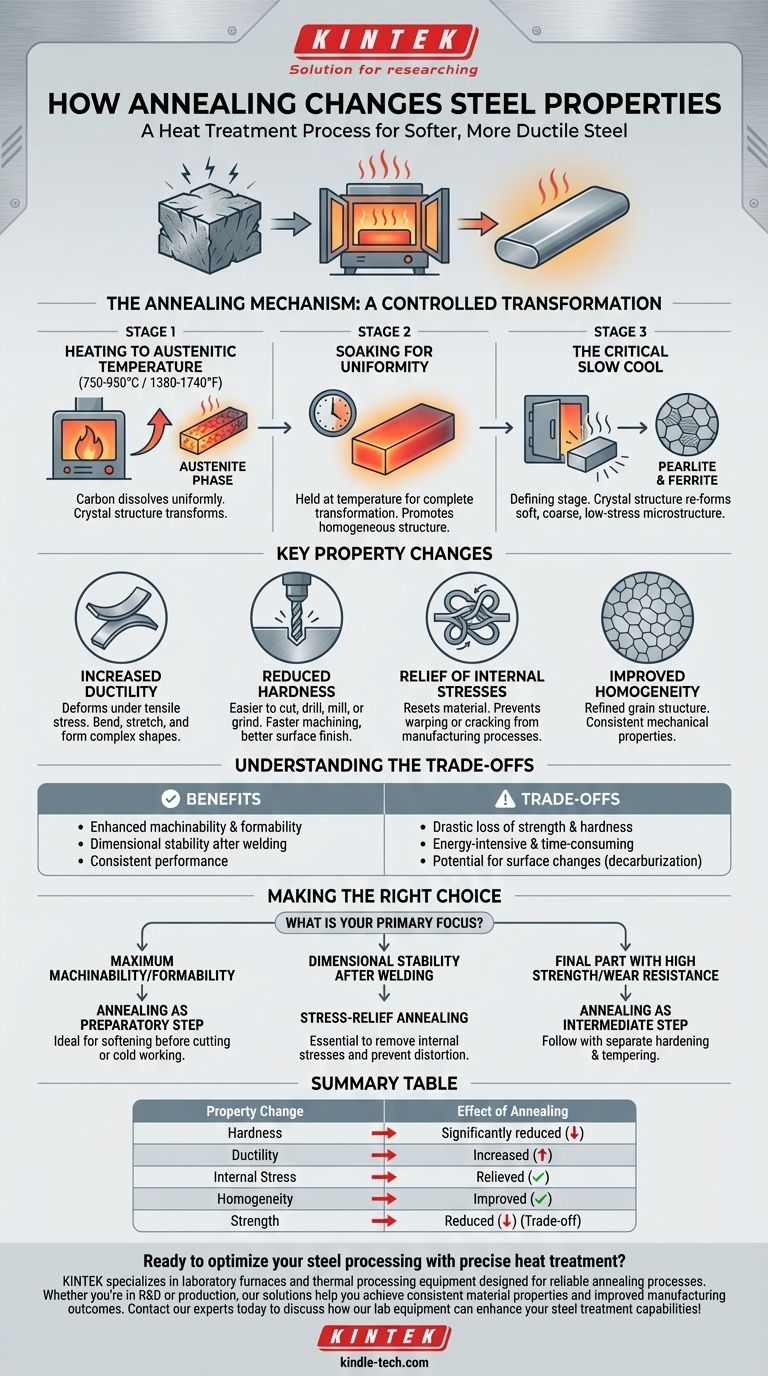
In essence, annealing is a heat treatment process that fundamentally makes steel softer, more ductile, and easier to work with. By heating the steel to a specific temperature and then cooling it very slowly, annealing alters the internal microstructure of the metal, relieving internal stresses and refining its grain structure.
The core purpose of annealing is not to create a final, high-strength product, but rather to reset the steel's properties. It prepares the material for subsequent manufacturing operations like machining or forming by making it as uniform and stress-free as possible.
