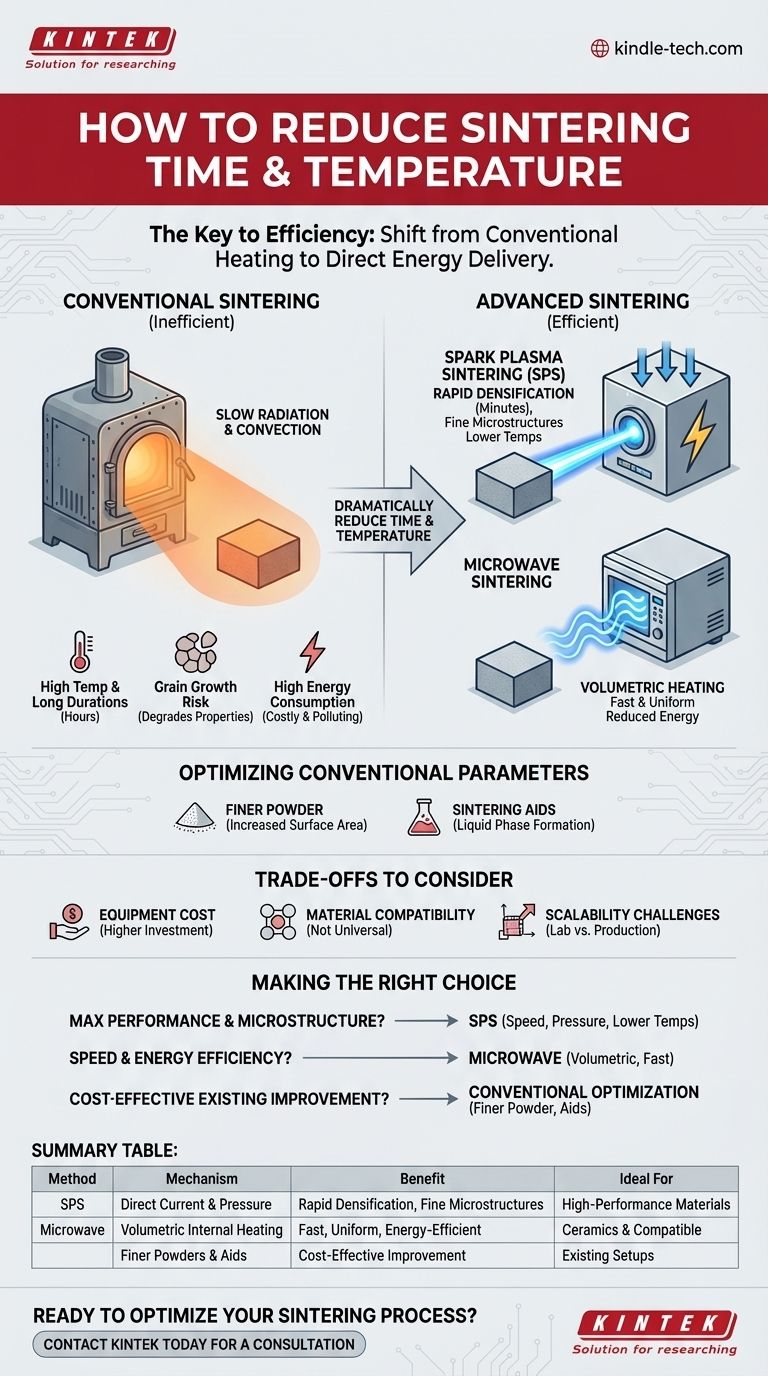
To fundamentally reduce the time and temperature of your sintering process, you must shift from conventional heating to more advanced methods. Techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) or Microwave Sintering deliver energy more directly to the material, enabling rapid densification at lower temperatures and in significantly shorter times, thereby preserving fine microstructures.
The core principle for improving sintering is not just about applying heat, but about how efficiently and directly that energy is delivered. Moving beyond slow, conventional furnace heating towards targeted methods dramatically reduces the required time and temperature, which is the key to preventing undesirable effects like grain growth.

The Limitations of Conventional Sintering
Before exploring solutions, it's crucial to understand why traditional methods are often inefficient. Conventional sintering relies on heating a furnace, which then slowly heats the material via radiation and convection.
High Temperatures and Long Durations
In a conventional furnace, the entire part must be heated from the outside in. This process requires holding the material at a very high temperature—often for many hours—to allow atomic diffusion to occur and densify the part.
