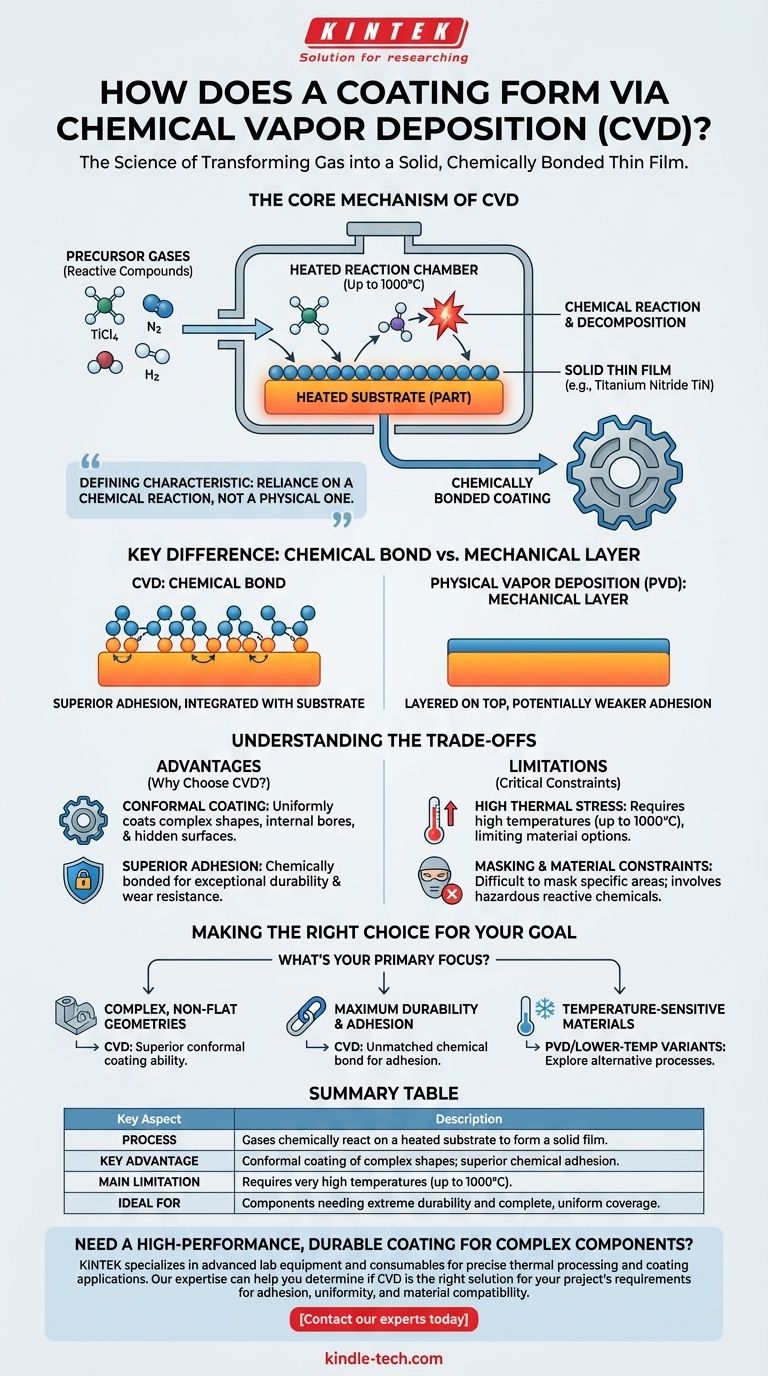
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) forms a coating by introducing reactive precursor gases into a chamber containing a heated part, or substrate. These gases decompose and react on the hot surface, creating a chemical reaction that deposits a new, solid thin film directly onto the part. This process creates a coating that is chemically bonded to the substrate, not just layered on top.
The defining characteristic of CVD is its reliance on a chemical reaction, not a physical one. By transforming gases into a solid film on a heated surface, CVD creates exceptionally adherent and uniform coatings, but the high temperatures required are a critical constraint that dictates which materials can be treated.

The Core Mechanism of CVD: From Gas to Solid
To truly understand CVD, you must visualize it as a controlled chemical manufacturing process happening on a microscopic scale, where the final product is a thin film integrated with the part's surface.
