At their core, all industrial furnaces operate on a simple principle: they use a controlled source of energy to generate heat within an insulated chamber. This process raises the temperature of materials to specific levels, inducing desired physical changes like hardening or chemical changes like sintering, all while maintaining precise control over the environment.
The term "industrial furnace" is broad. The key to understanding them is realizing the design is not about generating heat, but about how that heat is transferred and what kind of atmosphere the material is heated in. The specific method chosen depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome.
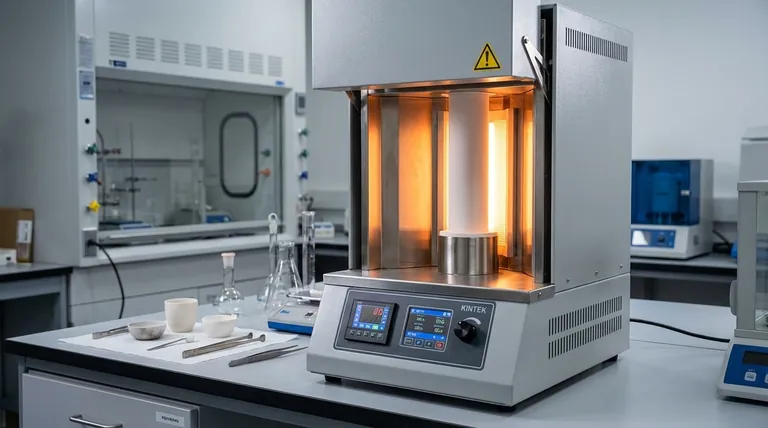

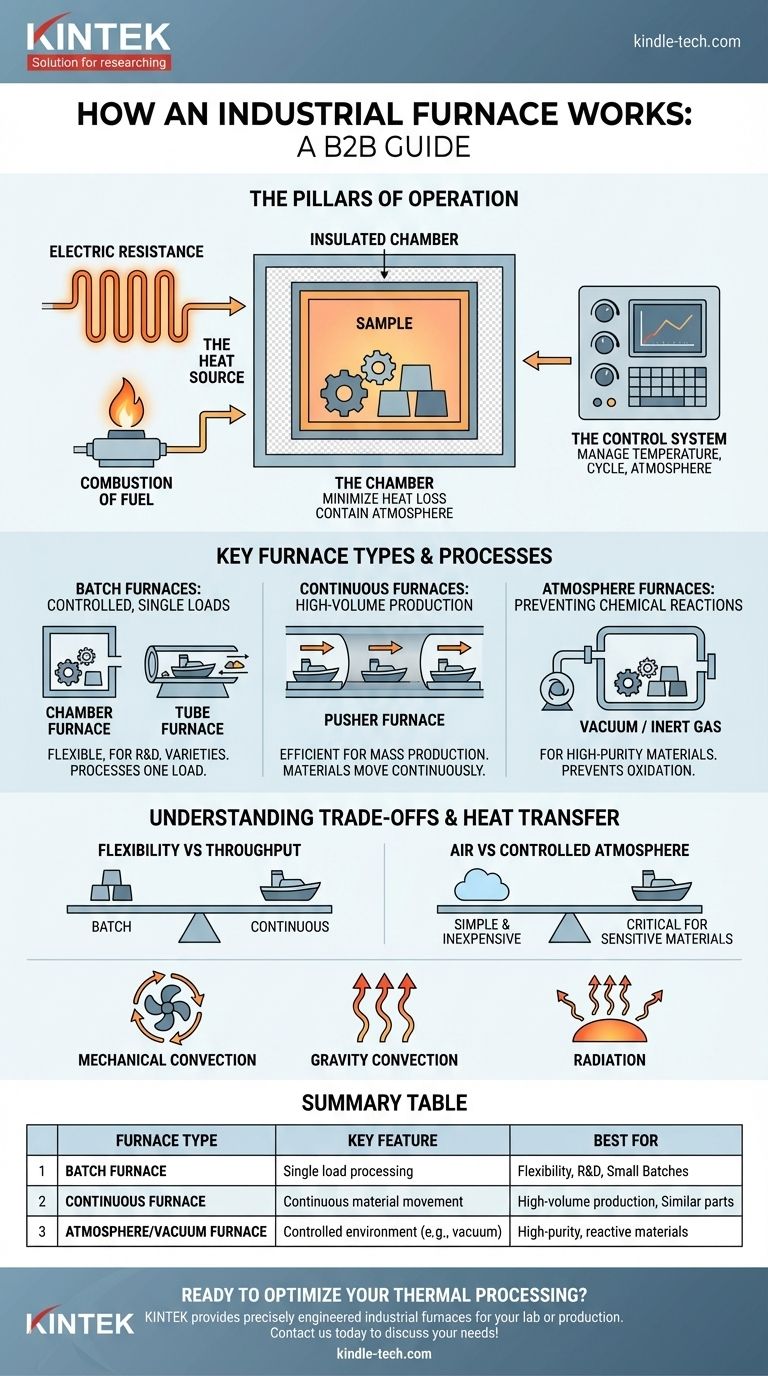
The Pillars of Furnace Operation
Every furnace, regardless of its specific type, is built upon three fundamental components working in concert. Understanding these pillars is the first step to mastering the technology.
