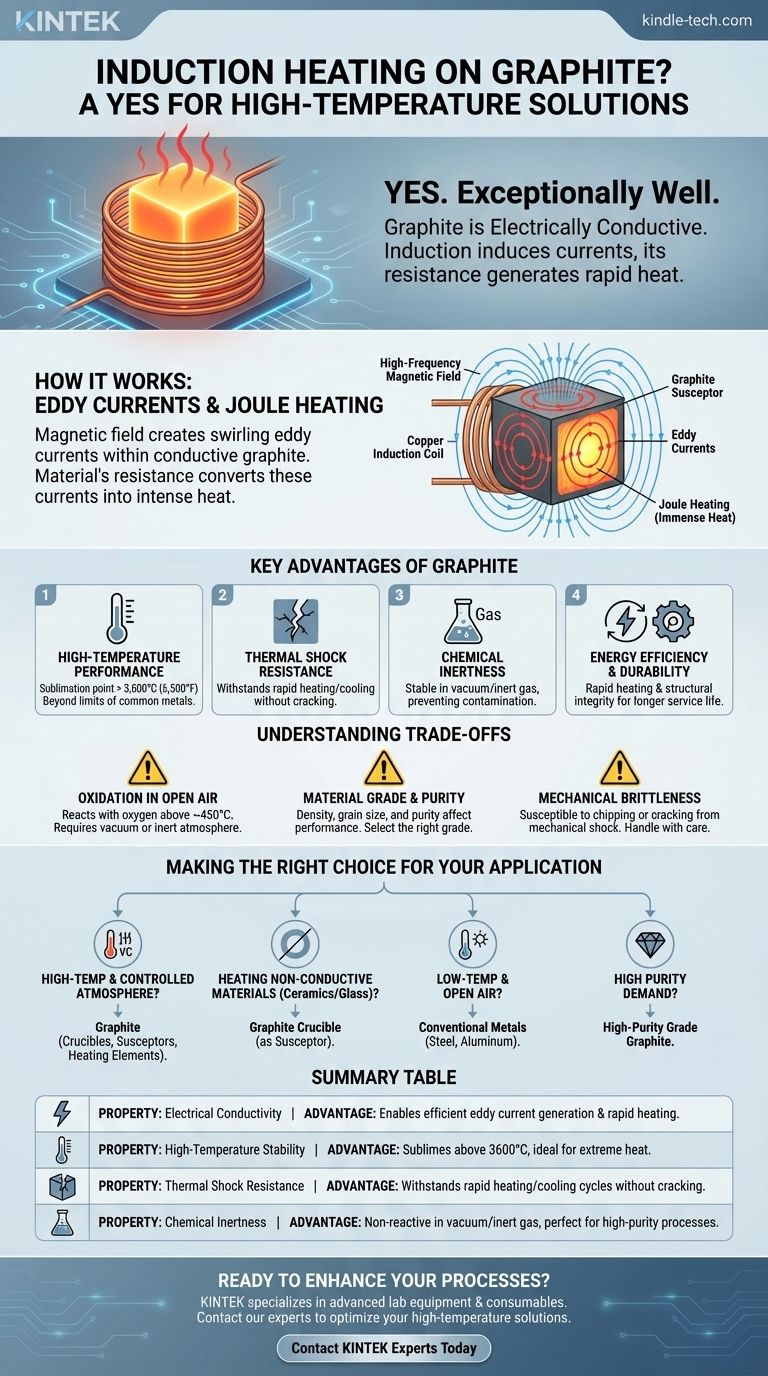
How Induction Heating Works with Graphite
Induction heating is a non-contact process. It uses a high-frequency alternating magnetic field, generated by a copper coil, to induce electrical currents within a target material.
The Principle of Electrical Conductivity
The magnetic field creates swirling electrical currents inside the material, known as eddy currents. The material's inherent resistance to the flow of these currents generates immense heat through a process called Joule heating.
Because graphite is electrically conductive, it readily supports the formation of these eddy currents. This allows it to be heated directly, quickly, and with precise control, without any physical contact from the induction coil.
Graphite as an Ideal Susceptor
In induction terminology, a material that is heated directly by the magnetic field is called a susceptor. Graphite is an excellent susceptor, not just because it's conductive, but because of its other unique properties that make it superior to many metals in specific applications.
Key Advantages of Using Graphite
Engineers and scientists choose graphite for induction heating for several critical reasons, especially in demanding, high-temperature environments.
High-Temperature Performance
Unlike most metals that melt, graphite has an extremely high sublimation point (over 3,600°C or 6,500°F). This allows it to be used in furnaces for processes that operate at temperatures far beyond the limits of common metals.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Graphite can withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking or failing. This makes it perfect for applications with quick heating and cooling cycles, increasing furnace turnaround times and productivity.
Chemical Inertness
In vacuum or inert gas environments, graphite is chemically stable and will not react with the materials being processed. This is critical in the semiconductor industry or when melting high-purity alloys where contamination from a metal crucible is unacceptable.
Energy Efficiency and Durability
Graphite's ability to heat up quickly translates to greater energy efficiency. Furthermore, its structural integrity at high temperatures gives it a longer service life compared to many alternative materials, increasing furnace uptime.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, graphite is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for successful implementation.
Oxidation in Open Air
Graphite's most significant limitation is its reaction with oxygen at high temperatures. When heated above approximately 450°C (842°F) in the presence of air, it will begin to oxidize, or burn away.
For this reason, graphite is almost always used for high-temperature induction applications inside a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to protect it.
Material Grade and Purity
Not all graphite is the same. The density, grain size, and purity of the graphite will affect its electrical conductivity, strength, and lifespan. Selecting the correct grade for your specific temperature and application is essential for predictable performance.
Mechanical Brittleness
Compared to metals, graphite is brittle. While it has high compressive strength, it can chip or crack if subjected to mechanical shock or mishandled. Care must be taken during the installation and loading of graphite components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing to use graphite depends entirely on the requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing in a controlled atmosphere: Graphite is an industry-standard and often superior choice for crucibles, susceptors, and heating elements.
- If your primary focus is heating non-conductive materials (like ceramics or glass): A graphite crucible is a perfect intermediary, acting as a clean, efficient susceptor that heats your material through conduction and radiation.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature heating in open air: A conventional metal like steel or aluminum is likely a more practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your application demands high purity: Ensure you use high-purity grade graphite to avoid contaminating the material you are heating.
When its properties are understood and leveraged correctly, graphite is an incredibly powerful and efficient material for induction heating applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage for Induction Heating |
|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Enables efficient eddy current generation and rapid heating. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Sublimes above 3600°C, ideal for extreme heat applications. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating/cooling cycles without cracking. |
| Chemical Inertness | Non-reactive in vacuum/inert gas, perfect for high-purity processes. |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with precision induction heating?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing robust solutions for your most demanding thermal applications. Our expertise in materials like graphite ensures you get the right components for superior performance, energy efficiency, and long-term durability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our graphite solutions can optimize your laboratory's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- At what temperature does graphite thermal decompose? The Critical Role of Atmosphere
- How does graphite react to heat? Unlocking Its Unique High-Temperature Strengths
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere



















