To determine if your furnace heating element is bad, you must first observe the system's performance. The most direct symptom, as noted in the reference, is your furnace blower running but pushing cool or room-temperature air through the vents. This immediately suggests a failure in the component responsible for generating heat.
A faulty heating element is a primary point of failure in electric furnaces. While cool air is the most common sign, a tripped circuit breaker or visible damage to the heating coils are also definitive indicators. A simple visual inspection is often enough, but a multimeter test provides absolute confirmation.
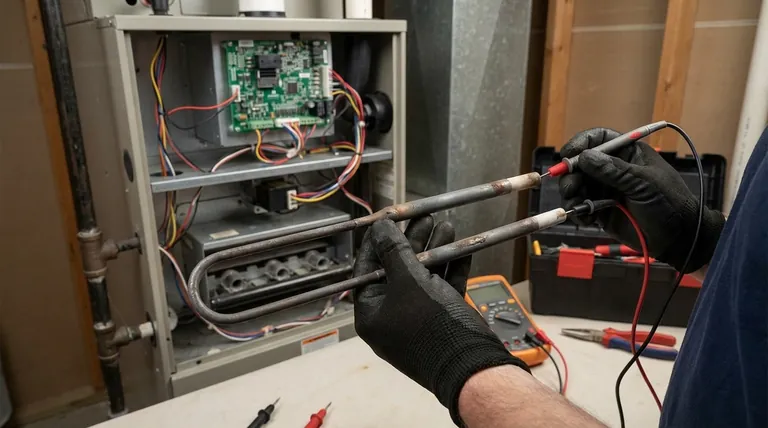
First, Confirm You Have an Electric Furnace
Before troubleshooting, it's critical to ensure your system is an electric furnace. Homeowners frequently confuse different furnace types, leading to incorrect diagnoses.
How an Electric Furnace Works
An electric furnace functions much like a large toaster or hair dryer. It uses one or more heating elements, which are resistive coils of wire. When electricity passes through these coils, they glow red-hot, and the furnace's blower fan pushes air over them to heat your home.
Gas vs. Electric Systems
A gas furnace does not have heating elements. It uses burners to ignite natural gas or propane inside a heat exchanger. If you have a gas line running to your furnace and see blue flames when it's operating, you have a gas furnace, and the problem lies elsewhere (such as the ignitor or flame sensor).
Key Symptoms of a Failing Heating Element
A bad element can manifest in several ways, ranging from subtle performance drops to a complete system shutdown.
The Blower Runs, But The Air is Cool
This is the classic symptom. The thermostat calls for heat, the blower fan engages, but the air coming from your vents never gets warm. This indicates the fan is working, but the elements are not heating up.
The Furnace Trips the Circuit Breaker
Heating elements can fail by "shorting out," where a break in the coil touches the metal frame. This creates a surge of electrical current that trips the breaker as a safety measure. If your furnace breaker trips immediately or shortly after a heating cycle begins, a bad element is a likely culprit.
Visible Damage to the Coils
Often, the proof of failure is visible. If you look at the heating element assembly, you may see clear signs of damage. Look for coils that are cracked, broken, bulging, or have obvious burn spots. A healthy element will look uniform and intact.
How to Safely Test the Heating Element
For a definitive diagnosis, you need to go beyond observing symptoms and perform a direct test. Safety is the absolute priority here.
Step 1: Turn Off All Power
Go to your home's main electrical panel and turn off the circuit breaker that powers your furnace. Electric furnaces operate on high voltage (240 volts), which is extremely dangerous. Never attempt to inspect or test internal components without cutting the power first.
Step 2: Perform a Visual Inspection
With the power off, remove the furnace's access panel. Locate the heating elements, which look like large springs or coils. Carefully inspect each one for the signs of damage mentioned above—breaks, cracks, or blistering. Often, a visual check is all you need to confirm the problem.
Step 3: Test for Continuity with a Multimeter
A multimeter provides the most conclusive evidence. Set it to the continuity setting (often marked with a sound wave icon). Touch one probe to each terminal of the heating element.
If the element is good, the multimeter will beep, indicating a complete, unbroken circuit. If the element is bad, the multimeter will remain silent, indicating a break in the coil.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Repair vs. Replace
Once you've confirmed a bad element, the next step is deciding how to proceed.
The Cost of a New Element
A replacement heating element is typically an affordable part, often costing less than a hundred dollars. This makes it a cost-effective repair compared to replacing other major furnace components.
The Complexity of the Repair
For an individual comfortable with basic electrical work, replacing a heating element is a manageable DIY project. It usually involves disconnecting a few wires, unfastening the old element, and securing the new one in its place.
When to Call a Professional
If you are not 100% confident in your ability to work safely with electricity, call a qualified HVAC technician. It is also wise to call a pro if multiple elements have failed simultaneously, as this could point to a larger underlying issue with a sequencer or limit switch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach should be guided by your comfort level with diagnostics and electrical work.
- If your primary focus is a quick diagnosis: Start by checking for cool air from the vents and then perform a power-off visual inspection for broken coils.
- If your primary focus is 100% certainty before buying parts: Use a multimeter to test for continuity after shutting off the power; this is the definitive electrical test.
- If your primary focus is safety and peace of mind: Contact a qualified HVAC technician, especially if you are at all uncomfortable working with high-voltage electricity.
Properly diagnosing the heating element empowers you to make a safe and cost-effective repair decision.
Summary Table:
| Symptom | What It Means | Next Step |
|---|---|---|
| Blower runs, but air is cool | Elements are not heating | Perform visual inspection |
| Circuit breaker trips repeatedly | Element may be shorted | Test for continuity with a multimeter |
| Visible cracks or breaks in coils | Physical failure of the element | Replace the faulty element |
Need a reliable replacement heating element or expert advice? KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including durable furnace components. Our team can help you find the right part to get your system running safely and efficiently. Contact our experts today for personalized support!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design



















