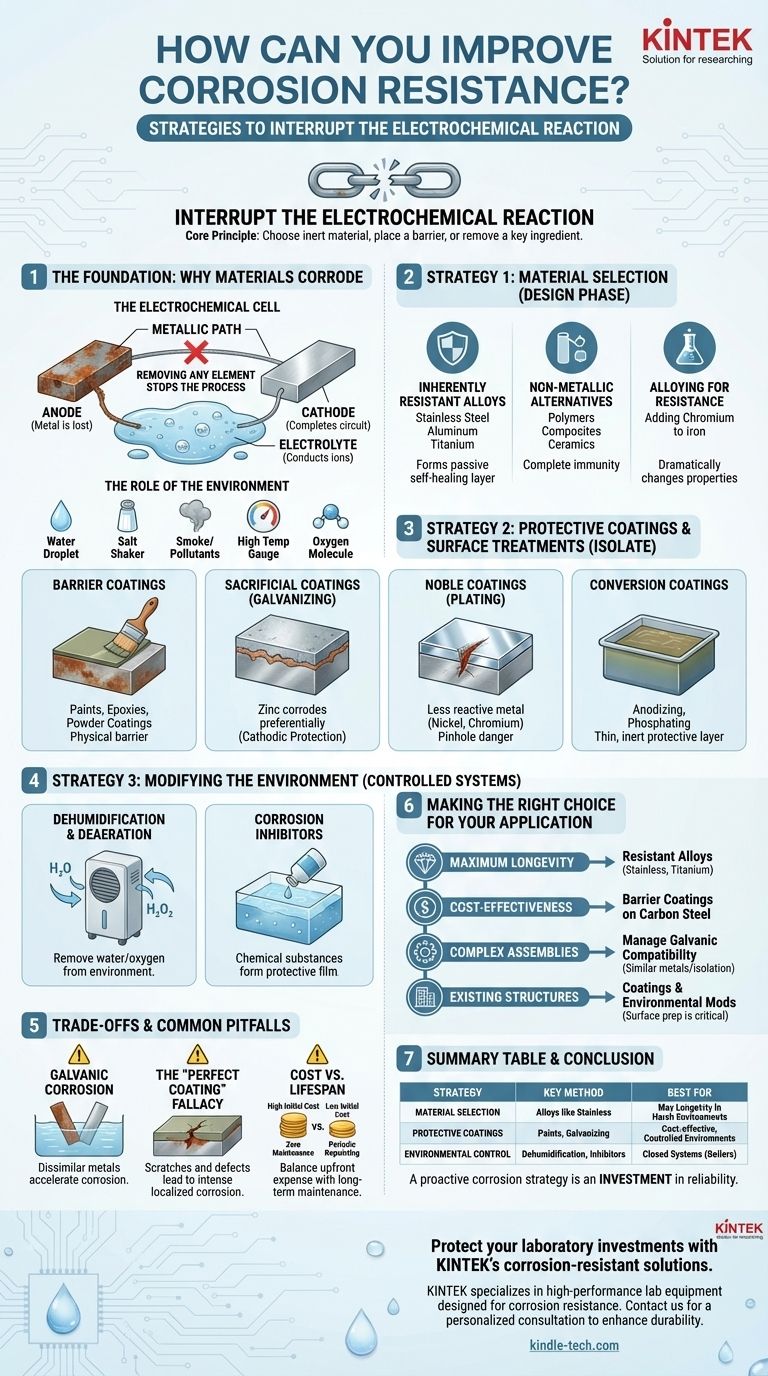
To improve corrosion resistance, the most effective strategies involve selecting an inherently resistant material, applying a protective coating to isolate the material from its environment, or actively modifying the environment to make it less corrosive. These approaches can be used individually or in combination to protect a component.
The core principle of corrosion control is to interrupt the electrochemical reaction that causes it. You can either choose a material that is naturally slow to react, place a barrier between the material and the corrosive environment, or change the environment itself to remove a key ingredient for the reaction.

The Foundation: Why Materials Corrode
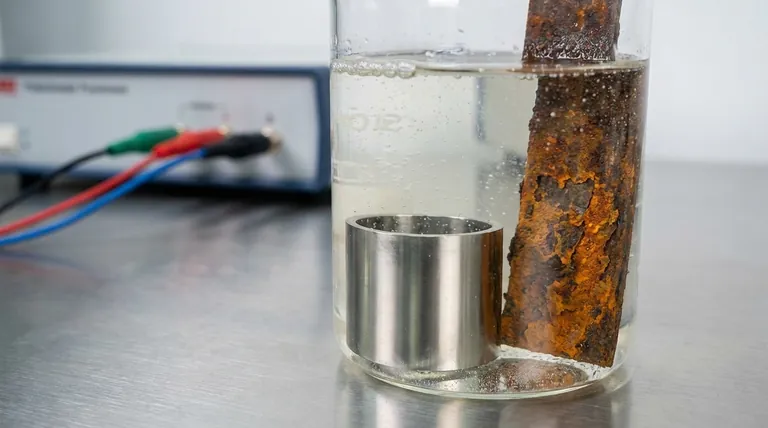
Before implementing a solution, it's crucial to understand that corrosion is fundamentally an electrochemical process. It is the natural tendency of refined metals to revert to a more stable chemical state, such as an oxide.
