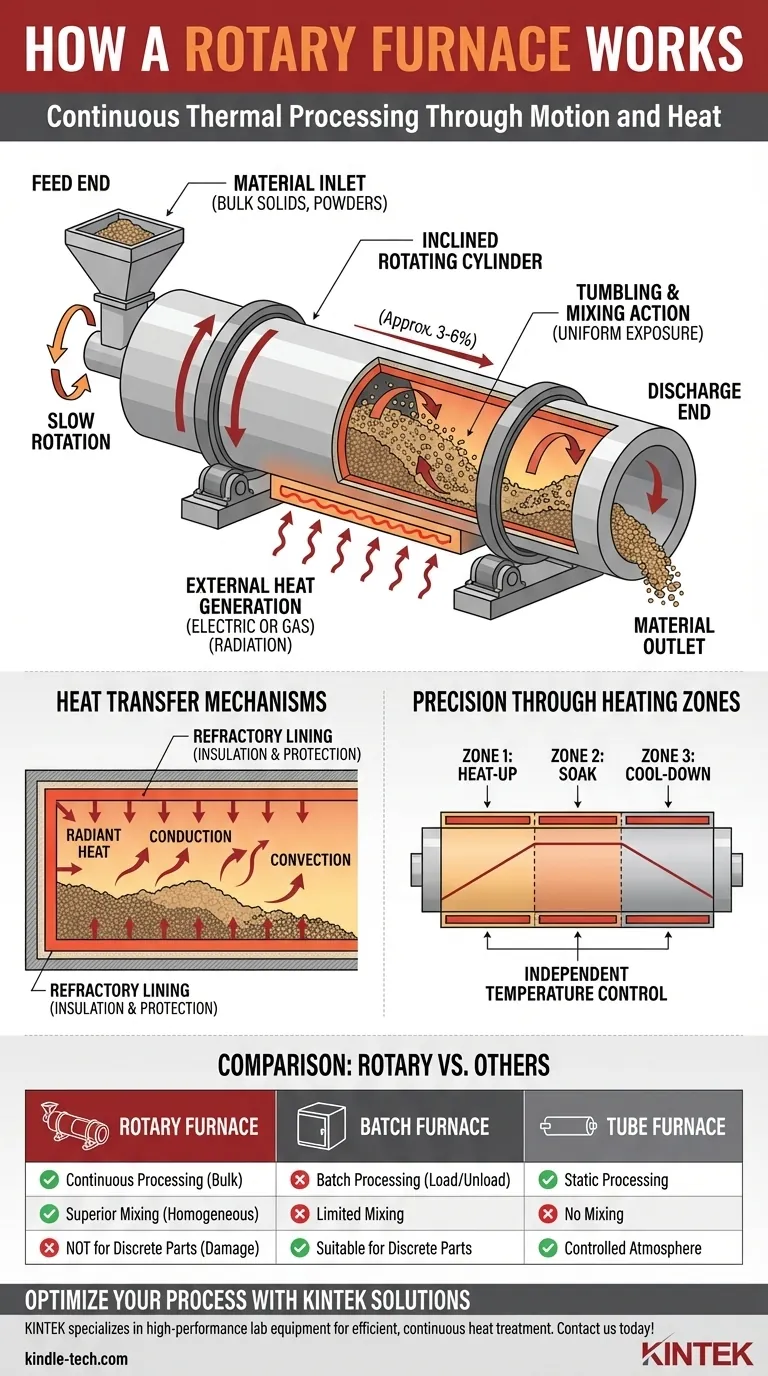
At its core, a rotary furnace is a continuously operating thermal processing unit that uses a combination of rotation and a slight incline to heat, mix, and transport materials simultaneously. The furnace itself is a long, cylindrical shell lined with heat-resistant material, which rotates slowly around its longitudinal axis. This simple yet effective design is engineered for processing large volumes of bulk solids, powders, or granular materials.
A rotary furnace's primary function is to leverage gravity and mechanical rotation to ensure every particle of a bulk material is uniformly exposed to heat. Its design ingeniously combines material transport, mixing, and thermal treatment into a single, continuous process.

The Core Principle: Combining Motion and Heat
The effectiveness of a rotary furnace comes from the elegant interplay between its mechanical movement and its thermal system. Unlike static furnaces that heat a stationary object, the rotary furnace actively manipulates the material throughout the process.
Mechanical Transport via Rotation and Inclination
The furnace body is a long steel cylinder supported by wheels and driven by a motor and gear system. Crucially, it is mounted at a slight inclination, typically between 3% and 6% from the horizontal.
As the cylinder rotates slowly, material fed into the higher, or "feed," end begins to tumble. This tumbling motion, combined with the downward slope, causes the material to gradually travel along the length of the furnace until it exits at the lower, or "discharge," end.
