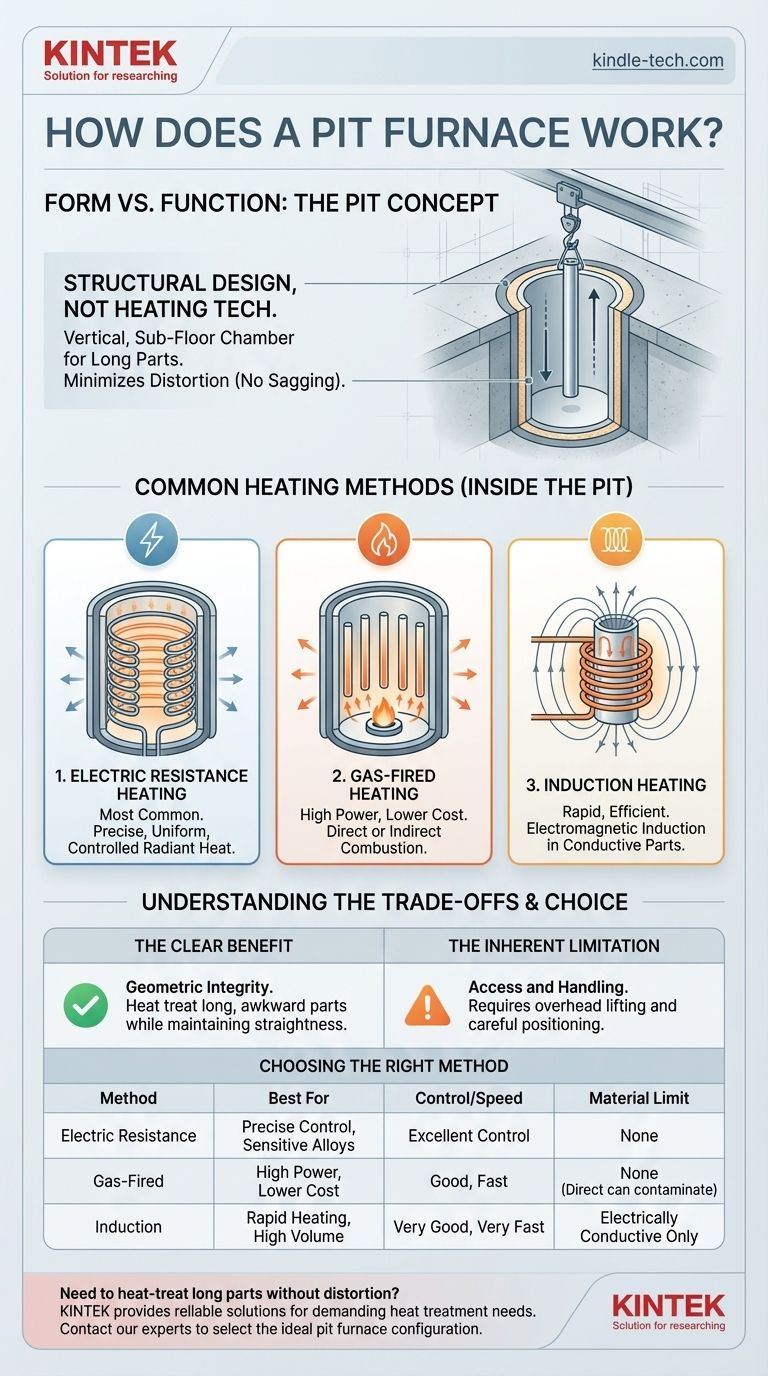
The term "pit furnace" refers to the furnace's physical orientation, not its method of generating heat. It is a vertical furnace installed in a pit below floor level, a design chosen specifically for heat-treating long or heavy components that need to be held vertically to prevent sagging or distortion at high temperatures. The actual heating can be accomplished through several methods, including electric resistance, gas combustion, or induction.
A pit furnace is fundamentally a structural design choice, not a heating technology. Its defining feature is its vertical, below-ground chamber, which is ideal for processing long parts like shafts and tubes without gravitational distortion. The method used to generate heat inside that chamber is a separate, critical decision.

