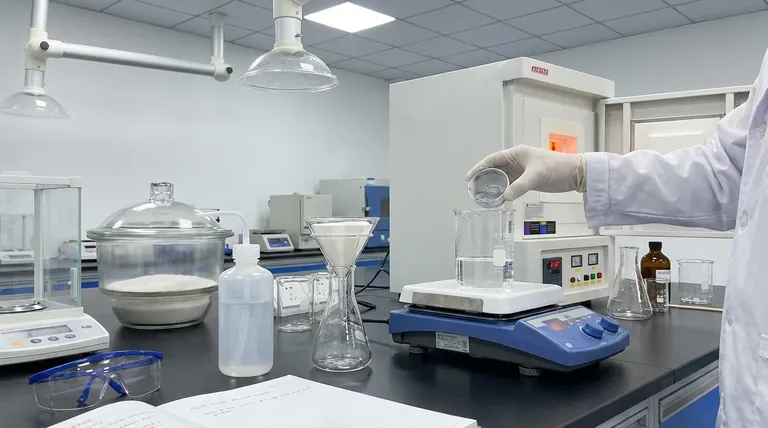
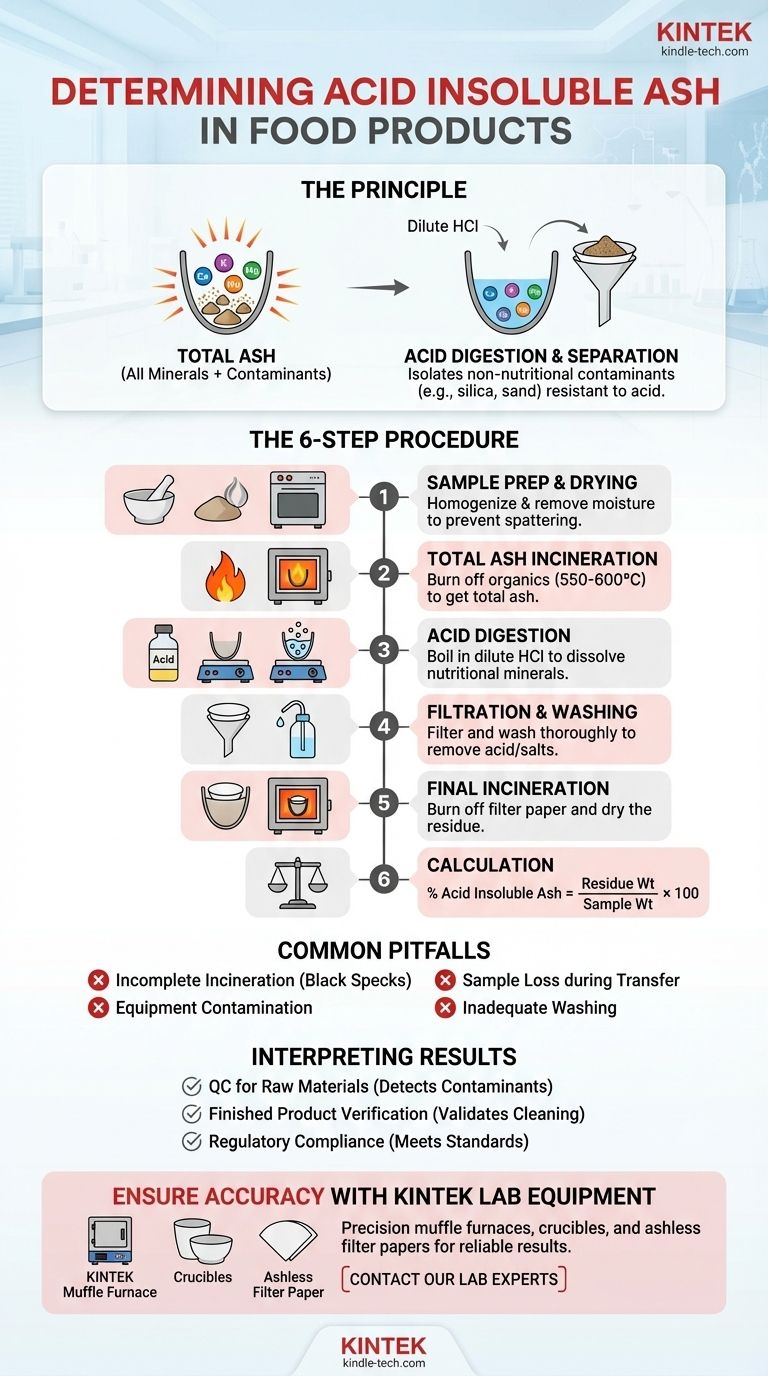
To determine acid insoluble ash, you must first incinerate a food sample to obtain its total ash content. This total ash is then boiled in a dilute hydrochloric acid solution. Any material that does not dissolve in the acid is considered acid insoluble ash; this residue is carefully filtered, washed, re-ignited in a furnace, and weighed to calculate the final percentage.
The determination of acid insoluble ash is not a measure of nutritional minerals but a crucial quality control test. It quantifies inorganic contaminants, primarily silica and sand, that should not be present in a finished food product.

The Principle Behind the Test
The acid insoluble ash test is a two-stage process designed to isolate specific types of inorganic matter. Understanding the distinction between the stages is key to interpreting the results.
Distinguishing Total Ash from Acid Insoluble Ash
Total ash represents the complete mineral content of a food. This is determined by burning off all organic matter (protein, fat, carbohydrates) in a high-temperature furnace, leaving only the inorganic minerals like calcium, potassium, magnesium, and sodium salts.
However, total ash also includes any undesirable inorganic material, such as soil, sand, or dust.
