To put it simply, graphene's reaction to heat is dual-natured and exceptional. It possesses one of the highest known thermal conductivities at room temperature, making it incredibly effective at spreading heat. Simultaneously, its strong carbon-carbon bonds give it remarkable thermal stability, allowing it to remain solid at extremely high temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
The core takeaway is that while graphene's theoretical thermal properties are record-breaking, its actual performance in any application is profoundly influenced by its quality, structure, and operating environment. Understanding these real-world limitations is the key to harnessing its potential.

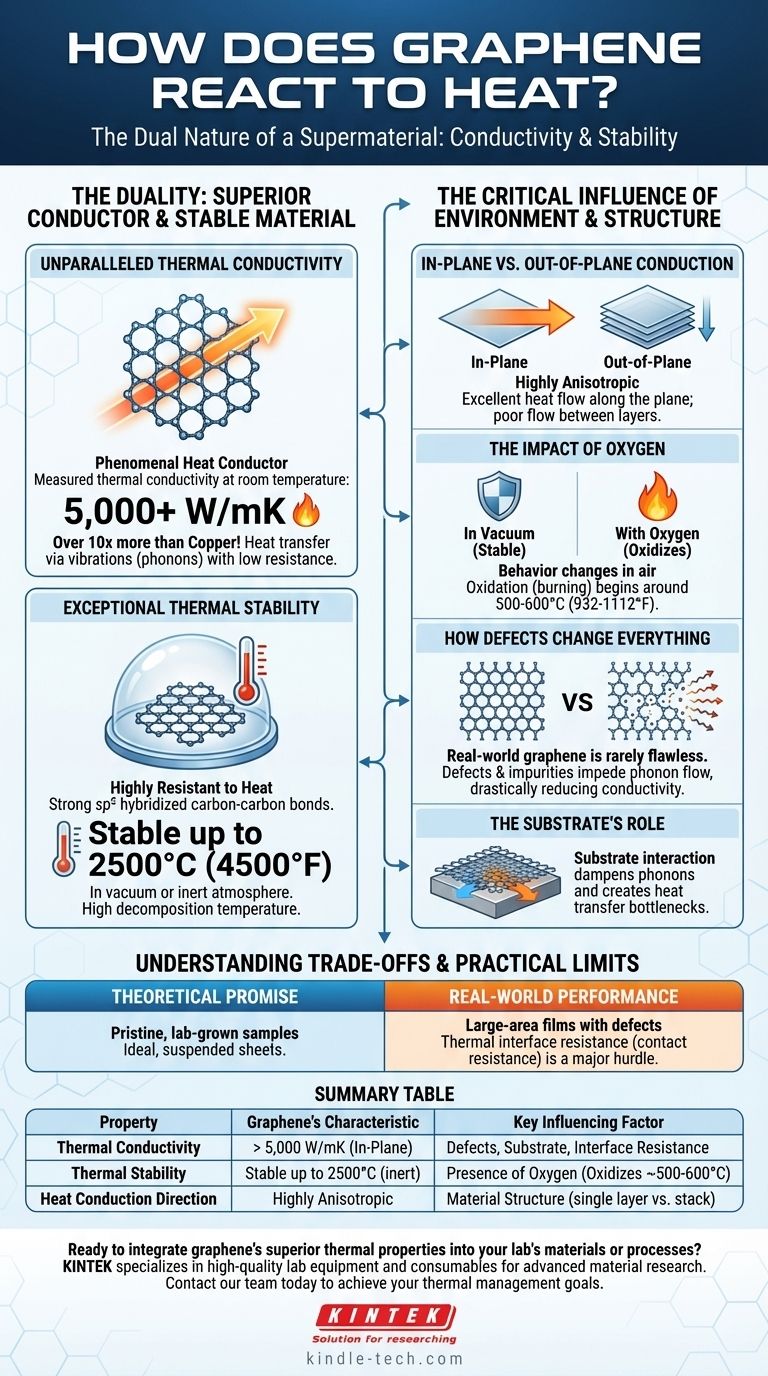
The Duality: Superior Conductor and Stable Material
Graphene's unique atomic structure—a single, flat layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice—is the source of its extraordinary thermal characteristics. These characteristics fall into two main categories: its ability to conduct heat and its ability to withstand heat.
Unparalleled Thermal Conductivity
Graphene is a phenomenal heat conductor. Its measured thermal conductivity can exceed 5,000 W/mK (Watts per meter-Kelvin) at room temperature, which is more than ten times that of copper and significantly higher than diamond.
