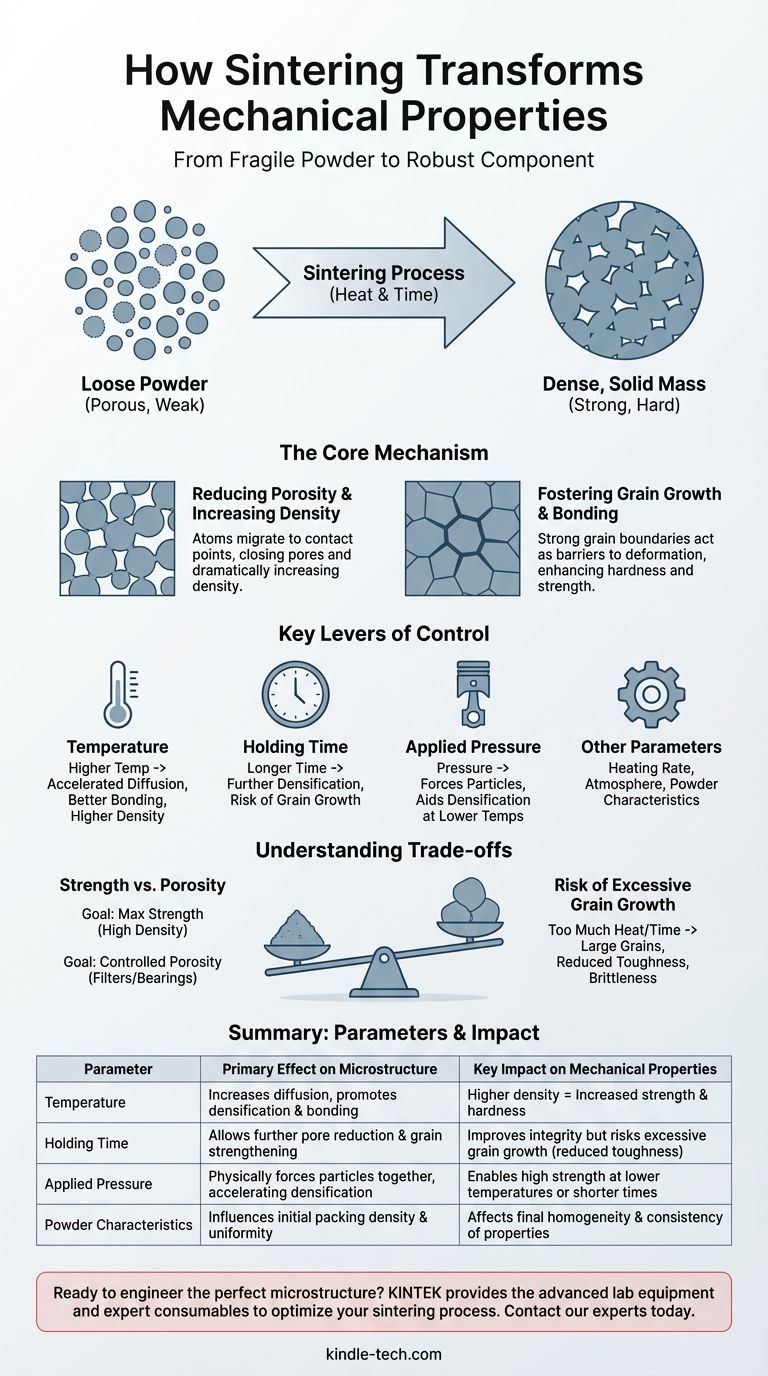
In short, sintering fundamentally enhances a material's mechanical properties by transforming a collection of loose particles into a dense, solid mass. This process increases strength, hardness, and durability by reducing internal voids and creating strong bonds between material grains, turning a fragile powder compact into a robust, engineered component.
Sintering is best understood not just as a heating process, but as a method of microstructural engineering. The final mechanical performance of a component is a direct consequence of controlling the sintering parameters—temperature, time, and pressure—to intentionally shape its internal grain structure and density.

The Core Mechanism: From Powder to Performance
Sintering creates a strong final part by fundamentally changing the material's internal structure on a microscopic level. The process uses thermal energy to drive diffusion, causing individual particles to bond together.
Reducing Porosity and Increasing Density
The most significant change during sintering is the reduction of porosity—the empty space between the initial powder particles.
As particles heat up, atoms migrate to the points of contact, forming "necks" that grow over time. This process pulls the particles closer together, shrinking the voids and dramatically increasing the overall density of the material.
A denser material is inherently stronger because forces are distributed across more solid matter, rather than being concentrated around the edges of pores, which act as stress risers and potential failure points.