The Electrochemical Cell
For corrosion to occur, four elements must be present: an anode (where the metal is lost), a cathode (which completes the circuit), a metallic path between them, and an electrolyte (a fluid, like water, that can conduct ions).
Removing any one of these elements will stop the corrosion process. All corrosion control methods are based on this principle.
The Role of the Environment
The environment provides the electrolyte and often accelerates the reaction. Key factors include the presence of water, salt, industrial pollutants, high temperatures, and oxygen. A more aggressive environment demands a more robust protection strategy.
Strategy 1: Material Selection
The most fundamental and often most effective decision is made during the design phase by choosing the right material for the job.
Inherently Resistant Alloys
Some metals form a passive layer—a very thin, stable, and non-reactive film that protects the underlying material from the environment.
Stainless steels (with chromium), aluminum alloys, and titanium are prime examples. The passive layer self-heals if scratched, providing continuous protection.
Non-Metallic Alternatives
For many applications, polymers, composites, and ceramics offer complete immunity to electrochemical corrosion. Where mechanical requirements permit, they are an excellent choice for eliminating corrosion concerns entirely.
Alloying for Resistance
Small additions of other elements can dramatically change a metal's corrosion properties. The most famous example is adding chromium to iron to create stainless steel, which is vastly more resistant to rust than carbon steel.
Strategy 2: Protective Coatings & Surface Treatments
If the base material is susceptible to corrosion, the next strategy is to isolate it from the environment with a surface layer.
Barrier Coatings
This is the most common approach. Paints, epoxies, and powder coatings create a physical barrier that prevents the electrolyte from reaching the metal surface. Their effectiveness depends entirely on the quality of the application and their integrity over time.
Sacrificial Coatings (Galvanizing)
This clever method involves coating a base metal (like steel) with a more reactive metal (like zinc). Because zinc is more electrochemically active, it corrodes preferentially, "sacrificing" itself to protect the steel beneath it. This is a form of cathodic protection.
Noble Coatings (Plating)
Plating a material like steel with a less reactive (more noble) metal such as nickel or chromium provides excellent protection. However, if this coating is ever scratched or develops a pinhole, it can accelerate corrosion at the defect because the small area of exposed steel becomes a highly active anode.
Conversion Coatings
These are chemical treatments that convert the surface of the metal into a thin, inert protective layer. Anodizing on aluminum and phosphating on steel are common examples that improve corrosion resistance and provide an excellent primer for painting.
Strategy 3: Modifying the Environment
In controlled systems like industrial boilers or closed-loop cooling circuits, you can change the environment to make it less corrosive.
Dehumidification and Deaeration
Removing water or oxygen from the environment is highly effective. Storing sensitive parts in a low-humidity environment or removing dissolved oxygen from boiler feedwater are common industrial practices.
Using Corrosion Inhibitors
These are chemical substances added to the electrolyte that adsorb onto the metal surface, forming a protective film and disrupting the electrochemical reaction. They are widely used in automotive coolants, fuels, and industrial process water.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
An effective corrosion strategy requires awareness of potential failure points.
Galvanic Corrosion: The Danger of Dissimilar Metals
When two different metals are in electrical contact within an electrolyte, a galvanic cell is created. The less noble metal will corrode at an accelerated rate to protect the more noble metal. This is a critical consideration in any assembly using multiple types of fasteners and structural components.
The "Perfect Coating" Fallacy
No coating is permanent or perfect. Scratches, impacts, and degradation from UV light or chemicals can create breaches. This can lead to intense localized corrosion that undermines the coating and can be more damaging than uniform surface rust.
Cost vs. Lifespan
A highly resistant alloy like titanium may have a very high initial cost but require zero maintenance, making it cheaper over the 30-year life of a product. Conversely, a painted carbon steel component may be inexpensive upfront but require periodic repainting, driving up the total cost of ownership.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal strategy depends entirely on your specific goals, environment, and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum longevity in a harsh environment: Prioritize inherently resistant alloys like stainless steel, titanium, or high-performance polymers.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a controlled environment: A well-applied barrier coating on a standard carbon steel is often the most practical choice.
- If you are designing a complex assembly with multiple metals: You must carefully manage galvanic compatibility by selecting similar metals or electrically isolating the components with non-conductive washers and gaskets.
- If you need to protect an existing structure: Your options are limited to coatings and environmental modifications, making proper surface preparation and coating application absolutely critical.
A proactive corrosion strategy is not an expense, but an investment in the reliability and lifespan of your design.
Summary Table:
| Strategy | Key Method | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Using alloys like stainless steel, titanium | Maximum longevity in harsh environments |
| Protective Coatings | Applying paints, galvanizing, or plating | Cost-effective protection for controlled environments |
| Environmental Control | Dehumidification, corrosion inhibitors | Closed systems like boilers or cooling circuits |
Protect your laboratory investments with KINTEK's corrosion-resistant solutions. Corrosion can compromise your equipment's accuracy and lifespan, leading to costly downtime and replacements. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables designed with corrosion resistance in mind, ensuring reliable results and long-term value for your laboratory.
Let our experts help you select the right materials and coatings for your specific application. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and see how we can enhance the durability of your lab operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What products are manufactured with titanium? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Materials
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges
- What is titanium disadvantages and advantages? Weighing Performance vs. Cost for Your Project













