In short, chirality is everything. The chirality of a carbon nanotube—the specific angle at which a sheet of graphene is "rolled" to form the tube—fundamentally determines its most critical electronic properties. This single structural parameter dictates whether the nanotube will behave as a highly conductive metal or as a semiconductor, a distinction that has profound implications for its use.
The way a graphene sheet is conceptually rolled into a tube defines its atomic structure, known as chirality. This structural twist is the primary factor that dictates the nanotube's electrical personality, making the difference between a nanoscale wire and a nanoscale transistor component.

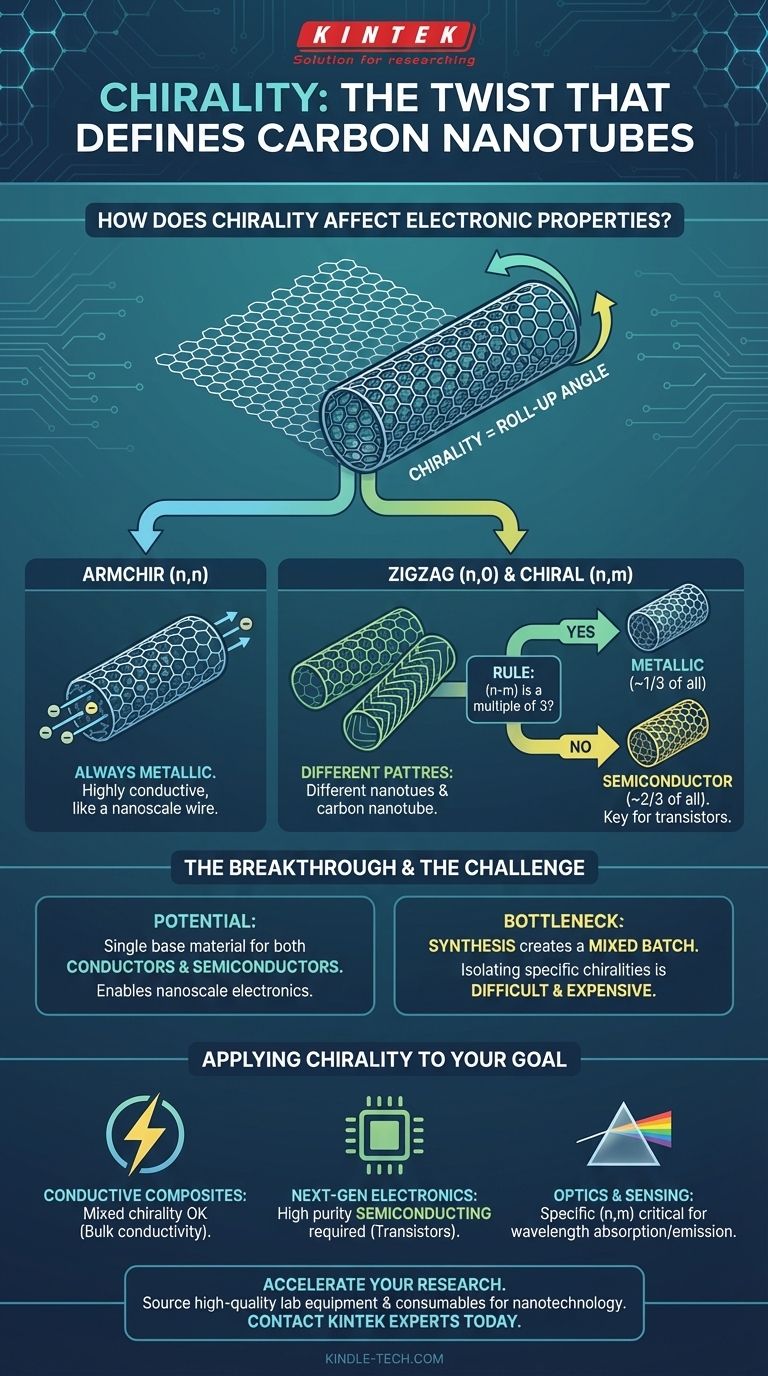
What is Chirality in a Carbon Nanotube?
To understand how chirality works, it's best to visualize a carbon nanotube as a single sheet of graphene, which is a one-atom-thick layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice, rolled into a seamless cylinder.
The Graphene Sheet Analogy
Imagine a flat sheet of chicken wire. You can roll it up in different ways. You could roll it straight, so the hexagonal patterns line up perfectly along the seam. You could also roll it at a slight angle.
This "roll-up" angle is the essence of chirality. It dictates the arrangement of the carbon atoms along the circumference and length of the nanotube.
