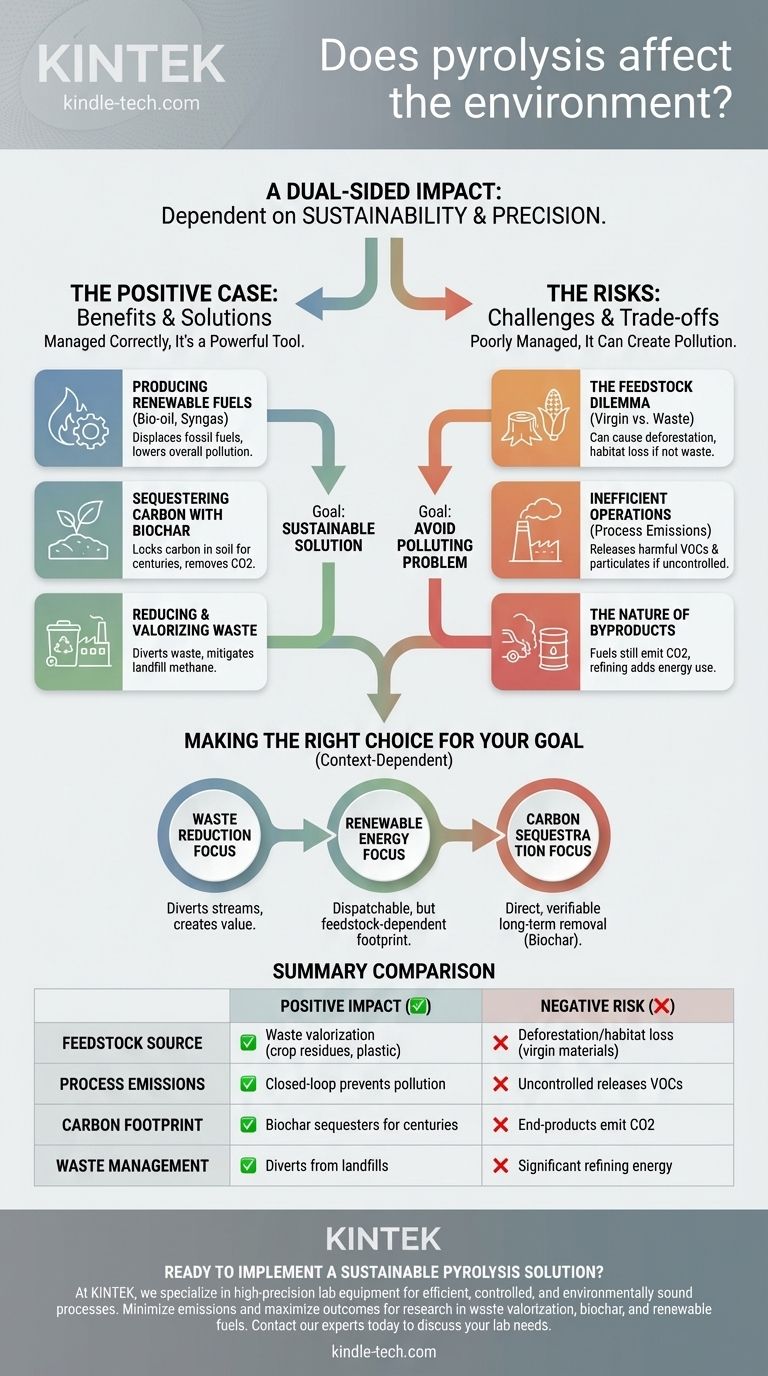
To be direct, pyrolysis has a significant and dual-sided impact on the environment. It is not inherently "good" or "bad." Instead, its environmental footprint is determined almost entirely by the sustainability of the raw materials used and the technical precision of the process itself. When managed correctly, it is a powerful tool for waste reduction and carbon sequestration; when managed poorly, it can create pollution and contribute to resource depletion.
The core takeaway is that the environmental performance of pyrolysis is a direct consequence of operational choices. The difference between a sustainable solution and a polluting problem lies in two areas: the source of the feedstock and the control over the process emissions.