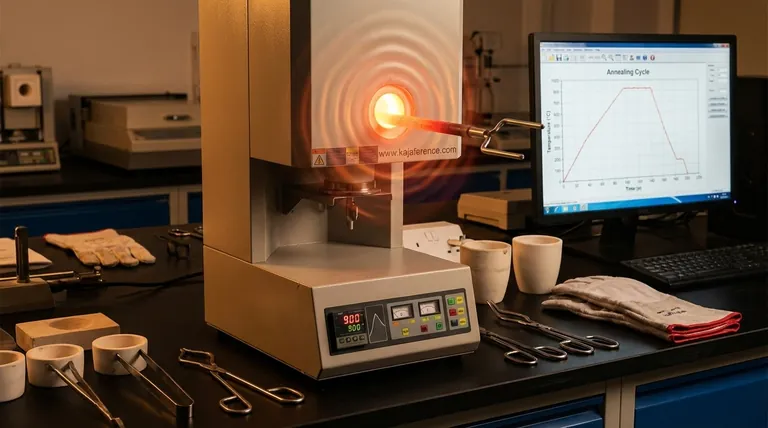

The Annealing Mechanism: A Controlled Transformation
The changes in steel's properties are a direct result of a three-stage process that manipulates its internal crystal structure, known as its microstructure.
Stage 1: Heating to Austenitic Temperature
The process begins by heating the steel above its upper critical temperature (typically between 750-950°C or 1380-1740°F, depending on the carbon content). At this temperature, the steel's crystal structure transforms into a phase called austenite, which allows the carbon within the steel to dissolve uniformly.
Stage 2: Soaking for Uniformity
The steel is then "soaked," or held at this high temperature for a specific duration. This ensures that the austenitic transformation is complete throughout the entire mass of the component, promoting a homogenous internal structure.
Stage 3: The Critical Slow Cool
This is the defining stage of the annealing process. The steel is cooled at a very slow and controlled rate, often by simply leaving it in the furnace and shutting it off. This slow cooling allows the crystal structure to re-form into a soft, coarse microstructure, typically pearlite and ferrite. This new structure has very low internal stress and hardness.
Key Property Changes in Annealed Steel
By refining the steel's microstructure, annealing produces several predictable and highly desirable changes in its mechanical properties.
Increased Ductility
Annealing significantly increases the steel's ability to deform under tensile stress, meaning it can be bent, stretched, or formed into complex shapes without fracturing. This property is critical for processes like stamping and deep drawing.
Reduced Hardness
The primary outcome of annealing is a dramatic reduction in hardness. This makes the steel much easier to cut, drill, mill, or grind. The result is faster machining times, reduced tool wear, and a better surface finish.
Relief of Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like casting, welding, or cold working (like bending or rolling) introduce significant internal stresses into the material. Annealing acts as a reset, relieving these stresses and preventing potential problems like warping or cracking later in the part's life.
Improved Homogeneity
The process refines the grain structure, making it more uniform throughout the material. This ensures that the mechanical properties are consistent across the entire component, leading to more predictable performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, annealing is a strategic choice that involves clear trade-offs. It is a preparatory step, not typically a final treatment for parts requiring high performance.
Drastic Loss of Strength
The single biggest trade-off is the loss of tensile strength and hardness. An annealed part is soft and not suitable for applications that require high wear resistance or the ability to bear heavy loads without further heat treatment.
Time and Energy Costs
Full annealing, with its long soaking times and extremely slow furnace cooling, is an energy-intensive and time-consuming process. This adds to the overall cost and production time of a component.
Potential for Surface Changes
If not performed in a controlled atmosphere, the high temperatures can cause carbon to leave the surface of the steel (decarburization), resulting in a soft outer skin that may be undesirable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Annealing should be selected based on the specific needs of your manufacturing process and the final application of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum machinability or formability: Annealing is the ideal preparatory step to make the steel as soft and ductile as possible before cutting or cold working.
- If your primary focus is ensuring dimensional stability after welding: A specific type of annealing, known as stress-relief annealing, is essential to remove internal stresses and prevent future distortion.
- If your primary focus is a final part with high strength and wear resistance: View annealing as an intermediate step. It prepares the material for easy machining, after which the finished part will require a separate hardening and tempering process to achieve its final desired properties.
Ultimately, annealing provides the control needed to make steel a predictable and cooperative material for manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Property Change | Effect of Annealing |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Significantly reduced for easier machining |
| Ductility | Increased for better formability |
| Internal Stress | Relieved to prevent warping/cracking |
| Homogeneity | Improved for consistent properties |
| Strength | Reduced (trade-off for machinability) |
Ready to optimize your steel processing with precise heat treatment? KINTEK specializes in laboratory furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for reliable annealing processes. Whether you're in R&D or production, our solutions help you achieve consistent material properties and improved manufacturing outcomes. Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can enhance your steel treatment capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