Defining Chirality with (n,m) Vectors
Scientists define the specific chirality of any carbon nanotube with a pair of integers known as the chiral vector (n,m). These numbers describe how to roll the graphene sheet to form the tube.
This isn't just an abstract classification. The values of n and m create three distinct categories of carbon nanotubes, each with a radically different personality.
The Defining Impact: Electrical Conductivity
The exact alignment of carbon atoms created by chirality opens or closes pathways for electrons to flow. This directly determines if the nanotube is a conductor or a semiconductor.
Armchair Nanotubes: The Metallic Conductors
When the chiral vector is (n,n), the nanotube is called "armchair." In this configuration, the hexagonal carbon rings line up perfectly along the axis of the tube.
This perfect alignment creates a continuous metallic pathway for electrons, meaning armchair nanotubes are always highly conductive, like a nanoscale copper wire.
Zigzag and Chiral Nanotubes: The Versatile Group
When the vector is (n,0), it's a "zigzag" nanotube. For all other (n,m) values, it's known as a "chiral" nanotube.
For these types, the electrical properties depend on a simple rule:
- If n - m is a multiple of 3, the nanotube is metallic.
- If n - m is not a multiple of 3, the nanotube is a semiconductor.
This means that approximately two-thirds of all possible nanotubes are semiconducting, while one-third are metallic.
Why This is a Breakthrough and a Bottleneck
The ability to have either a conductor or a semiconductor at the nanoscale from the same base material is revolutionary for electronics. A semiconducting nanotube can be used to create a transistor, the fundamental building block of a computer chip.
However, this is also the single greatest challenge. During synthesis, we typically produce a mixture of all chiralities—a blend of metallic and semiconducting tubes. This mixed batch is unusable for creating complex electronic circuits.
Understanding the Key Challenge
The promise of carbon nanotube electronics is immense, but it is held back by the very property that makes it so powerful: the extreme sensitivity of its properties to chirality.
The Synthesis Problem: A Lack of Control
The primary challenge is the lack of control during synthesis. Current large-scale production methods create a random assortment of chiralities. We cannot yet reliably "grow" only one specific type of (n,m) nanotube on demand.
The Separation Hurdle
Because we cannot produce pure batches, the alternative is to separate the mixture after production. This involves complex and expensive processes to isolate the semiconducting tubes from the metallic ones. Achieving the near-100% purity required for advanced electronics remains a significant technical and economic hurdle.
Impact on Other Properties
While the effect on electrical conductivity is the most dramatic, chirality also influences a nanotube's optical properties. Each specific (n,m) structure absorbs and emits very specific wavelengths of light, making them useful in sensors and spectroscopy. Chirality also has a more subtle effect on mechanical properties like strength and stiffness.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your application's sensitivity to chirality will determine the type of carbon nanotube material you need.
- If your primary focus is creating conductive composites or inks: A mix of chiralities is often acceptable, as the goal is simply bulk conductivity provided by the metallic tubes in the mixture.
- If your primary focus is developing next-generation electronics (like transistors): You require a sample with near-perfect purity of a specific semiconducting chirality. This is the most difficult and expensive requirement.
- If your primary focus is in optics, photovoltaics, or sensing: The specific (n,m) value is critical, as it determines the exact wavelengths of light the nanotube will absorb and emit.
Ultimately, understanding and controlling chirality is the key to unlocking the full, transformative potential of carbon nanotubes.
Summary Table:
| Chirality Type | Chiral Vector (n,m) | Electrical Property |
|---|---|---|
| Armchair | (n, n) | Always Metallic |
| Zigzag/Chiral | (n, m) | Metallic if (n-m) is multiple of 3; Semiconducting otherwise |
Ready to source the right carbon nanotubes for your specific application? Whether you need metallic tubes for conductive composites or high-purity semiconducting tubes for advanced electronics, KINTEK has the expertise and materials to meet your lab's needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how our high-quality lab equipment and consumables can accelerate your nanotechnology research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- What is deposition uniformity and how is it measured? Optimize Film Consistency & Quality Control
- Why carbon nanotubes are better than graphene? Matching Material Geometry to Your Engineering Challenge
- Is carbon nanotube a good conductor of electricity? Unlocking Superconductivity at the Nanoscale
- How are thin films used? Unlock Advanced Surface Properties for Your Materials
- What is thin film in nanotechnology? The Essential Building Block for Advanced Tech
- Does deposition require heat? Unlocking the Right Thin Film Process for Your Materials
- What catalyst is used in growing carbon nanotubes by chemical vapor deposition? Key Metals for Controlled Synthesis



















