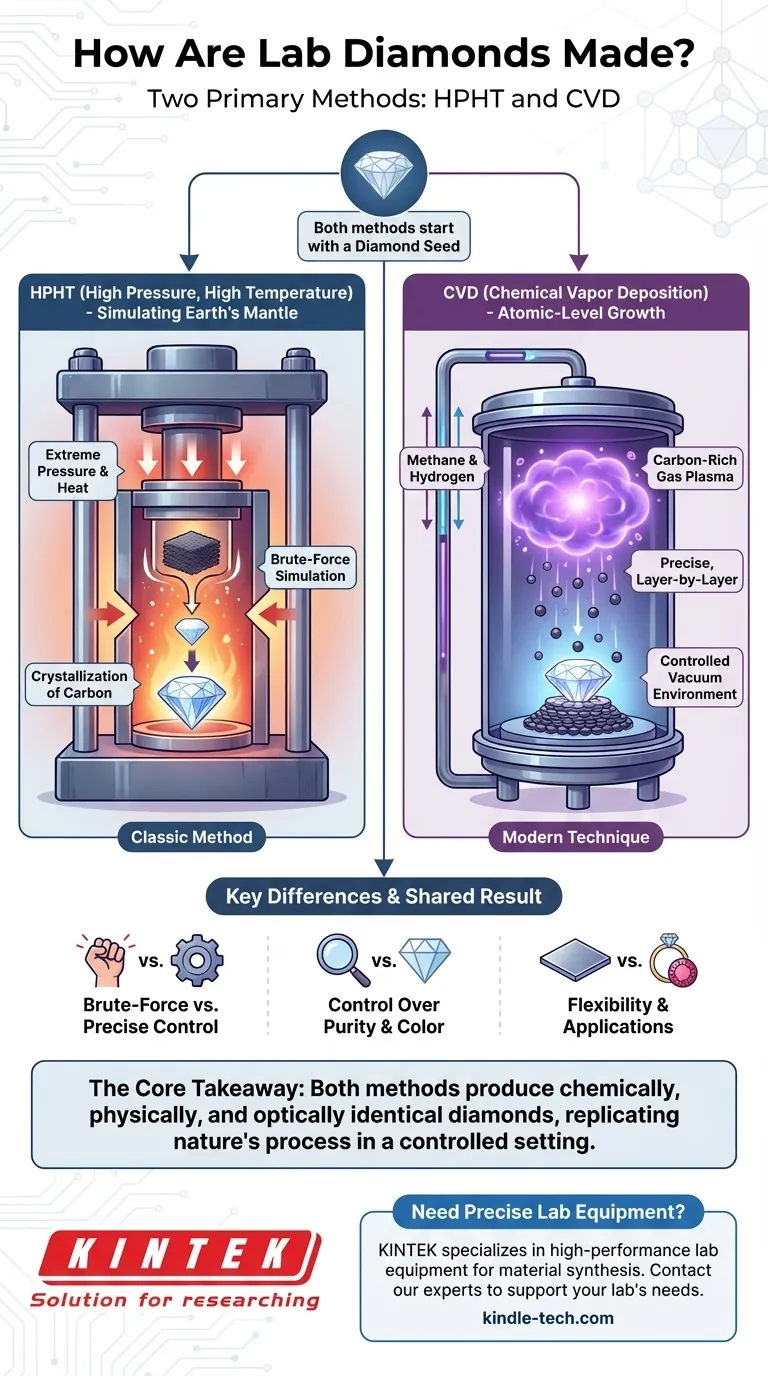
Lab-grown diamonds are created using one of two primary methods. The first is High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT), which mimics the intense conditions deep within the Earth where natural diamonds form. The second, more recent method is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which grows a diamond atom-by-atom from a carbon-rich gas in a controlled vacuum chamber.
The core takeaway is that while the methods differ, both HPHT and CVD produce diamonds that are chemically, physically, and optically identical to mined diamonds. The choice of method simply reflects a different approach to replicating nature's process in an accelerated, controlled laboratory setting.