Fostering Grain Growth and Bonding
Sintering doesn't just eliminate pores; it creates a cohesive network of interlocked grains. The atomic diffusion that closes pores also forms and strengthens the grain boundaries, the interfaces where different crystalline grains meet.
Strong, well-formed grain boundaries are critical for mechanical integrity. They act as barriers to dislocation movement, which is the primary mechanism of plastic deformation in crystalline materials. This directly results in increased hardness and strength.
The Key Levers of Control
To achieve a desired set of mechanical properties, you must precisely manipulate the key parameters of the sintering cycle. Each variable offers a different level of control over the final microstructure.
Sintering Temperature
Temperature is the most dominant factor. Higher temperatures provide more thermal energy, accelerating the atomic diffusion required for densification and grain bonding.
Generally, increasing the temperature leads to higher density and, therefore, improved mechanical properties like strength and wear resistance.
Holding Time
This is the duration the material is held at the peak sintering temperature. A longer holding time allows the diffusion process to continue, further reducing porosity and strengthening grain boundaries.
However, extended time also promotes grain growth, which can become a negative factor if not carefully managed.
Applied Pressure
In processes like hot pressing or spark plasma sintering (SPS), external pressure is applied. This pressure physically forces particles together, significantly aiding densification.
Pressure allows you to achieve high density at lower temperatures or in shorter times compared to pressureless sintering, offering another layer of control.
Other Critical Parameters
Factors like the heating rate, the composition of the furnace atmosphere, and even the size and shape of the initial powder all influence the final microstructure and resulting mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing sintering is not about maximizing every parameter; it's about finding the right balance to achieve a specific goal. Pushing for one property often comes at the expense of another.
Strength vs. Porosity
The relationship between temperature and properties is complex. For example, one sintering temperature might yield the highest compressive strength, while a different, lower temperature might produce the most desirable porosity and shrinkage for a specific application.
This demonstrates that the "best" parameters are entirely dependent on the component's intended function. A structural part requires maximum strength, while a ceramic filter requires controlled porosity.
The Risk of Excessive Grain Growth
While grain bonding is essential, excessive grain growth can be detrimental. If the temperature is too high or the holding time is too long, grains can become overly large.
Large grains can sometimes lead to reduced toughness or increased brittleness, as cracks have fewer grain boundaries to cross, allowing them to propagate more easily. The ideal microstructure often involves a fine, uniform grain size.
Optimizing Sintering for Your Goal
The right approach depends entirely on your primary engineering objective. Use these principles as a starting guide for process development.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: Aim for the highest possible density by optimizing temperature, time, and pressure to eliminate nearly all porosity.
- If your primary focus is controlled porosity (e.g., for filters or self-lubricating bearings): Use lower temperatures and shorter holding times to intentionally preserve a network of open pores while still achieving sufficient particle bonding for structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: You must carefully manage temperature and heating rates to control shrinkage, as aggressive sintering can lead to warping or deviation from design tolerances.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency and throughput: You may need to find a compromise, such as using faster heating rates or slightly lower temperatures, that achieves acceptable mechanical properties within a shorter, more economical process window.
By deliberately manipulating the variables of sintering, you transition from simply heating a material to precisely engineering its final performance.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Parameter | Primary Effect on Microstructure | Key Impact on Mechanical Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Increases atomic diffusion, promotes densification and grain bonding. | Higher density = Increased strength and hardness. |
| Holding Time | Allows for further pore reduction and grain boundary strengthening. | Improves integrity but risks excessive grain growth (reduced toughness). |
| Applied Pressure | Physically forces particles together, accelerating densification. | Enables high strength at lower temperatures or shorter times. |
| Powder Characteristics | Influences the initial packing density and uniformity of the green body. | Affects the final homogeneity and consistency of properties. |
Ready to engineer the perfect microstructure for your components?
The precise control of sintering parameters is key to achieving your target mechanical properties. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert consumables needed to master this vital process. Whether you're developing high-strength structural parts, porous filters, or cost-effective components, our solutions help you optimize density, grain size, and performance.
Let's discuss your sintering goals. Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a laboratory oven in biomass treatment? Ensure Accurate Dry-Basis Analysis
- What are the physical properties of pyrolysis? Unlocking the Complex Nature of Pyrolysis Oil
- Does sintering increase porosity? How to Control Porosity for Stronger Materials
- What is a cheaper alternative to injection moulding? Find the Right Process for Your Volume
- What is the temperature of a pyrolysis reactor? Master Thermal Control for Optimal Product Yields
- How does a high-speed homogenizer prepare m-BN and PNF dispersions? Achieve Uniform Molecular-Level Integration
- What are the uses of sintering method? A Guide to Fabricating High-Performance Parts
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations



