The Critical Role of Tumbling and Mixing
The constant rotation does more than just move the material forward; it actively mixes and tumbles it. This action, known as cascading, is vital for process uniformity.
As the material bed is lifted by the rotating wall and then tumbles back down, new layers are constantly exposed. This ensures that the material does not just heat on the surface but is heated homogeneously throughout its volume, preventing hot spots and unprocessed cold spots.
A Look Inside the Heating System
The mechanical system works in concert with a carefully designed thermal system to achieve precise temperature control. Heat is generated externally and transferred to the material inside the rotating drum.
Heat Generation and Transfer
Heating is typically accomplished with high-quality electric heating elements or gas burners positioned outside the rotating cylinder. These elements generate intense heat primarily through radiation.
This radiant energy heats the furnace wall and the internal atmosphere. The heat is then transferred to the material bed through both direct conduction from the hot wall and convection from the heated air inside the chamber.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
To ensure precise control over the entire process, modern rotary furnaces often feature multiple heating zones. For example, a furnace might be divided into three zones along its length.
Each zone's temperature can be controlled independently. This allows for a specific temperature profile to be programmed—perhaps a gradual heat-up zone, a sustained high-temperature "soak" zone, and a controlled cool-down zone near the discharge end.
The Importance of the Refractory Lining
The inside of the steel cylinder is lined with a thick layer of refractory material, such as specialized bricks or castable ceramics. This lining serves two critical purposes.
First, it acts as an insulator, minimizing heat loss and improving energy efficiency. Second, it protects the outer steel shell from the extreme internal temperatures and potential chemical reactions or abrasion from the process material.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rotary vs. Other Furnaces
No single furnace design is perfect for every application. The rotary furnace excels in specific scenarios but has limitations that make other designs more suitable for different tasks.
Advantage: Continuous Processing of Bulk Materials
The primary advantage is its ability to process a continuous flow of bulk solids like minerals, powders, catalysts, or waste products. This is far more efficient for high-volume production than a batch furnace, which must be loaded and unloaded for each cycle.
Advantage: Superior Mixing and Homogenization
Compared to a static tube furnace, where the material does not move, the rotary furnace provides unparalleled mixing. This is critical for processes like calcination, roasting, or drying where uniform chemical reactions and physical changes are required.
Limitation: Not for Discrete Parts or Sensitive Geometries
A rotary furnace is completely unsuitable for processing individual, large components or objects with delicate geometries. The tumbling action would cause damage. For these applications, a pusher furnace or batch furnace is the correct choice.
Limitation: Potential for Dust and Abrasion
The tumbling action can generate dust, which may require a collection system at the discharge end. Furthermore, abrasive materials can cause significant wear and tear on the refractory lining over time, necessitating periodic maintenance and replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of furnace technology must be driven by the nature of your material and your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is processing large volumes of bulk solids (minerals, powders, pellets): The rotary furnace is the ideal technology for its continuous transport and superior mixing capabilities.
- If your primary focus is treating discrete parts or components in sequence: A pusher furnace, which moves items on trays, offers continuous processing without the tumbling action.
- If your primary focus is static, high-purity heat treatment in a controlled atmosphere: A standard batch or tube furnace provides a stable, sealed environment that a rotary furnace cannot.
Understanding the fundamental interplay of motion and heat is the key to selecting the right thermal processing technology for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Combines mechanical rotation with a slight incline to move and tumble materials. |
| Heating Method | External burners or electric elements heat via radiation; heat transfers through conduction and convection. |
| Key Advantage | Continuous processing with superior mixing for uniform heat treatment of bulk solids. |
| Ideal For | High-volume materials like minerals, powders, catalysts, and granular substances. |
| Limitations | Not suitable for discrete parts; potential dust generation and refractory wear from abrasion. |
Need a reliable thermal processing solution for your bulk materials? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including rotary furnaces designed for efficient, continuous heat treatment of powders, minerals, and granular substances. Our expertise ensures precise temperature control, durability, and process uniformity for your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how our rotary furnaces can optimize your production and enhance your results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is calcination a burning process? Discover the Key Differences in Thermal Processing
- What is the difference between fast pyrolysis and slow pyrolysis? Choose the Right Process for Your Biofuel Goals
- What is fluidized bed pyrolysis? Efficiently Convert Waste into Bio-Oil and Fuels
- How can we convert plastic waste into useful products? Explore Mechanical vs. Chemical Recycling
- What is the efficiency of a rotary furnace? Maximizing Uniform Heat Treatment
- What are the weaknesses of pyrolysis? Navigating High Costs and Operational Hurdles
- What is the purpose of calciner? Boost Cement Production Efficiency & Clinker Formation
- What is the difference between pyrolysis and incomplete combustion? The Critical Role of Oxygen in Thermal Processes



