The Essential Ingredients: Substrate and Precursors
The process begins with two key components: the substrate, which is the part to be coated, and precursor gases.
These are not inert gases; they are specific, reactive chemical compounds in a gaseous state. For example, to create a Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating, precursors like Titanium Tetrachloride (TiCl4), Nitrogen (N2), and Hydrogen (H2) are used.
The Reaction Chamber: A Controlled Environment
The entire process takes place inside a sealed CVD reactor. This chamber is typically held under vacuum to remove any contaminants that could interfere with the reaction.
A sophisticated gas delivery system introduces the precise mixture of precursor gases into the chamber. The environment must be meticulously controlled to achieve the desired coating properties.
The Critical Role of Heat
Heat is the catalyst for the entire CVD process. The substrate is heated to very high temperatures, often up to 1000°C.
This intense thermal energy provides the activation energy needed for the precursor gases to break apart and react with each other and with the heated surface of the substrate.
The Deposition and Chemical Bond
Once the gases react on the hot substrate, they transform from a gaseous state into a solid one, depositing a thin, dense film.
Crucially, this is not a mechanical layer sitting on top of the surface. It is a chemical bond, where the atoms of the coating are directly integrated with the atoms of the substrate. This fundamental characteristic is what gives CVD coatings their superior adhesion.
Understanding the Trade-offs of the CVD Process
No single technology is a universal solution. The chemical nature of CVD creates a distinct set of advantages and limitations that you must weigh for any application.
Advantage: Conformal Coating
Unlike line-of-sight processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), the precursor gases in CVD flow like a vapor to envelop the entire substrate.
This means CVD can uniformly coat complex shapes, internal bores, and hidden surfaces, ensuring complete coverage.
Advantage: Superior Adhesion
Because the coating is chemically bonded to the substrate rather than physically deposited, its adhesion is exceptionally strong. This results in a highly durable and wear-resistant surface that is far less likely to chip or flake.
Limitation: High Thermal Stress
The very high temperatures required can be a significant drawback. This thermal load can alter the properties of the base material, limiting CVD's use on certain alloys, tempered parts, or plastics.
Furthermore, as the part and coating cool, differences in thermal expansion can create stress, which limits the practical thickness of the film that can be applied.
Limitation: Masking and Material Constraints
The pervasive nature of the gas makes it difficult to mask or protect specific areas of a part from being coated.
Additionally, the reactive chemicals involved can be hazardous and require specialized, controlled laboratory environments, adding to the complexity and cost of the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right coating technology depends entirely on the specific requirements of your component and its intended function.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-flat geometries: CVD's ability to coat all surfaces uniformly without being limited by line-of-sight makes it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and adhesion: The chemical bond formed by CVD provides exceptional adhesion that is often unmatched by physical deposition methods.
- If you are working with temperature-sensitive materials: The high heat of traditional CVD is a major constraint, and you must explore lower-temperature variants or alternative processes like PVD.
Understanding this interplay between chemical reaction and thermal energy is the key to effectively leveraging the power of CVD.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Gases chemically react on a heated substrate to form a solid film. |
| Key Advantage | Conformal coating of complex shapes; superior chemical adhesion. |
| Main Limitation | Requires very high temperatures (up to 1000°C). |
| Ideal For | Components needing extreme durability and complete, uniform coverage. |
Need a high-performance, durable coating for complex components?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing and coating applications. Our expertise can help you determine if CVD is the right solution for your project's requirements for adhesion, uniformity, and material compatibility.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and achieve your coating goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and ALD? Choosing the Right Thin Film Deposition Method
- What is effect of carbon nanotubes in plant growth? A Double-Edged Sword for Agriculture
- What is RTP technique for annealing? Achieve Ultra-Fast, Low Thermal Budget Processing for Semiconductors
- How does the quality of modern HPHT and CVD diamonds compare? Achieve Flawless Results with Precision Lab Technology
- What are some examples of solid and gaseous precursors used in the CVD of graphene? Optimize Your Synthesis Process
- What are some of the different methods of chemical vapour deposition? Choose the Best CVD Process for Your Application
- What are the typical substrate temperature operating regimes for various deposition technologies? Optimize Thin Films
- What is the effect of pressure and ion energy in the sputtering process? Optimize Film Density & Step Coverage



