The acid insoluble ash test isolates this undesirable fraction. It separates the nutritionally relevant mineral salts, which readily dissolve in acid, from the acid-resistant contaminants.
Why Hydrochloric Acid is Used
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is used because it effectively dissolves the mineral salts that are naturally part of the food's composition (e.g., carbonates, phosphates).
Materials like silica (the primary component of sand and soil) are chemically stable and do not dissolve in dilute HCl. This chemical difference is the fundamental principle that allows for their separation and quantification.
The Step-by-Step Determination Procedure
The process requires precision at every stage to ensure an accurate and repeatable result. It builds upon the general method of dry ashing.
Step 1: Sample Preparation
A representative sample of the food product, typically between 1 and 10 grams, is required. The sample must be homogenous, often by grinding it into a fine powder.
Crucially, the sample must be thoroughly dried in an oven to remove all moisture. This prevents spattering during incineration, which would cause a loss of sample and an inaccurate result.
Step 2: Total Ash Incineration (Dry Ashing)
The dried sample is placed in a pre-weighed crucible and heated in a muffle furnace at high temperatures, usually between 550°C and 600°C.
This process continues until all organic matter has been burned away, leaving a white or grayish residue. This residue is the total ash. The crucible is then cooled in a desiccator and weighed.
Step 3: Acid Digestion
The crucible containing the total ash is treated with a measured volume of dilute hydrochloric acid (typically 10% HCl). The mixture is gently heated to a boil for approximately 5 minutes.
This step dissolves the nutritionally valuable mineral salts, leaving the acid-insoluble contaminants behind.
Step 4: Filtration and Washing
The contents of the crucible are filtered through a sheet of ashless filter paper. This special paper is designed to burn away completely, leaving no residue of its own.
The residue collected on the filter paper is washed thoroughly with hot, deionized water. This washing is critical to remove all traces of the acid and any dissolved salts, ensuring only the insoluble material remains.
Step 5: Final Incineration and Weighing
The filter paper containing the washed residue is carefully transferred back into the original crucible. The crucible is heated again in the muffle furnace to burn off the filter paper and dry the residue completely.
After incineration, the crucible is cooled in a desiccator to prevent moisture absorption and then weighed precisely. The final weight represents the acid insoluble ash.
Step 6: Calculation
The percentage of acid insoluble ash is calculated using a simple formula:
% Acid Insoluble Ash = (Weight of Acid Insoluble Residue / Initial Weight of Sample) × 100
Common Pitfalls and Sources of Error
Achieving an accurate result depends on meticulous laboratory practice. Awareness of common errors is essential for reliable analysis.
Incomplete Incineration
If the initial ashing step is not complete, black specks of carbon will remain in the total ash. This unburned organic matter will be carried through the process and will falsely inflate the final weight of the acid insoluble ash.
Contamination from Equipment
Crucibles, glassware, and even the surrounding lab environment can introduce contaminants. All equipment must be scrupulously clean. Crucibles should be pre-heated to a constant weight before the sample is added to burn off any impurities.
Loss During Transfer
Physical loss of the sample is a significant source of error. This can happen during the initial weighing, if the sample spatters during heating, or when transferring the residue during the filtration step. Each transfer must be done with extreme care.
Inadequate Washing
If the residue on the filter paper is not washed completely, soluble salts or acid will remain. These will contribute to the final weight, leading to an overestimation of the acid insoluble ash content.
Making Sense of the Results
The final percentage of acid insoluble ash is a direct and powerful indicator of product purity and processing efficacy.
- If your primary focus is quality control for raw materials: A high result indicates contaminated ingredients (e.g., soil on spices, sand in grains), which may need to be rejected or subjected to further cleaning.
- If your primary focus is finished product verification: This test validates the effectiveness of your cleaning and processing steps (like washing vegetables or sifting flour), ensuring external contaminants have been removed.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance: Many food standards, particularly for spices, herbs, and certain plant-based products, have maximum permissible limits for acid insoluble ash that must be met.
Ultimately, mastering this analysis empowers you to safeguard product integrity and ensure consumer safety.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sample Preparation & Drying | Ensure homogeneity and prevent spattering during incineration. |
| 2 | Total Ash Incineration | Burn off organic matter to isolate total mineral content. |
| 3 | Acid Digestion | Dissolve nutritional minerals, leaving acid-insoluble contaminants. |
| 4 | Filtration & Washing | Isolate residue and remove all traces of acid and dissolved salts. |
| 5 | Final Incineration & Weighing | Burn off filter paper and obtain the final weight of the insoluble residue. |
| 6 | Calculation | Determine the percentage of acid insoluble ash relative to the initial sample weight. |
Ensure the accuracy and reliability of your food quality control tests with KINTEK's precision lab equipment. Our muffle furnaces, crucibles, and ashless filter papers are designed to deliver consistent, contamination-free results for acid insoluble ash determination and other critical analyses.
Whether you're testing raw materials or verifying finished product purity, KINTEK provides the durable, high-performance tools you need to meet regulatory standards and safeguard your brand's integrity.
Contact our lab experts today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What does a lab muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in laboratory? Master Precise High-Temp Heating
- What role does a high-temperature muffle furnace play in the production of inorganic metal oxide nanofibers?
- What is the purpose of a muffle? To Ensure Pure, Contamination-Free Heating in Your Lab
- Why is a high-temperature box-type resistance furnace essential for LCF/LCFA membranes? Achieve 100% Gas-Tight Sintering
- What are the applications of dry ashing? A Guide to Precise Mineral Analysis
- What is sintering in a muffle furnace? Master Precision Thermal Processing for Advanced Materials
- What is the function of a high-stability muffle furnace in 8YSZ pretreatment? Optimize Your Ceramic Raw Materials



















