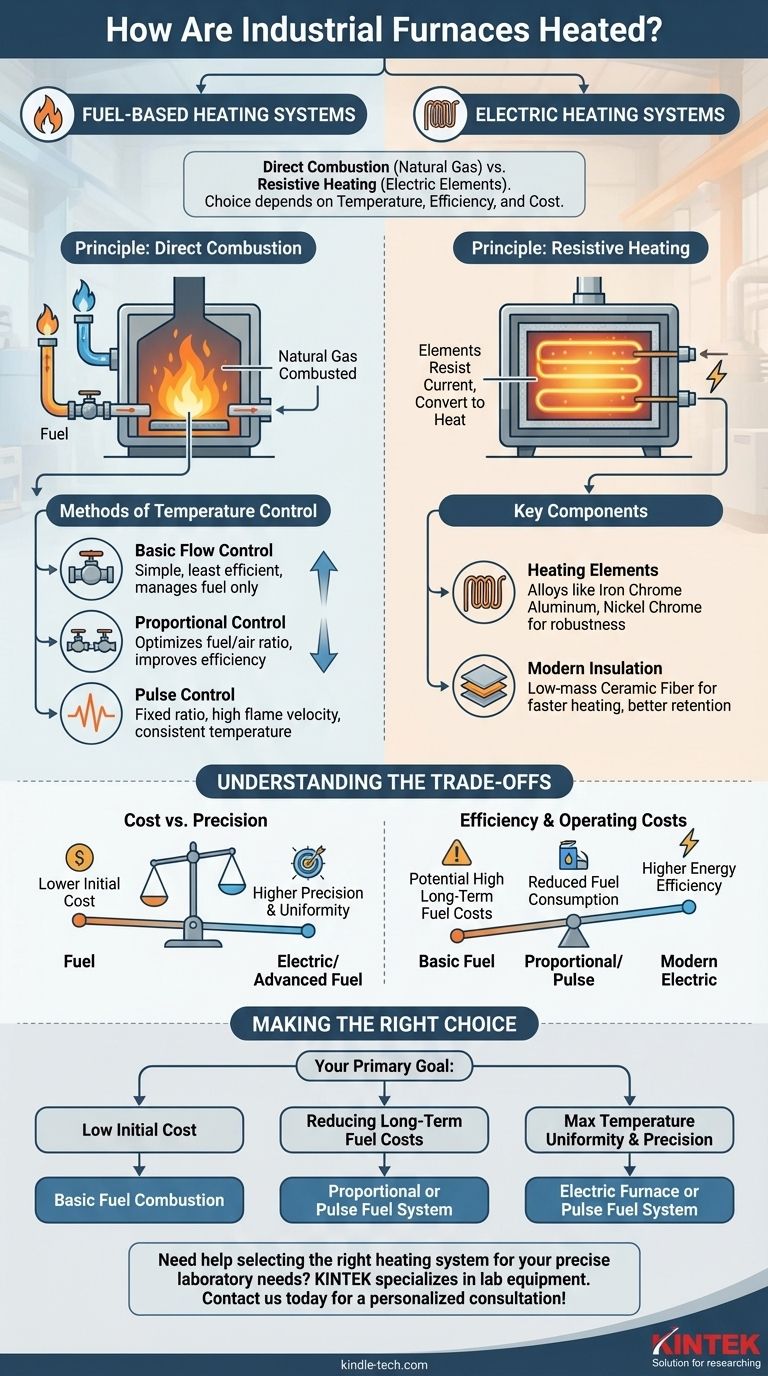
Industrial furnaces are heated using one of two primary methods: the direct combustion of fuel, such as natural gas, or the conversion of electricity into heat via resistive heating elements. The choice between these methods depends on the specific requirements for temperature control, efficiency, and cost for the industrial process.
The core decision in furnace heating isn't simply fuel versus electric. It is a strategic choice between the raw power and lower initial cost of combustion and the precision and thermal efficiency offered by modern electric systems.

Fuel-Based Heating Systems
Fuel combustion is a traditional and powerful method for generating high temperatures in an industrial setting. These systems work by directly burning fuel within the furnace's internal chamber.
The Principle of Direct Combustion
The most common fuel is natural gas, which is combusted to release thermal energy. This direct heating method is effective for achieving very high temperatures required for processes like melting metals or firing ceramics.
Methods of Temperature Control
The efficiency and consistency of a fuel furnace depend heavily on its control system.
- Basic Flow Control: This is the simplest and least expensive method, managing only the flow of fuel. However, it is the least efficient as it doesn't optimize the air-to-fuel mixture.
- Proportional Control: A more advanced system that controls both the fuel and air supply. By maintaining an optimal ratio, it significantly improves fuel efficiency and lowers long-term operating costs.
- Pulse Control: This sophisticated system maintains a fixed, highly efficient ratio of fuel and air. It achieves consistent temperature distribution by ensuring a high flame velocity throughout the entire process cycle.
Electric Heating Systems
Electric furnaces generate heat by passing an electrical current through a heating element, which resists the flow of electricity and converts that energy into heat.
How Electric Heat is Generated
This process relies on resistive heating elements. The design and material of these elements are critical to the furnace's performance, determining its maximum temperature and operational lifespan.
Common Heating Element Materials
For most industrial applications, heating elements are made from robust alloys like iron chrome aluminum or nickel chrome alloys. While precious metals are used in specialized research or glass manufacturing, their high cost makes them impractical for general industrial use.
The Role of Modern Insulation
The performance of electric furnaces has been greatly enhanced by advancements in insulation. Low-mass, vacuum-formed ceramic fiber insulation provides superior thermodynamic capacity, allowing the furnace to heat up faster and retain heat more effectively.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating method involves balancing cost, control, and operational needs. There is no single "best" solution for all applications.
Cost vs. Precision
Fuel-based systems, particularly those with basic controls, often have a lower initial investment cost. However, electric furnaces and advanced pulse-control fuel systems provide far greater temperature precision and uniformity, which is critical for sensitive processes.
Efficiency and Operating Costs
While basic fuel systems are cheap to install, their inefficiency can lead to high long-term fuel costs. Proportional and pulse control systems are designed specifically to reduce fuel consumption and lower operating expenses. Similarly, the improved thermodynamic properties of modern electric furnaces with advanced insulation lead to higher overall energy efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific industrial goal will determine the most suitable heating technology.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost: A basic, fuel-only combustion system is the most straightforward and inexpensive option.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term fuel costs: A proportional or pulse-controlled fuel system provides the best return through superior fuel efficiency.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity and precision: An electric furnace with modern ceramic insulation or a pulse-controlled fuel system will deliver the most consistent results.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating system is about aligning the technology's capabilities with the precise demands of your industrial application.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Combustion | High power, lower initial cost | High-temperature processes like metal melting |
| Electric Resistance | Superior temperature precision & uniformity | Processes requiring exact thermal control |
| Advanced Fuel Control | Optimized fuel efficiency (Proportional/Pulse) | Reducing long-term operating costs |
Need help selecting the right heating system for your industrial furnace? The choice between fuel and electric heating directly impacts your process efficiency, product quality, and operating costs. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving precise laboratory heating needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs to find the perfect solution for your application. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