The Positive Case: How Pyrolysis Can Benefit the Environment
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition, breaking down materials like biomass or plastic at high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment. This produces valuable outputs and offers several environmental advantages.
Producing Renewable Fuels
Pyrolysis converts waste streams into bio-oil and syngas (synthesis gas). These products can be used as fuel for energy generation, reducing the immediate need to burn fossil fuels. By displacing coal, oil, or natural gas, this process helps lower the overall pollution associated with traditional energy production.
Sequestering Carbon with Biochar
The solid byproduct of biomass pyrolysis is a stable, carbon-rich material called biochar. When added to soil, biochar does not easily decompose, effectively locking its carbon content away for centuries. This makes it a powerful tool for carbon sequestration, actively removing CO2 from the atmospheric cycle.
Reducing and Valorizing Waste
Pyrolysis provides a method to process challenging waste streams, including agricultural residues, wood waste, and even certain plastics and municipal solid waste. This process of waste valorization turns potential landfill burdens into useful products, mitigating methane emissions from dumps and extending the life of landfill sites.
Understanding the Environmental Risks and Trade-offs
The potential benefits of pyrolysis are compelling, but they are not guaranteed. Achieving a positive environmental outcome requires navigating significant operational and sourcing challenges.
The Feedstock Dilemma: Waste vs. Virgin Material
The single most important factor is the source of the material being processed, known as the feedstock. Using genuine waste products—like crop residues or non-recyclable plastics—is clearly beneficial.
However, if the demand for feedstock leads to the harvesting of virgin forests or the use of purpose-grown crops, the process can cause deforestation, habitat loss, and competition with food production. An environmentally sound pyrolysis operation must be built on a truly sustainable feedstock supply chain.
The Risk of Inefficient Operations
A poorly designed or operated pyrolysis unit can be a source of pollution. If the process is not properly sealed and controlled, harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulates, and other pollutants can escape into the atmosphere. The "clean" reputation of pyrolysis is entirely dependent on high-quality engineering and rigorous operational oversight.
The Nature of the Byproducts
While bio-oil and syngas can replace fossil fuels, they are not zero-emission energy sources. Burning them still releases CO2 and other pollutants, though they are often considered carbon-neutral if the feedstock is from a sustainable, biogenic source. The oil often requires significant refining before it can be used as a transport fuel, adding another layer of energy consumption to the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To assess the environmental impact of a pyrolysis project, you must first define its primary objective. The technology's suitability is entirely context-dependent.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Pyrolysis is an exceptionally effective technology for diverting specific waste streams from landfills and creating value.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: It provides a dispatchable (on-demand) energy source, but its true carbon footprint is determined by the sustainability of its feedstock.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: The production of stable biochar from waste biomass is one of the most direct and verifiable methods for long-term carbon removal.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a sophisticated tool whose environmental impact is defined not by the technology itself, but by the wisdom and integrity with which it is applied.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Positive Environmental Impact | Negative Environmental Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock Source | Uses waste (e.g., crop residues, non-recyclable plastic) for valorization. | Can drive deforestation/habitat loss if virgin materials are used. |
| Process Emissions | Closed-loop systems prevent pollution, producing renewable fuels (bio-oil, syngas). | Poorly controlled units can release harmful VOCs and particulates. |
| Carbon Footprint | Biochar byproduct sequesters carbon in soil for centuries. | End-product fuels still emit CO2 when burned, though often carbon-neutral. |
| Waste Management | Diverts waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions. | Requires significant energy for refining outputs, adding to lifecycle impact. |
Ready to implement a sustainable pyrolysis solution in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-precision lab equipment that ensures your pyrolysis processes are efficient, controlled, and environmentally sound. Whether you're researching waste valorization, biochar production, or renewable fuels, our reliable systems help you minimize emissions and maximize positive outcomes.
Let us help you turn your environmental goals into reality. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the right equipment for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