The Problem of Grain Growth
This prolonged exposure to high heat is the primary cause of grain growth. As atoms diffuse to eliminate pores, they also rearrange to form larger, more stable crystal grains. Overly large grains can significantly degrade the mechanical properties, such as strength and hardness, of the final product.
High Energy Consumption
Heating a large furnace to extreme temperatures for hours is inherently energy-intensive. This results in high operational costs and a significant environmental footprint, especially in large-scale production.
Advanced Sintering: A More Direct Approach
Advanced methods overcome the limitations of conventional heating by delivering energy to the powder compact in a more direct and rapid manner.
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
SPS, also known as Field Assisted Sintering Technology (FAST), simultaneously applies both uniaxial pressure and a pulsed DC electrical current to the material.
The electrical current passes directly through the powder compact and the die, causing extremely rapid Joule heating. This, combined with the applied pressure, accelerates densification dramatically, often completing in minutes what would take a conventional furnace hours.
Microwave Sintering
This method uses microwave radiation to heat the material. Unlike conventional heating, microwaves can penetrate the material and heat it volumetrically—from the inside out.
This internal heating is much faster and more uniform, reducing thermal gradients and the total energy required. It is particularly effective for ceramic materials that couple well with microwave energy.
Optimizing Conventional Parameters
If you are limited to a conventional furnace, you can still improve the process by focusing on the material itself.
Using a finer starting powder significantly increases the surface area, which is the primary driving force for sintering. This can enable densification at lower temperatures or in shorter times.
Another strategy is to introduce sintering aids. These are small amounts of additives that can form a liquid phase at the sintering temperature, which dramatically accelerates the atomic transport needed for densification.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While advanced methods offer significant benefits, they are not a universal solution. It's critical to understand their limitations.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Both Spark Plasma Sintering and Microwave Sintering systems are significantly more expensive and complex to operate than a standard high-temperature furnace. This initial investment can be a major barrier.
Material Compatibility
Not all materials are suited for every method. Highly conductive metals can be difficult to heat effectively with microwaves. In SPS, the material must have some electrical conductivity, and there can be chemical reactions between the material and the graphite die at high temperatures.
Scalability Challenges
Advanced sintering techniques are often excellent at the laboratory scale but can face challenges when scaling up to produce large or complex industrial parts. The uniformity of pressure in SPS or microwave fields in large chambers becomes more difficult to control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your optimal strategy depends entirely on your primary objective, balancing performance, cost, and speed.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and fine microstructure: Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is often the superior choice due to its combination of speed, pressure, and lower temperatures.
- If your primary focus is speed and energy efficiency, especially for ceramics: Microwave Sintering offers a compelling advantage by heating the material volumetrically and rapidly.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective improvement of an existing process: Concentrate on optimizing your raw materials by using finer powders and introducing appropriate sintering aids.
Ultimately, optimizing your sintering process means choosing the most intelligent way to deliver energy to your material, not simply the most.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Mechanism | Primary Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Direct pulsed current & pressure | Rapid densification, fine microstructures | High-performance materials (metals, ceramics) |
| Microwave Sintering | Volumetric internal heating | Fast, energy-efficient, uniform heating | Ceramics & compatible materials |
| Conventional Optimization | Finer powders & sintering aids | Cost-effective improvement | Existing furnace setups |
Ready to optimize your sintering process and achieve superior results?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including sintering solutions tailored to your specific material and production goals. Our experts can help you determine the best approach—whether it's high-performance Spark Plasma Sintering, energy-efficient Microwave Sintering, or optimizing your conventional setup.
Contact us today to discuss how we can help you reduce sintering time and temperature, improve product quality, and lower energy costs. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature muffle furnace play in determining the VS content? Precision in Compost Analysis
- What does ash represent in a sample? A Key Indicator of Mineral Content and Purity
- What are the hazards of laboratory oven? Avoid Burns, Toxic Fumes, and Fire Risks
- What are the applications of microwave sintering? Faster, More Uniform Ceramic Processing
- How does a muffle furnace with a PID controller impact doped zinc oxide nanoparticles? Precise Synthesis Control
- What are muffle furnaces used for? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the function of an external heating high-temperature furnace in SCWG? Optimize Your Biomass Gasification Research
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace necessary for fluidized bed reactors? Ensure Peak Material Stability



