Deconstructing the Pit Furnace: Form vs. Function
A common point of confusion is mistaking the furnace's shape for its energy source. In reality, the "pit" configuration is a solution to a specific mechanical problem, while the heating element is the solution to a thermal problem.
The Defining Feature: A Vertical, Sub-Floor Chamber
The furnace consists of a cylindrical or rectangular insulated chamber sunk into a pit in the factory floor.
Parts are loaded and unloaded vertically from the top, typically using an overhead crane. This design keeps the main body of the furnace out of the way, saving valuable floor space.
The Core Purpose: Minimizing Distortion
The primary reason for using a pit furnace is to manage gravity's effect on long, slender parts during heat treatment.
When a long shaft, tube, or screw is heated to high temperatures in a horizontal furnace, its own weight can cause it to bend or sag. By suspending the part vertically, these distorting stresses are eliminated, ensuring dimensional stability.
Common Heating Methods in Pit Furnaces
While the pit defines the shape, the technology inside generates the heat. The choice of heating method depends on the material, required temperature precision, and operational cost.
Electric Resistance Heating
This is the most common method for pit furnaces used in heat treatment applications like annealing, tempering, and hardening.
Much like a conventional oven, electric heating elements line the inner walls of the furnace. An electric current passes through these high-resistance elements, generating uniform, precisely controllable radiant heat.
Gas-Fired Heating
For applications where pinpoint temperature control is less critical than raw heating power and lower operating cost, gas-fired systems are used.
A burner combusts a fuel like natural gas or propane. This can be "direct-fired," where the combustion products enter the chamber, or "indirect-fired," where the flame heats radiant tubes that in turn heat the chamber, protecting the workpiece from the flame.
Induction Heating
As described in induction furnace principles, this method uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat directly within the workpiece itself.
In a pit furnace context, a copper coil would be lowered into the chamber around the conductive metal part. An alternating current in the coil induces powerful eddy currents within the part, causing it to heat up rapidly and efficiently from the inside out. This method is exceptionally fast but is limited to conductive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pit furnace and its heating system involves balancing distinct advantages and limitations.
The Clear Benefit: Geometric Integrity
The single greatest advantage is the ability to heat treat long, awkward, or heavy parts while maintaining their straightness and dimensional accuracy. For components like aircraft landing gear, large industrial shafts, or gun barrels, this is non-negotiable.
The Inherent Limitation: Access and Handling
The below-ground design can complicate access for maintenance compared to a horizontal or box furnace. Loading and unloading also require reliable overhead lifting equipment and careful positioning of the workpiece.
Heating Method Determines Performance
The choice between electric, gas, or induction is a critical trade-off:
- Electric Resistance offers the best temperature uniformity and control, crucial for sensitive alloys, but can have higher operating costs.
- Gas-Fired systems are often cheaper to run and provide immense heating power, but with less precise temperature control and potential for atmospheric contamination in direct-fired designs.
- Induction is the fastest and most energy-efficient method, but the equipment is specialized and only works on electrically conductive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal furnace is a combination of the right physical form and the right heating technology for the job.
- If your primary focus is treating long, slender parts that risk distortion: A pit furnace is the correct physical configuration, regardless of the heating method.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise and uniform temperatures for sensitive alloys: An electrically heated pit furnace is the superior choice for its control and cleanliness.
- If your primary focus is rapidly and efficiently heating high volumes of conductive parts: An induction heating system installed within a pit furnace provides unmatched speed and energy efficiency.
Ultimately, selecting the right industrial furnace means matching the equipment's design and function to your specific material and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Resistance | Gas-Fired | Induction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | Precise temperature control, sensitive alloys | High power, lower operating cost | Rapid heating, conductive metals |
| Temperature Control | Excellent | Good | Very Good |
| Heating Speed | Moderate | Fast | Very Fast |
| Material Limitation | None | None (Direct-fired can contaminate) | Electrically Conductive Only |
Need to heat-treat long, heavy, or slender parts without distortion?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for demanding laboratory and industrial heat treatment needs. Our expertise can help you select the ideal pit furnace configuration—whether electric, gas, or induction—to ensure your components maintain geometric integrity and meet your precise material specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover the right furnace for your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout



