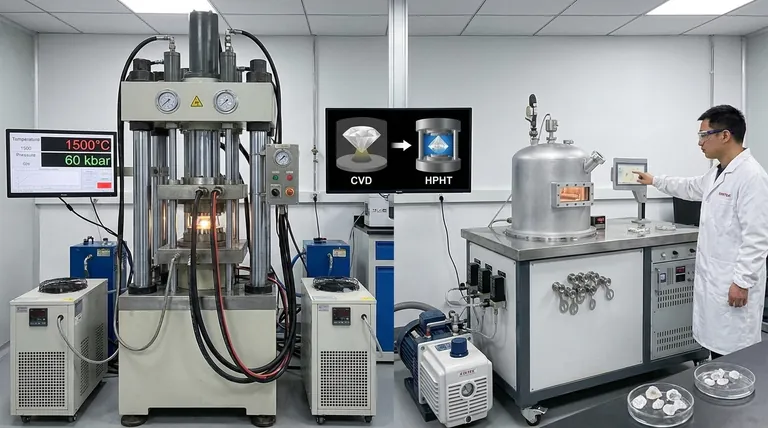

The Two Paths to a Lab-Grown Diamond
Both methods for creating a diamond begin with the same fundamental component: a diamond seed. This is a microscopic slice of a previously grown diamond that acts as the foundational template for new carbon atoms to bond to.
Method 1: High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT)
The HPHT method is the original process, designed to directly replicate the natural diamond-forming conditions found in the Earth's mantle.
A small diamond seed is placed into a chamber with a source of pure carbon, such as graphite.
The chamber is then subjected to immense pressures and extremely high temperatures. This intense environment dissolves the carbon source, allowing it to crystallize onto the diamond seed, growing a new, larger diamond.
Method 2: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
The CVD method is a more recent innovation that builds a diamond in layers, representing a form of atomic-level additive manufacturing.
A diamond seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The chamber is then filled with a mixture of carbon-containing gases, primarily methane and hydrogen.
These gases are heated to extreme temperatures, often with microwaves, until they break down into a plasma. This process frees carbon atoms, which then "rain" down and deposit onto the diamond seed, slowly building up the crystal layer by layer.
Understanding the Key Differences
While both processes result in a genuine diamond, their foundational principles and the control they offer are distinct. The method used can influence the characteristics of the final stone.
Simulating the Mantle vs. Building Atom by Atom
HPHT is a brute-force simulation of nature. It uses overwhelming pressure and heat to force carbon into a diamond crystal structure.
CVD, in contrast, is a more precise, bottom-up process. It offers greater control by carefully managing the chemical environment where the diamond grows one atomic layer at a time.
Control Over Purity and Color
The CVD process allows for more granular control over the chemical impurities within the diamond.
Historically, removing nitrogen—which causes a yellow tint—was a challenge. Modern CVD techniques allow for the creation of exceptionally pure and colorless diamonds by maintaining a pristine gas environment during growth.
Flexibility and Applications
The CVD method's flexibility makes it suitable for growing diamonds over large, flat areas.
This capability is essential not just for jewelry but for industrial and technological applications, such as creating durable coatings, high-performance optics, and advanced electronic components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, neither method is inherently "better" for producing a gemstone; they are simply different technological pathways to the same result. Both are capable of producing flawless, high-quality diamonds.
- If your primary focus is on the classic method: The HPHT process is the original technique that most directly mimics the intense pressure and heat of natural diamond formation.
- If your primary focus is on modern technology: The CVD process represents a more recent, high-tech approach that offers precise atomic control and builds the diamond layer by layer.
Regardless of the manufacturing path taken, the result is a stone with the same brilliance, durability, and chemical makeup as a diamond sourced from the Earth.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process Description | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature) | Mimics Earth's mantle using extreme pressure & heat to crystallize carbon onto a seed. | Brute-force simulation; classic method. |
| CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | Uses a carbon-rich gas in a vacuum chamber to grow a diamond atom-by-atom onto a seed. | Precise, layer-by-layer growth; modern technique. |
Need precise, reliable equipment for your lab's material synthesis or research? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including systems for advanced material growth and analysis. Whether you're exploring diamond synthesis or other advanced materials, our expertise can help you achieve accurate and repeatable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating



