The Heat Source
This is the engine of the furnace. Most commonly, heat is generated by electric resistance elements, which glow hot when current is passed through them, or by the combustion of fuel, like natural gas. The choice impacts operating cost, temperature range, and atmospheric control.
The Chamber
The chamber is the insulated enclosure that contains the heat and the material being processed. Its primary jobs are to minimize heat loss (efficiency) and to contain a specific atmosphere, whether that's normal air, a vacuum, or a specialized mix of inert gases.
The Control System
This is the brain of the operation. Modern furnace controllers precisely manage temperature, cycle duration, and atmospheric conditions. This ensures the process is repeatable, accurate, and safe, delivering consistent results batch after batch.
Key Furnace Types and Their Processes
The "how" of a furnace is defined by its process: is it heating a single batch, a continuous stream of parts, or operating in a special atmosphere?
Batch Furnaces: For Controlled, Single Loads
These furnaces process one load, or "batch," at a time. A chamber furnace is the most common example, where parts are loaded into a simple heated box. A tube furnace is a variation where parts are placed inside a work tube that is then heated externally, providing a more isolated and controlled environment for the sample.
Continuous Furnaces: For High-Volume Production
Designed for mass production, these furnaces move materials through the heat continuously. A pusher furnace, for example, operates with a train of "boats" or trays. As a new tray is pushed into the entrance, the entire train moves forward, and a finished tray is removed from the exit. This maximizes throughput.
Atmosphere Furnaces: For Preventing Chemical Reactions
Many materials react negatively with oxygen at high temperatures, leading to oxidation (scaling or rust). A vacuum furnace solves this by first using pumps to remove all the air from the chamber. Once in a vacuum, the parts are heated. This is critical for high-purity metals, aerospace components, and medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or operating a furnace involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" type, only the right type for a specific job.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
The fundamental trade-off is flexibility versus throughput. Batch furnaces are highly flexible, able to handle different parts and processes easily. Continuous furnaces are far more efficient for producing large quantities of the same part but are expensive and difficult to change over.
Air vs. Controlled Atmosphere
Heating in ambient air is simple and inexpensive. However, for sensitive materials, a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere is non-negotiable to preserve the material's integrity. This adds significant complexity and cost, from the vacuum pumps to the need for a perfectly sealed chamber.
Heat Transfer and Uniformity
The method of heat transfer impacts speed and evenness. Mechanical convection, which uses fans to circulate hot air, provides fast and highly uniform heating. Gravity convection, where hot air naturally rises, is simpler but slower and less uniform. Furnaces in a vacuum rely primarily on radiation, which can be less uniform depending on part geometry and placement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace technology is a strategic decision based on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of similar parts: A continuous furnace, like a pusher type, is designed for maximum throughput and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is treating high-purity or reactive materials: A vacuum or controlled atmosphere furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for research or varied small batches: A chamber or tube batch furnace offers the most versatility for single-load processing.
Understanding these core principles moves you from simply using a furnace to strategically controlling your material outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Furnace | Processes one load at a time | Flexibility, R&D, varied small batches |
| Continuous Furnace | Materials move through heat continuously | High-volume production of similar parts |
| Atmosphere/Vacuum Furnace | Controlled environment (e.g., vacuum, inert gas) | High-purity, reactive materials, preventing oxidation |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? The right industrial furnace is critical for achieving consistent, high-quality results in your lab or production line. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing precisely engineered lab equipment, including a wide range of industrial furnaces tailored to your specific material and process requirements. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your application, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and performance. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the steps in vacuum brazing? Achieve Superior, Clean Metallurgical Bonds
- What is the flash sintering method? Achieve Rapid, Low-Energy Ceramic Densification
- Why is a high-temperature furnace used for annealing Mo-La2O3 alloy powders? Ensure Structural Integrity
- Why is a molybdenum heating furnace utilized for TiB2-Al2O3 composites? Control Preheating for Precision Synthesis
- Why is a vacuum furnace or an atmosphere furnace using nitrogen essential for CFRP pyrolysis? Preserve Fiber Integrity
- What is the vacuum arc remelting process? Producing Ultra-Pure, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- Why is a high-temperature annealing furnace necessary for coated electrodes? Unlock Catalytic Performance & Durability
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature annealing furnace in Ni-30Cr research? Master Alloy Homogenization



