This efficiency comes from the way heat travels through its lattice. Heat energy is transferred via vibrations, known as phonons. The strong covalent bonds and low mass of graphene's carbon atoms create a near-perfect, low-resistance pathway for these phonons to travel, allowing heat to dissipate with incredible speed.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Beyond conducting heat, graphene is also highly resistant to it. The sp² hybridized bonds that hold the carbon atoms together are among the strongest in nature.
This robust structure gives graphene a very high decomposition temperature. In a vacuum or an inert (non-reactive) atmosphere, graphene can remain stable at temperatures well above 2500°C (4500°F).
The Critical Influence of Environment and Structure
The record-breaking numbers associated with graphene describe a perfect, suspended, single-layer sheet in a vacuum. In any practical application, this is never the case. Several factors can dramatically alter its thermal behavior.
In-Plane vs. Out-of-Plane Conduction
Graphene is highly anisotropic. Heat travels exceptionally well along the two-dimensional plane of the sheet (in-plane) but very poorly between stacked layers (out-of-plane).
This means that while a single sheet is a great heat spreader, a stack of graphene sheets (like graphite) is a much less effective conductor in the vertical direction. This is a critical design constraint for applications like thermal interface materials.
The Impact of Oxygen
While stable in a vacuum, graphene's behavior changes in the presence of air. Like other forms of carbon, it will oxidize (burn) when heated.
This oxidation process typically begins at much lower temperatures, often around 500-600°C (932-1112°F). This makes the operating environment a key factor for any high-temperature application.
How Defects and Impurities Change Everything
Real-world graphene is rarely flawless. Defects such as vacancies (missing atoms), grain boundaries (where different crystal domains meet), and impurities disrupt the perfect lattice.
Each of these imperfections acts as a scattering point that impedes the flow of phonons, drastically reducing the material's effective thermal conductivity. The performance of commercially produced graphene is often a fraction of its theoretical potential due to these structural flaws.
The Substrate's Role
In most uses, graphene isn't suspended in a void; it's placed on a substrate (like silicon). The interaction between the graphene layer and the substrate material can dampen phonons and create a bottleneck for heat transfer, lowering the overall system performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Limits
It is vital to distinguish between graphene's intrinsic properties and its performance within an engineered system. The difference between the two is where most practical challenges arise.
Theoretical Promise vs. Real-World Performance
The headline-grabbing values for thermal conductivity belong to pristine, lab-grown samples. Large-area graphene films produced by methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) will always have defects that lower performance. The engineering challenge is not just to use graphene, but to use high-quality graphene.
The Challenge of Thermal Interface Resistance
Even with a perfect graphene sheet, a major hurdle is thermal contact resistance. This is the resistance to heat flow at the boundary between graphene and another material. If heat cannot efficiently get into and out of the graphene layer, its high conductivity becomes irrelevant. Minimizing this interface resistance is a major focus of research and development.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application determines which of graphene's thermal properties is most important.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat dissipation (e.g., electronics cooling): Your success depends on using high-quality, large-flake graphene and engineering a minimal thermal contact resistance between the graphene and the heat source.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural integrity (e.g., composites): You should leverage graphene's stability within a protective, oxygen-free matrix material, where it can add strength at temperatures that would degrade other fillers.
- If your primary focus is thermal insulation: You can exploit the poor out-of-plane conductivity by using structures like graphene aerogels or vertically aligned foams, which trap heat effectively.
Ultimately, mastering graphene's thermal properties means moving beyond its ideal state and engineering solutions that account for the complexities of its real-world form and environment.
Summary Table:
| Property | Graphene's Characteristic | Key Influencing Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | > 5,000 W/mK (In-Plane) | Defects, Substrate, Interface Resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 2500°C (inert) | Presence of Oxygen (Oxidizes ~500-600°C) |
| Heat Conduction Direction | Highly Anisotropic (In-Plane vs. Out-of-Plane) | Material Structure (e.g., single layer vs. stack) |
Ready to integrate graphene's superior thermal properties into your lab's materials or processes? KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced material research and development. Whether you are working on next-generation electronics cooling, high-temperature composites, or innovative insulation, our expertise can support your project. Contact our team today to discuss how we can help you achieve your thermal management goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges
- How does hardness change with temperature? Understand the Inverse Relationship to Prevent Failure
- What is titanium disadvantages and advantages? Weighing Performance vs. Cost for Your Project
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations



















