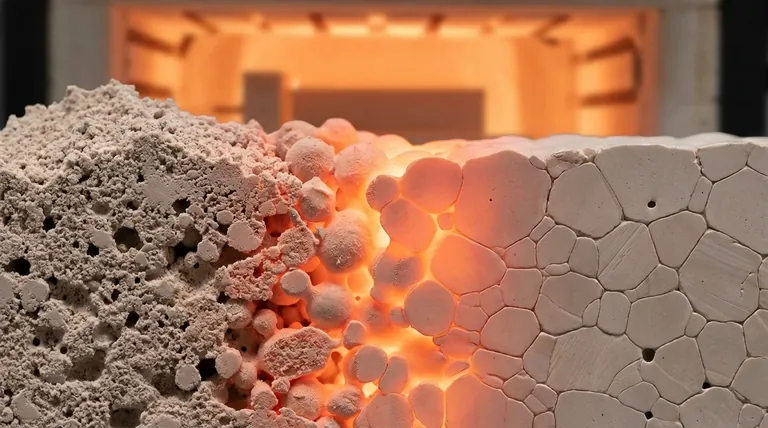
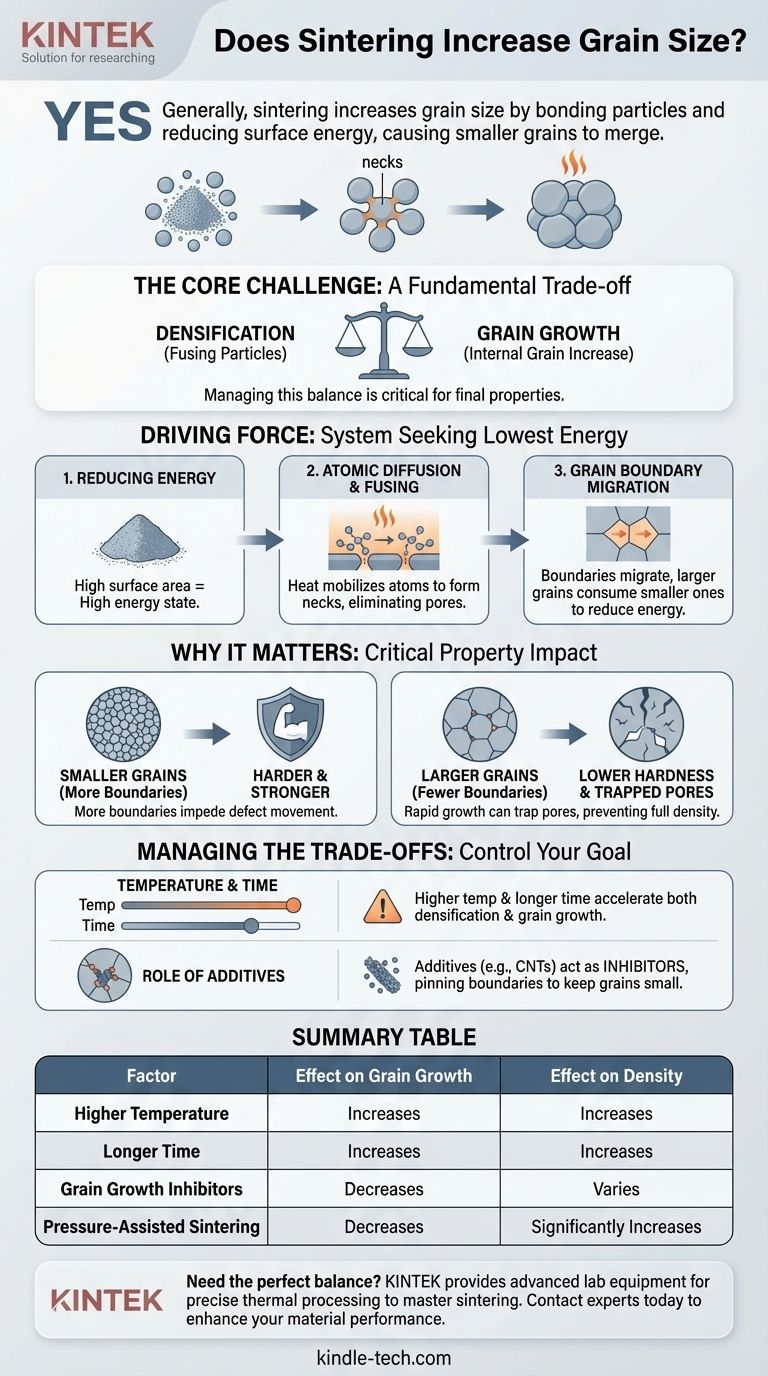
Yes, as a general rule, sintering increases grain size. This process, which bonds powder particles together using heat, is driven by the reduction of surface energy. As particles fuse, the boundaries between them migrate and merge, inevitably causing smaller grains to be consumed by larger ones.
The core challenge of sintering is a fundamental trade-off: the conditions required to increase a material's density by fusing particles also promote the growth of its internal grains. Managing this balance is critical to controlling the final properties of the material.

The Driving Force Behind Grain Growth
To understand why sintering causes grains to grow, we must look at the underlying physics of the process. It's fundamentally about a system seeking its lowest possible energy state.
### Reducing System Energy
A fine powder has an enormous amount of surface area relative to its volume. This high surface area represents a high-energy state. The sintering process, driven by thermal energy (heat), allows the material to reduce this total energy by eliminating that surface area.
### Atomic Diffusion and Particle Fusing
At high temperatures, atoms become mobile and diffuse across the surfaces of adjacent particles. This movement of material forms "necks" or bridges between particles, bonding them together and starting to eliminate the pores between them.
### Grain Boundary Migration
As particles fuse, the original boundaries that defined each individual particle begin to disappear. The remaining crystal structures, now called grains, have boundaries between them. To further reduce the system's energy, these grain boundaries migrate and coalesce, leading to an increase in the average grain size. Larger grains consume smaller ones because this reduces the total area of high-energy grain boundaries.
Why Grain Size Is a Critical Property
The size of the grains within a final, sintered part has a direct and significant impact on its mechanical performance. This is why controlling grain growth is not an academic exercise but a practical necessity.
### The Impact on Hardness and Strength
A material with smaller, finer grains has more grain boundaries. These boundaries act as obstacles that impede the movement of internal defects (dislocations), which is how a material deforms.
More boundaries mean it takes more force to deform the material, making it harder and stronger. As grain size increases, the number of boundaries decreases, which can lead to a reduction in hardness.
### The Connection to Final Density
The goal of sintering is to create a dense, solid part by eliminating porosity. While grain growth and densification happen simultaneously, they are competing processes.
If grain growth occurs too rapidly, it can isolate pores within the new, larger grains. These trapped pores are extremely difficult to remove, preventing the part from reaching full density.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The central conflict in any sintering process is balancing the desirable outcome of densification against the often undesirable side effect of grain growth.
### Temperature and Time
Higher sintering temperatures and longer holding times accelerate atomic diffusion, which is necessary for good densification. However, these same conditions also provide more energy and time for grain boundaries to migrate, leading to more significant grain growth.
### The Role of Additives
As seen with materials like carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in aluminum, additives can be used as grain growth inhibitors. These particles pin the grain boundaries, physically preventing them from migrating and keeping the final grain size small even during the thermal process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the relationship between densification and grain growth is the key to engineering materials with specific properties. Your approach should depend on your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and strength: Your goal is to suppress grain growth. Use the lowest effective sintering temperature, minimize time at temperature, and consider using grain growth inhibitors.
- If your primary focus is achieving near-full density: You must promote densification without allowing runaway grain growth. Advanced techniques like pressure-assisted sintering (e.g., Hot Pressing or SPS) can accelerate densification at lower temperatures, effectively winning the race against grain growth.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is about precisely controlling heat and pressure to navigate the inescapable link between particle consolidation and grain growth.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Grain Growth | Effect on Density |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Temperature | Increases | Increases |
| Longer Time | Increases | Increases |
| Grain Growth Inhibitors | Decreases | Varies |
| Pressure-Assisted Sintering | Decreases | Significantly Increases |
Need to achieve the perfect balance of density and grain size in your sintered materials? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Whether your goal is maximum strength through fine grains or near-full density, our solutions can help you master the sintering process. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and material performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?



















