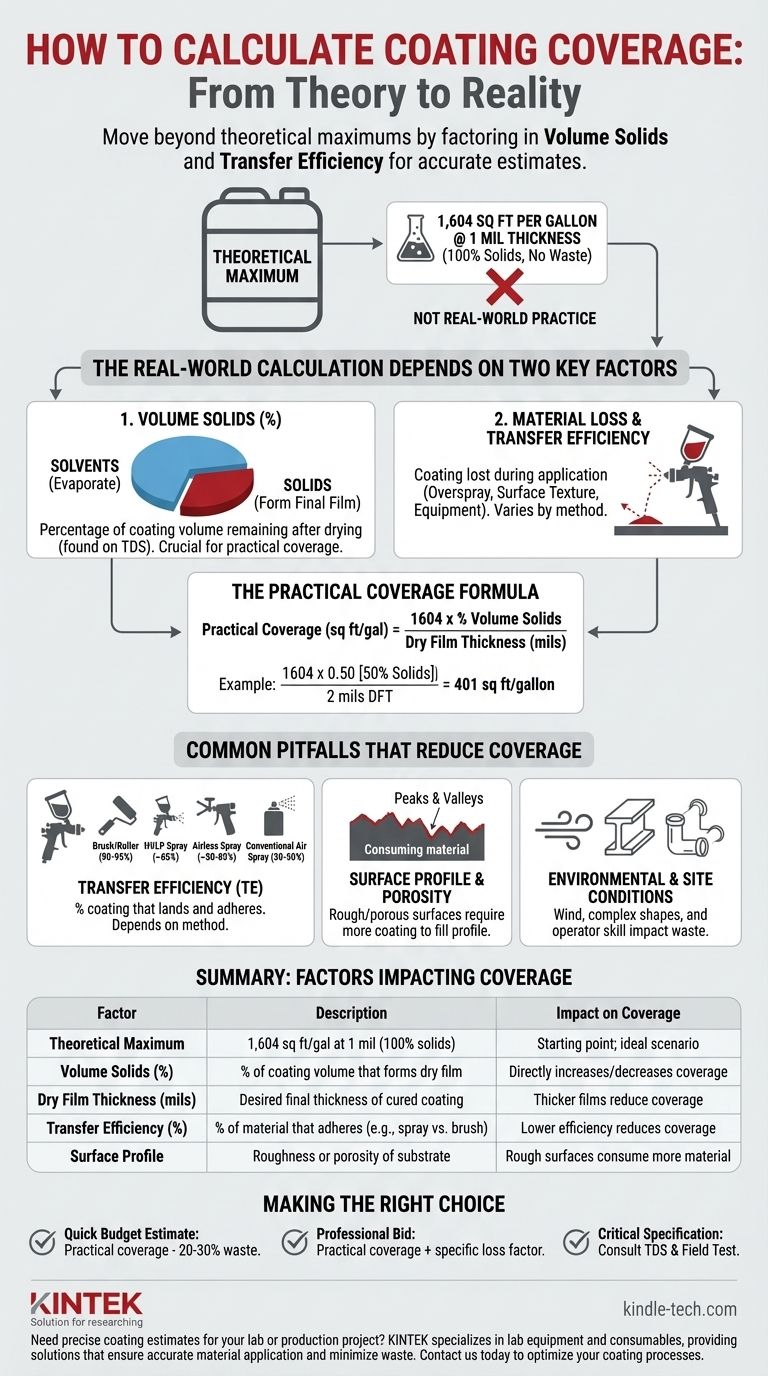
To calculate coating coverage, you must move beyond the theoretical maximum by adjusting for the coating's actual solids content and the inevitable material loss during application. The theoretical constant is 1,604 square feet per gallon at a 1 mil thickness, but this number assumes 100% of the material forms the final film with zero waste, which is never the case in practice. The true calculation depends on the coating's volume solids and the application's transfer efficiency.
Your coating's coverage is not determined by the volume in the can, but by the volume of solids that actually remain on the surface after drying. Factoring in material lost to overspray, surface texture, and equipment is essential for any accurate, real-world estimate.

The Foundation: Theoretical Spreading Rate
The "1,604 Square Foot Gallon"
The number 1,604 is a physical constant. It represents the total area that one U.S. gallon of liquid would cover if spread out to a uniform thickness of 1 mil (one-thousandth of an inch).
This figure is the absolute best-case scenario and serves as the starting point for all coverage calculations. It is a pure volume equation that assumes no part of the liquid evaporates or is lost.
From Theory to Practice: The Role of Volume Solids
What Are Volume Solids?
Liquid coatings are a mix of solids (the resins and pigments that form the protective film) and liquids (the solvents that keep the coating fluid for application). When the coating dries, the solvents evaporate, leaving only the solids behind.
Volume solids is the percentage of the coating's volume that will remain on the surface as the final, dry film. This number is the single most important factor for determining real-world coverage and is always found on the product's technical data sheet (TDS).
The Practical Coverage Formula
To find the realistic coverage, you adjust the theoretical maximum by the percentage of volume solids. You must also account for the desired Dry Film Thickness (DFT), which is the final thickness of the cured coating on the surface.
The formula for practical coverage is:
Practical Coverage (sq ft/gal) = (1604 x % Volume Solids) / Dry Film Thickness (in mils)
For example, a coating with 50% volume solids applied at a specified 2 mils DFT would have a practical coverage of (1604 x 0.50) / 2 = 401 sq ft/gallon.
Common Pitfalls That Reduce Coverage
Simply calculating practical coverage is not enough. In every project, a certain percentage of the coating is lost and never reaches the surface. You must account for these factors to determine how much material to purchase.
Transfer Efficiency (TE)
Transfer Efficiency is the percentage of coating that actually lands and adheres to the target surface. The rest is lost to overspray, drips, or material left in hoses and spray equipment.
The application method is the primary driver of TE. Typical estimates are:
- Brush and Roller: 90-95%
- HVLP Spray: ~65%
- Airless Spray: ~50-80% (varies with conditions)
- Conventional Air Spray: 30-50%
Surface Profile and Porosity
A rough, textured, or porous surface requires more coating than a smooth, sealed one. A significant amount of the initial material is used to fill the "peaks and valleys" of the surface profile before it can begin building the specified film thickness.
Environmental and Site Conditions
High wind is a major cause of material loss from overspray. Coating complex shapes, such as I-beams, piping, or intricate parts, will always result in more waste than coating a simple, flat wall. An operator's skill level also plays a significant role in minimizing waste.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use these principles to tailor your calculation to the specific needs of your project.
- If your primary focus is a quick budget estimate: Use the practical coverage formula based on volume solids and DFT, then reduce the result by 20-30% to account for typical waste.
- If your primary focus is bidding a professional job: You must calculate the practical coverage and then apply a specific loss factor based on the application method, surface profile, and job site complexity.
- If your primary focus is meeting a critical specification: Always consult the manufacturer's technical data sheet and perform a field test on a small area to confirm the actual consumption rate before ordering for the full project.
Understanding the difference between theoretical ideals and on-the-job realities is the key to accurate and cost-effective coating estimation.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Theoretical Maximum | 1,604 sq ft/gal at 1 mil (100% solids) | Starting point; ideal scenario |
| Volume Solids (%) | % of coating volume that forms the dry film | Directly increases/decreases coverage |
| Dry Film Thickness (mils) | Desired final thickness of the cured coating | Thicker films reduce coverage |
| Transfer Efficiency (%) | % of material that adheres to the surface (e.g., spray vs. brush) | Lower efficiency reduces coverage |
| Surface Profile | Roughness or porosity of the substrate | Rough surfaces consume more material |
Need precise coating estimates for your lab or production project? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions that ensure accurate material application and minimize waste. Our expertise helps laboratories and industrial clients achieve consistent, specification-compliant results. Contact us today to optimize your coating processes and improve efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer













